8.7 KiB
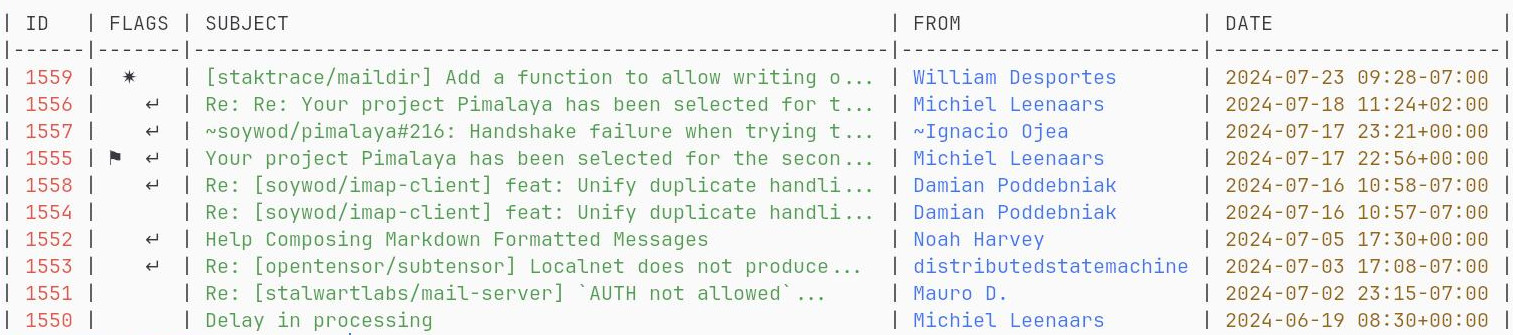
$ himalaya envelope list --account posteo --folder Archives.FOSS --page 2
Features
- Interactive configuration via wizard (requires
wizardfeature) - Mailbox/folder management (create, list, expunge, purge, delete)
- Envelope listing, filtering and sorting
- Message composition based on
$EDITOR - Message manipulation (copy, move, delete)
- Multi-accounting
- JSON output with
--output json - Basic backends:
- IMAP (requires
imapfeature) - Maildir (requires
maildirfeature) - Notmuch (requires
notmuchfeature)
- IMAP (requires
- Sending backends:
- SMTP (requires
smtpfeature) - Sendmail (requires
sendmailfeature)
- SMTP (requires
- PGP encryption:
- via shell commands (requires
pgp-commandsfeature) - via GPG bindings (requires
pgp-gpgfeature) - via native implementation (requires
pgp-nativefeature)
- via shell commands (requires
- Global system keyring for managing secrets (requires
keyringfeature) - OAuth 2.0 authorization (requires
oauth2feature)
Himalaya CLI is written in Rust, and relies on cargo features to enable or disable functionalities.
Default features can be found in the features section of the Cargo.toml.
Installation 
Prebuilt binary
Himalaya CLI can be installed with a prebuilt binary:
# As root:
$ curl -sSL https://raw.githubusercontent.com/pimalaya/himalaya/master/install.sh | sudo sh
# As a regular user:
$ curl -sSL https://raw.githubusercontent.com/pimalaya/himalaya/master/install.sh | PREFIX=~/.local sh
These commands install the latest binary from the GitHub releases section.
Binaries are built with default cargo features. If you want to enable or disable a feature, please use another installation method.
Cargo
Himalaya CLI can be installed with cargo:
$ cargo install himalaya
# With only IMAP support:
$ cargo install himalaya --no-default-features --features imap
You can also use the git repository for a more up-to-date (but less stable) version:
$ cargo install --git https://github.com/pimalaya/himalaya.git himalaya
Arch Linux
Himalaya CLI can be installed on Arch Linux with either the community repository:
$ pacman -S himalaya
or the user repository:
$ git clone https://aur.archlinux.org/himalaya-git.git
$ cd himalaya-git
$ makepkg -isc
If you use yay, it is even simplier:
$ yay -S himalaya-git
Fedora Linux/CentOS/RHEL
Himalaya CLI can be installed on Fedora Linux/CentOS/RHEL via COPR repo:
$ dnf copr enable atim/himalaya
$ dnf install himalaya
Nix
Himalaya CLI can be installed with Nix:
$ nix-env -i himalaya
You can also use the git repository for a more up-to-date (but less stable) version:
$ nix-env -if https://github.com/pimalaya/himalaya/archive/master.tar.gz
# or, from within the source tree checkout
$ nix-env -if .
If you have the Flakes feature enabled:
$ nix profile install himalaya
# or, from within the source tree checkout
$ nix profile install
# you can also run Himalaya directly without installing it:
$ nix run himalaya
Sources
Himalaya CLI can be installed from sources.
First you need to install the Rust development environment (see the rust installation documentation):
$ curl https://sh.rustup.rs -sSf | sh
Then, you need to clone the repository and install dependencies:
$ git clone https://github.com/pimalaya/himalaya.git
$ cd himalaya
$ cargo check
Now, you can build Himalaya:
$ cargo build --release
Binaries are available under the target/release folder.
Configuration
Just run himalaya, the wizard will help you to configure your default account.
You can also manually write your own configuration, from scratch:
- Copy the content of the documented
./config.sample.toml - Paste it in a new file
~/.config/himalaya/config.toml - Edit, then comment or uncomment the options you want
FAQ
How to debug Himalaya CLI?
The simplest way is to use --debug and --trace arguments.
The advanced way is based on environment variables:
RUST_LOG=<level>: determines the log level filter, can be one ofoff,error,warn,info,debugandtrace.RUST_SPANTRACE=1: enables the spantrace (a span represent periods of time in which a program was executing in a particular context).RUST_BACKTRACE=1: enables the error backtrace.RUST_BACKTRACE=full: enables the full error backtrace, which include source lines where the error originated from.
Logs are written to the stderr, which means that you can redirect them easily to a file:
RUST_LOG=debug himalaya 2>/tmp/himalaya.log
How the wizard discovers IMAP configs?
All the lookup mechanisms use the email address domain as base for the lookup. It is heavily inspired from the Thunderbird Autoconfiguration protocol. For example, for the email address test@example.com, the lookup is performed as (in this order):
- check for
autoconfig.example.com - look up of
example.comin the ISPDB (the Thunderbird central database) - look up
MX example.comin DNS, and formx1.mail.hoster.com, look uphoster.comin the ISPDB - look up
SRV example.comin DNS - try to guess (
imap.example.com,smtp.example.com…)
Sponsoring
Special thanks to the NLnet foundation and the European Commission that helped the project to receive financial support from:
- NGI Assure in 2022
- NGI Zero Entrust in 2023
If you appreciate the project, feel free to donate using one of the following providers: