
Self Hosting Guide
#### A guide for getting started with Self Hosting devices including software and hardware that will make you a better and more efficient Self Hosting.
**Note: You can easily convert this markdown file to a PDF in [VSCode](https://code.visualstudio.com/) using this handy extension [Markdown PDF](https://marketplace.visualstudio.com/items?itemName=yzane.markdown-pdf).**

# Table of Contents
1. [Getting Started with Self-Hosting](https://github.com/mikeroyal/Self-Hosting-Guide#getting-started-with-self-hosting)
- [Tools for Self-Hosting](https://github.com/mikeroyal/Self-Hosting-Guide#tools-for-self-hosting)
* [Containers](https://github.com/mikeroyal/Self-Hosting-Guide#containers)
* [CI/CD](https://github.com/mikeroyal/Self-Hosting-Guide#cicd)
* [Development](https://github.com/mikeroyal/Self-Hosting-Guide#development)
* [Remote Access](https://github.com/mikeroyal/Self-Hosting-Guide#Remote-Access)
* [Virtualization](https://github.com/mikeroyal/Self-Hosting-Guide#Virtualization)
* [Password Management](https://github.com/mikeroyal/Self-Hosting-Guide#password-management)
* [Network Tools](https://github.com/mikeroyal/Self-Hosting-Guide#network-tools)
* [Monitoring](https://github.com/mikeroyal/Self-Hosting-Guide#monitoring)
* [Communications](https://github.com/mikeroyal/Self-Hosting-Guide#communications)
* [Business Management](https://github.com/mikeroyal/Self-Hosting-Guide#business-management)
* [Collaboration & Synchronization](https://github.com/mikeroyal/Self-Hosting-Guide#Collaboration--Synchronization)
* [Encryption](#Encryption)
* [Backups](https://github.com/mikeroyal/Self-Hosting-Guide#backups)
* [Home Server](https://github.com/mikeroyal/Self-Hosting-Guide#home-server)
* [Media Server](https://github.com/mikeroyal/Self-Hosting-Guide#media-server)
* [Video and Audio Processing](#Video-and-Audio-Processing)
* [Podcasting](#Podcasting)
* [Audiobooks](#Audiobooks)
* [Maps](https://github.com/mikeroyal/Self-Hosting-Guide#maps)
* [Bookmarks](#Bookmarks)
* [Photos](https://github.com/mikeroyal/Self-Hosting-Guide#photos)
* [Note-Taking](#Note-Taking)
* [Gaming](https://github.com/mikeroyal/Self-Hosting-Guide#gaming)
* [Foundations/Projects](https://github.com/mikeroyal/Self-Hosting-Guide#foundationsprojects)
- [System Hardware](#System-Hardware)
- [Operating Systems](#Operating-Systems)
- [Storage](https://github.com/mikeroyal/Self-Hosting-Guide#storage)
- [File systems](https://github.com/mikeroyal/Self-Hosting-Guide#file-systems)
- [Books](https://github.com/mikeroyal/Self-Hosting-Guide#books)
- [Podcasts](https://github.com/mikeroyal/Self-Hosting-Guide#podcasts)
- [YouTube Channels](https://github.com/mikeroyal/Self-Hosting-Guide#youtube-channels)
- [Tutorials & Resources](https://github.com/mikeroyal/Self-Hosting-Guide#tutorials--resources)
- [Useful Subreddits to Follow](https://github.com/mikeroyal/Self-Hosting-Guide#subreddits)
2. [WireGuard](https://github.com/mikeroyal/Self-Hosting-Guide#wireguard)
* [What is WireGuard?](#what-is-wireguard)
* [What is Tailscale?](#what-is-tailscale)
* [What is Netmaker?](#what-is-netmaker)
* [WireGuard Tools](#wireguard-tools)
* [Setting up WireGuard with PiVPN](#setting-up-wireguard-with-pivpn)
* [Setting up WireGuard on Unraid](#setting-up-wireguard-on-unraid)
* [Setting up WireGuard on pfSense](#setting-up-wireguard-on-pfsense)
* [Setting up WireGuard on OpenWRT](#setting-up-wireguard-on-openwrt)
* [Setting up WireGuard on Home Assistant](#setting-up-wireguard-on-home-assistant)
3. [Nextcloud](https://github.com/mikeroyal/Self-Hosting-Guide#nextcloud)
4. [Raspberry Pi](https://github.com/mikeroyal/Self-Hosting-Guide#raspberry-pi)
* [Models of Raspberry Pi boards](#models-of-raspberry-pi-boards)
* [Raspberry Pi Learning Resources](#raspberry-pi-learning-resources)
* [Raspberry Pi Operating Systems](#raspberry-pi-operating-systems)
* [Raspberry Pi Tools](#raspberry-pi-tools)
- [Getting Started with Home Assistant(HA)](#Home-Assistant)
- [Getting Started with Homebridge](#Homebridge)
- [Getting Started with ESPHome](#ESPHome)
- [Turning Raspberry Pi into a Router](#Turning-Raspberry-Pi-into-a-Router)
- [Setting up Watchdog Time (WDT) on Raspberry Pi](#setting-watchdog-timer-wdt-on-raspberry-pi)
* [Raspberry Pi Upgrades](#raspberry-pi-upgrades)
5. [Grafana](https://github.com/mikeroyal/Self-Hosting-Guide#Grafana)
6. [Networking](https://github.com/mikeroyal/Self-Hosting-Guide#networking)
7. [Docker](https://github.com/mikeroyal/Self-Hosting-Guide#docker)
8. [Kubernetes](https://github.com/mikeroyal/Self-Hosting-Guide#kubernetes)
9. [Ansible](https://github.com/mikeroyal/Self-Hosting-Guide#ansible)
10. [Databases](https://github.com/mikeroyal/Self-Hosting-Guide#databases)
11. [Telco 5G](https://github.com/mikeroyal/Self-Hosting-Guide#telco-5g)
12. [Open Source Security](https://github.com/mikeroyal/Self-Hosting-Guide#open-source-security)
13. [Differential Privacy](https://github.com/mikeroyal/Self-Hosting-Guide#differential-privacy)
14. [Machine Learning](https://github.com/mikeroyal/Self-Hosting-Guide#machine-learning)
15. [IoT Protocols](https://github.com/mikeroyal/Self-Hosting-Guide#iot-protocols)
16. [Operating systems (OS)](https://github.com/mikeroyal/Self-Hosting-Guide#operating-systems)
17. [Middleware](https://github.com/mikeroyal/Self-Hosting-Guide#middleware)
18. [Node Flow editors](https://github.com/mikeroyal/Self-Hosting-Guide#node-flow-editors)
19. [Toolkits](https://github.com/mikeroyal/Self-Hosting-Guide#toolkits)
20. [Data visualization](https://github.com/mikeroyal/Self-Hosting-Guide#data-visualization)
21. [Search](https://github.com/mikeroyal/Self-Hosting-Guide#search)
22. [Hardware](https://github.com/mikeroyal/Self-Hosting-Guide#hardware)
23. [In-memory data grids](https://github.com/mikeroyal/Self-Hosting-Guide#in-memory-data-grids)
24. [Home automation](https://github.com/mikeroyal/Self-Hosting-Guide#home-automation)
25. [Robotics](https://github.com/mikeroyal/Self-Hosting-Guide#robotics)
26. [Mesh networks](https://github.com/mikeroyal/Self-Hosting-Guide#mesh-networks)
27. [Blockchain Development](https://github.com/mikeroyal/Self-Hosting-Guide#blockchain-development)
28. [Node.js Development](https://github.com/mikeroyal/Self-Hosting-Guide#nodejs-development)
29. [C/C++ Development](https://github.com/mikeroyal/Self-Hosting-Guide#cc-development)
30. [Java Development](https://github.com/mikeroyal/Self-Hosting-Guide#java-development)
31. [Python Development](https://github.com/mikeroyal/Self-Hosting-Guide#python-development)
32. [Rust Development](https://github.com/mikeroyal/Self-Hosting-Guide#rust-development)
33. [Swift Development](https://github.com/mikeroyal/Self-Hosting-Guide#swift-development)
34. [XML Development](https://github.com/mikeroyal/Self-Hosting-Guide#xml-development)
# Getting Started with Self-Hosting
[Back to the Top](https://github.com/mikeroyal/Self-Hosting-Guide#table-of-contents)
[Self-Hosting](https://www.reddit.com/r/selfhosted/) is the practice of locally hosting(on premises & private web servers) and managing software applications by a person or organization instead of monthly subscriptions from [Software as a service (SaaS) providers](https://azure.microsoft.com/en-us/overview/what-is-saas/).
Most self-hosted software can be installed using [Docker](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Docker_(software)), a packaging system which allows software to bundle their configuration and dependencies and isolate them from your operating system. Software using docker can be installed using the command line or via graphical interfaces such as [Portainer](https://github.com/portainer/portainer). Software is installed with Docker by downloading an image file containing the application, then creating a copy that sets up its own dependencies and configuration within what is called a container. Without containers you would often need to install different versions of the same programming languages or tools to satisfy the dependencies for the software you want to use which can get complicated.

## Tools for Self-Hosting
[Back to the Top](https://github.com/mikeroyal/Self-Hosting-Guide#table-of-contents)
### Containers
[Back to the Top](#table-of-contents)
**Container** is a standard unit of software that packages up code and all its dependencies(including CPU, memory, file storage, and network connections) so the application runs quickly and reliably from one computing environment to another.
* [Application Container Security Guide | NIST (PDF)](https://nvlpubs.nist.gov/nistpubs/SpecialPublications/NIST.SP.800-190.pdf)
**Container Image** is a lightweight, standalone, executable package of software that includes everything needed to run an application such as the code, runtime, system tools, system libraries, and settings.
**Best places to get Container Images:**
* [DockerHub Container Images](https://hub.docker.com/search?image_filter=official&q=&type=image)
* [LinuxServer.io Container Images](https://fleet.linuxserver.io/)
* [Quay Container Images](https://quay.io/search)
[Docker Compose](https://github.com/docker/compose) is a tool that was developed to help define and share multi-container applications. With Compose, we can create a YAML file to define the services and with a single command, can spin everything up or tear it all down.
[Kompose](https://kompose.io/) is a conversion tool for Docker Compose to container orchestrators such as [Kubernetes](https://kubernetes.io/) or [OpenShift](https://openshift.com/).
[Containerd](https://containerd.io/) is a daemon that manages the complete container lifecycle of its host system, from image transfer and storage to container execution and supervision to low-level storage to network attachments and beyond. It is available for Linux and Windows.
[Podman](https://podman.io/) is a daemonless, open source, Linux native tool designed to make it easy to find, run, build, share and deploy applications using Open Containers Initiative (OCI) Containers and Container Images. Podman provides a command line interface (CLI) familiar to anyone who has used the Docker Container Engine.
[Lima](https://github.com/lima-vm/lima) is a tool that launches Linux virtual machines with automatic file sharing and port forwarding (similar to WSL2), and [containerd](https://containerd.io/). It's a great free and open-source alternative for [Docker Desktop](https://www.docker.com/products/docker-desktop).
[Colima](https://github.com/abiosoft/colima) is a container runtimes on macOS (and Linux) with minimal setup.
[Portainer Community Edition](https://github.com/portainer/portainer) is a lightweight service delivery platform for containerized applications that can be used to manage Docker, Swarm, Kubernetes and ACI environments. It is designed to be as simple to deploy as it is to use.
[Yacht](https://github.com/SelfhostedPro/Yacht) is a container management UI with a focus on templates and 1-click deployments.
[Kitematic](https://kitematic.com/) is a simple application for managing Docker containers on Mac, Linux and Windows letting you control your app containers from a graphical user interface (GUI).
[Open Container Initiative](https://opencontainers.org/about/overview/) is an open governance structure for the express purpose of creating open industry standards around container formats and runtimes.
[Buildah](https://buildah.io/) is a command line tool to build Open Container Initiative (OCI) images. It can be used with Docker, Podman, Kubernetes.
[Red Hat Quay](https://quay.io/) is a project that Builds, Stores, and Distributes your Applications and Containers.
[Clair](https://github.com/quay/clair) is an open source project for the static analysis of vulnerabilities in application containers (currently including [OCI](https://github.com/opencontainers/image-spec/blob/master/spec.md) and [Docker](https://github.com/docker/docker/blob/master/image/spec/v1.2.md)).
[Shipwright](https://github.com/SelfhostedPro/Shipwright) is a WebUI to generate templates for Yacht, Portainer, Docker-Compose, and Unraid.
[Autoheal](https://hub.docker.com/r/willfarrell/autoheal) monitors and restarts unhealthy docker containers.
[Dozzle](https://hub.docker.com/r/amir20/dozzle) is a small lightweight application with a web based interface to monitor Docker logs. It doesn’t store any log files. It is for live monitoring of your container logs only.
[Diun](https://crazymax.dev/diun/) is a tool that receive notifications when a Docker image is updated on a Docker registry.
[WatchTower](https://hub.docker.com/r/containrrr/watchtower) is a process for automating Docker container base image updates.
[Nginx Proxy](https://github.com/nginx-proxy/nginx-proxy) is an automation tool that sets up a container running nginx and [docker-gen](https://github.com/nginx-proxy/docker-gen). Docker-gen generates reverse proxy configs for nginx and reloads nginx when containers are started and stopped.
[Visual Studio Code Dev Containers](https://github.com/microsoft/vscode-dev-containers) is an extension that lets you use a [Docker container](https://docker.com/) as a full-featured development environment. It allows you to open any folder inside (or mounted into) a container and take advantage of Visual Studio Code's full feature set. A [devcontainer.json file](https://code.visualstudio.com/docs/devcontainers/containers#_create-a-devcontainerjson-file) in your project tells VS Code how to access (or create) a development container with a well-defined tool and runtime stack.
### CI/CD
[Back to the Top](#table-of-contents)
* **CI/CD: Continuous Integration and Continuous Delivery**
[Drone](https://drone.io/) is a Continuous Delivery system built on container technology. Drone uses a simple YAML configuration file, a superset of docker-compose, to define and execute Pipelines inside Docker containers.
[Travis CI](https://travis-ci.org/) is a hosted continuous integration service used to build and test software projects hosted at GitHub.
[Circle CI](https://circleci.com/) is a continuous integration and continuous delivery platform that helps software teams work smarter, faster.
[Buddy](https://buddy.works/) is a fully-featured DevOps platform with no learning curve that packs everything you need from a CI/CD tool.
[Buildbot](https://www.buildbot.net/) is a continuous integration tool which automates the compile or test cycle required to validate changes to the project code base. It queues jobs, executes the jobs when the required resources are available, and reports the results.
### Development
[Back to the Top](#table-of-contents)
[Proxmox VE(Virtual Environment)](https://www.proxmox.com/en/proxmox-ve) is an open-source platform for enterprise virtualization. It has a built-in web interface that you can use to easily manage VMs and containers, software-defined storage and networking, high-availability clustering, and multiple out-of-the-box tools on a single solution.
[Code-Server](https://github.com/coder/code-server) is Visual Studio Code running on a remote server, accessible through the browser.
[Visual Studio Live Share](https://visualstudio.microsoft.com/services/live-share/) is a service/extension that enables you to collaboratively edit and debug with others in real time, regardless of the programming languages you're using or app types you're building. You can instantly and securely share your current project, start a joint debugging session, share terminal instances, forward localhost web apps, have voice calls, and more.
[GistPad](https://marketplace.visualstudio.com/items?itemName=vsls-contrib.gistfs) is a Visual Studio Code extension that allows you to edit GitHub Gists and repositories from the comfort of your favorite editor. You can open, create, delete, fork and star gists and repositories, and then seamlessly begin editing files as if they were local, without ever cloning, pushing or pulling anything.
[Live Server](https://marketplace.visualstudio.com/items?itemName=ritwickdey.LiveServer) is an extension for Visual Studio Code that launches a development local Server with live reload feature for static & dynamic pages.
[Gitea](https://gittea.dev/) is a community managed painless self-hosted Git service.
[GitLab](https://about.gitlab.com/) is an open source end-to-end software development platform with built-in version control, issue tracking, code review, CI/CD, and more. Self-host GitLab on your own servers, in a container, or on a cloud provider.
[Soft Serve](https://github.com/charmbracelet/soft-serve) is a tasty, self-hostable Git server for the command line.
[Glow](https://github.com/charmbracelet/glow) is a terminal based markdown reader designed from the ground up to bring out the beauty—and power—of the CLI. It's used to discover markdown files, read documentation directly on the command line and stash markdown files to your own private collection, so you can read them anywhere.
[Node-Red](https://nodered.org/) is a low-code programming for event-driven applications.
### Remote Access
[Back to the Top](#table-of-contents)
[FreeRDP](https://github.com/FreeRDP/FreeRDP) is a free remote desktop protocol library and clients.
[Rustdesk](https://rustdesk.com/) is an open source virtual/remote desktop infrastructure for everyone. Display and control your PC (Windows, macOS, and Linux) and Android devices.
[TinyPilot](https://tinypilotkvm.com/) is a tool that enables KVM over IP letting you control any computer remotely.
[X2Go](https://wiki.x2go.org/) is open source remote desktop software for Linux that uses a modified NX 3 protocol. It gives remote access to a Linux system's GUI.
[Apache Guacamole](https://guacamole.apache.org/) is a clientless remote desktop gateway. It supports standard protocols like VNC, RDP, and SSH.
[Remotely](https://github.com/immense/Remotely) is a remote control and remote scripting solution, built with .NET 6, Blazor, SignalR Core, and WebRTC.
[P2P Remote Desktop](https://github.com/miroslavpejic85/p2p) is a portable, no configuration or installation needed remote desktop tool.
[Cloudflare Tunnel](https://developers.cloudflare.com/cloudflare-one/connections/connect-apps/install-and-setup/tunnel-guide) is a tunneling daemon that proxies traffic from the Cloudflare network to your origins. This daemon sits between Cloudflare network and your origin (a webserver). This attracts client requests and sends them to you via this daemon, without requiring you to poke holes on your firewall and your origin(webserver) can remain as closed as possible.
[WireGuard®](https://www.wireguard.com/) is a straight-forward, fast and modern VPN that utilizes state-of-the-art cryptography. It aims to be faster, simpler, leaner, and more useful than IPsec while avoiding the massive headache. WireGuard is designed as a general-purpose VPN for running on embedded interfaces and super computers alike, fit for many circumstances. Initially released for the Linux kernel, it is now cross-platform (Windows, macOS, BSD, iOS, Android) and widely deployable.
[NetBird](https://netbird.io/) is an open-source VPN management platform built on top of WireGuard® making it easy to create secure private networks for your organization or home.
[Tailscale](https://github.com/tailscale) is a WireGuard-based app that makes secure, private networks easy for teams of any scale. It works like an overlay network between the computers of your networks using all kinds of NAT traversal sorcery.
[Headscale](https://github.com/juanfont/headscale) is an open source, self-hosted implementation of the Tailscale coordination server.
[MeshCentral](https://meshcentral.com/) is a full computer management web site. It can run your own web server to remotely manage and control computers on a local network or anywhere on the internet. Once you get the server started, create device group and download and install an agent on each computer you want to manage.
[VNC Viewer](https://www.realvnc.com/en/connect/download/viewer/) is a free remote desktop application that use can use on your iPhone, iPad, Mac, Windows and Linux computers from anywhere in the world.
[TightVNC](https://www.tightvnc.com/) is a free remote desktop application. It can see the desktop of a remote machine and control it with your local mouse and keyboard, just like you would do it sitting in the front of that computer.
### Virtualization
[Back to the Top](#table-of-contents)
[HVM (Hardware Virtual Machine)](https://docs.aws.amazon.com/AWSEC2/latest/UserGuide/virtualization_types.html) is a virtualization type that provides the ability to run an operating system directly on top of a virtual machine without any modification, as if it were run on the bare-metal hardware.
[PV(ParaVirtualization)](https://wiki.xenproject.org/wiki/Paravirtualization_(PV)) is an efficient and lightweight virtualization technique introduced by the Xen Project team, later adopted by other virtualization solutions. PV does not require virtualization extensions from the host CPU and thus enables virtualization on hardware architectures that do not support Hardware-assisted virtualization.
[Network functions virtualization (NFV)](https://www.vmware.com/topics/glossary/content/network-functions-virtualization-nfv) is the replacement of network appliance hardware with virtual machines. The virtual machines use a hypervisor to run networking software and processes such as routing and load balancing. NFV allows for the separation of communication services from dedicated hardware, such as routers and firewalls. This separation means network operations can provide new services dynamically and without installing new hardware. Deploying network components with network functions virtualization only takes hours compared to months like with traditional networking solutions.
[Software Defined Networking (SDN)](https://www.vmware.com/topics/glossary/content/software-defined-networking) is an approach to networking that uses software-based controllers or application programming interfaces (APIs) to communicate with underlying hardware infrastructure and direct traffic on a network. This model differs from that of traditional networks, which use dedicated hardware devices (routers and switches) to control network traffic.
[Virtualized Infrastructure Manager (VIM)](https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/net_mgmt/network_function_virtualization_Infrastructure/3_2_2/install_guide/Cisco_VIM_Install_Guide_3_2_2/Cisco_VIM_Install_Guide_3_2_2_chapter_00.html) is a service delivery and reduce costs with high performance lifecycle management Manage the full lifecycle of the software and hardware comprising your NFV infrastructure (NFVI), and maintaining a live inventory and allocation plan of both physical and virtual resources.
[Management and Orchestration(MANO)](https://www.etsi.org/technologies/open-source-mano) is an ETSI-hosted initiative to develop an Open Source NFV Management and Orchestration (MANO) software stack aligned with ETSI NFV. Two of the key components of the ETSI NFV architectural framework are the NFV Orchestrator and VNF Manager, known as NFV MANO.
[Magma](https://www.magmacore.org/) is an open source software platform that gives network operators an open, flexible and extendable mobile core network solution. Their mission is to connect the world to a faster network by enabling service providers to build cost-effective and extensible carrier-grade networks. Magma is 3GPP generation (2G, 3G, 4G or upcoming 5G networks) and access network agnostic (cellular or WiFi). It can flexibly support a radio access network with minimal development and deployment effort.
[OpenRAN](https://open-ran.org/) is an intelligent Radio Access Network(RAN) integrated on general purpose platforms with open interface between software defined functions. Open RANecosystem enables enormous flexibility and interoperability with a complete openess to multi-vendor deployments.
[Open vSwitch(OVS)](https://www.openvswitch.org/)is an open source production quality, multilayer virtual switch licensed under the open source Apache 2.0 license. It is designed to enable massive network automation through programmatic extension, while still supporting standard management interfaces and protocols (NetFlow, sFlow, IPFIX, RSPAN, CLI, LACP, 802.1ag).
[Edge](https://www.ibm.com/cloud/what-is-edge-computing) is a distributed computing framework that brings enterprise applications closer to data sources such as IoT devices or local edge servers. This proximity to data at its source can deliver strong business benefits, including faster insights, improved response times and better bandwidth availability.
[Multi-access edge computing (MEC)](https://www.etsi.org/technologies/multi-access-edge-computing) is an Industry Specification Group (ISG) within ETSI to create a standardized, open environment which will allow the efficient and seamless integration of applications from vendors, service providers, and third-parties across multi-vendor Multi-access Edge Computing platforms.
[Virtualized network functions(VNFs)](https://www.juniper.net/documentation/en_US/cso4.1/topics/concept/nsd-vnf-overview.html) is a software application used in a Network Functions Virtualization (NFV) implementation that has well defined interfaces, and provides one or more component networking functions in a defined way. For example, a security VNF provides Network Address Translation (NAT) and firewall component functions.
[Cloud-Native Network Functions(CNF)](https://www.cncf.io/announcements/2020/11/18/cloud-native-network-functions-conformance-launched-by-cncf/) is a network function designed and implemented to run inside containers. CNFs inherit all the cloud native architectural and operational principles including Kubernetes(K8s) lifecycle management, agility, resilience, and observability.
[Physical Network Function(PNF)](https://www.mpirical.com/glossary/pnf-physical-network-function) is a physical network node which has not undergone virtualization. Both PNFs and VNFs (Virtualized Network Functions) can be used to form an overall Network Service.
[Network functions virtualization infrastructure(NFVI)](https://docs.vmware.com/en/VMware-vCloud-NFV/2.0/vmware-vcloud-nfv-reference-architecture-20/GUID-FBEA6C6B-54D8-4A37-87B1-D825F9E0DBC7.html) is the foundation of the overall NFV architecture. It provides the physical compute, storage, and networking hardware that hosts the VNFs. Each NFVI block can be thought of as an NFVI node and many nodes can be deployed and controlled geographically.
[Virtualization-based Security (VBS)](https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/windows-hardware/design/device-experiences/oem-vbs) is a hardware virtualization feature to create and isolate a secure region of memory from the normal operating system.
[Hypervisor-Enforced Code Integrity (HVCI)](https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/windows-hardware/drivers/bringup/device-guard-and-credential-guard) is a mechanism whereby a hypervisor, such as Hyper-V, uses hardware virtualization to protect kernel-mode processes against the injection and execution of malicious or unverified code. Code integrity validation is performed in a secure environment that is resistant to attack from malicious software, and page permissions for kernel mode are set and maintained by the hypervisor.
[NVIDIA virtual GPU (vGPU)](https://www.nvidia.com/en-us/data-center/virtual-solutions/) is a software enables powerful GPU performance for workloads ranging from graphics-rich virtual workstations to data science and AI, enabling IT to leverage the management and security benefits of virtualization as well as the performance of NVIDIA GPUs required for modern workloads.
[AMD MxGPU](https://www.amd.com/en/graphics/workstation-virtual-graphics) is a hardware-based virtualized GPU solution, is built on industry standard SR-IOV (Single-Root I/O Virtualization) technology and allows multiple virtualized users per physical GPU to work remotely.
[Proxmox Virtual Environment(VE)](https://www.proxmox.com/en/) is a complete open-source platform for enterprise virtualization. It inlcudes a built-in web interface that you can easily manage VMs and containers, software-defined storage and networking, high-availability clustering, and multiple out-of-the-box tools on a single solution.
[KVM (for Kernel-based Virtual Machine)](https://www.linux-kvm.org/page/Main_Page) is a full virtualization solution for Linux on x86 hardware containing virtualization extensions (Intel VT or AMD-V). It consists of a loadable kernel module, kvm.ko, that provides the core virtualization infrastructure and a processor specific module, kvm-intel.ko or kvm-amd.ko.
[QEMU](https://www.qemu.org) is a fast processor emulator using a portable dynamic translator. QEMU emulates a full system, including a processor and various peripherals. It can be used to launch a different Operating System without rebooting the PC or to debug system code.
[Quickemu](https://github.com/wimpysworld/quickemu) is a program that quickly create and run optimised Windows, macOS and Linux desktop virtual machines.
[Hyper-V](https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/virtualization/hyper-v-on-windows/) enables running virtualized computer systems on top of a physical host. These virtualized systems can be used and managed just as if they were physical computer systems, however they exist in virtualized and isolated environment. Special software called a hypervisor manages access between the virtual systems and the physical hardware resources. Virtualization enables quick deployment of computer systems, a way to quickly restore systems to a previously known good state, and the ability to migrate systems between physical hosts.
[Cloud Hypervisor](https://github.com/cloud-hypervisor/cloud-hypervisor) is an open source Virtual Machine Monitor (VMM) that runs on top of [KVM](https://www.kernel.org/doc/Documentation/virtual/kvm/api.txt). The project focuses on exclusively running modern, cloud workloads, on top of a limited set of hardware architectures and platforms. Cloud workloads refers to those that are usually run by customers inside a cloud provider. Cloud Hypervisor is implemented in [Rust](https://www.rust-lang.org/) and is based on the [rust-vmm](https://github.com/rust-vmm) crates.
[VirtManager](https://github.com/virt-manager/virt-manager) is a graphical tool for managing virtual machines via libvirt. Most usage is with QEMU/KVM virtual machines, but Xen and libvirt LXC containers are well supported. Common operations for any libvirt driver should work.
[oVirt](https://www.ovirt.org) is an open-source distributed virtualization solution, designed to manage your entire enterprise infrastructure. oVirt uses the trusted KVM hypervisor and is built upon several other community projects, including libvirt, Gluster, PatternFly, and Ansible. Founded by Red Hat as a community project on which Red Hat Enterprise Virtualization is based allowing for centralized management of virtual machines, compute, storage and networking resources, from an easy-to-use web-based front-end with platform independent access.
[Firecracker](http://firecracker-microvm.io/) is an open source virtualization technology that is purpose-built for creating and managing secure, multi-tenant container and function-based services that provide serverless operational models. It runs workloads in lightweight virtual machines, called microVMs, which combine the security and isolation properties provided by hardware virtualization technology with the speed and flexibility of containers.
[Foreman](https://theforeman.org/) is a free open source project that gives you the power to easily automate repetitive tasks, quickly deploy applications, and proactively manage your servers life cycle, on-premises or in the cloud.
[Harvester](https://harvesterhci.io/) is an open source hyper-converged infrastructure (HCI) software built on Kubernetes.
[Anthos](https://cloud.google.com/anthos/docs/concepts/overview) is a modern application management platform that provides a consistent development and operations experience for cloud and on-premises environments.
[HyperKit](https://github.com/moby/hyperkit) is a toolkit for embedding hypervisor capabilities in your application. It includes a complete hypervisor, based on [xhyve](https://github.com/mist64/xhyve)/[bhyve](https://bhyve.org/), which is optimized for lightweight virtual machines and container deployment. It is designed to be interfaced with higher-level components such as the [VPNKit](https://github.com/moby/vpnkit) and [DataKit](https://github.com/moby/datakit). HyperKit currently only supports macOS using the [Hypervisor.framework](https://developer.apple.com/library/mac/documentation/DriversKernelHardware/Reference/Hypervisor/index.html) making it a core component of Docker Desktop for Mac.
[Intel® Graphics Virtualization Technology (Intel® GVT)](https://github.com/intel/gvt-linux) is a full GPU virtualization solution with mediated pass-through, starting from 4th generation Intel Core (TM) processors with Intel processor graphics(Broadwell and newer). It can be used to virtualize the GPU for multiple guest virtual machines, effectively providing near-native graphics performance in the virtual machine and still letting your host use the virtualized GPU normally.
[Apple Hypervisor](https://developer.apple.com/documentation/hypervisor) is a frameowrk that builds virtualization solutions on top of a lightweight hypervisor, without third-party kernel extensions. Hypervisor provides C APIs so you can interact with virtualization technologies in user space, without writing kernel extensions (KEXTs). As a result, the apps you create using this framework are suitable for distribution on the [Mac App Store](https://www.appstore.com/).
[Apple Virtualization Framework](https://developer.apple.com/documentation/virtualization) is a framework that provides high-level APIs for creating and managing virtual machines on Apple silicon and Intel-based Mac computers. This framework is used to boot and run a Linux-based operating system in a custom environment that you define. It also supports the [Virtio specification](https://www.redhat.com/en/virtio-networking-series), which defines standard interfaces for many device types, including network, socket, serial port, storage, entropy, and memory-balloon devices.
[Apple Paravirtualized Graphics Framework](https://developer.apple.com/documentation/paravirtualizedgraphics) is a framework that implements hardware-accelerated graphics for macOS running in a virtual machine, hereafter known as the guest. The operating system provides a graphics driver that runs inside the guest, communicating with the framework in the host operating system to take advantage of Metal-accelerated graphics.
[Xen](https://github.com/xen-project/xen) is focused on advancing virtualization in a number of different commercial and open source applications, including server virtualization, Infrastructure as a Services (IaaS), desktop virtualization, security applications, embedded and hardware appliances, and automotive/aviation.
[Ganeti](https://github.com/ganeti/ganeti) is a virtual machine cluster management tool built on top of existing virtualization technologies such as Xen or KVM and other open source software. Once installed, the tool assumes management of the virtual instances (Xen DomU).
[Packer](https://www.packer.io/) is an open source tool for creating identical machine images for multiple platforms from a single source configuration. Packer is lightweight, runs on every major operating system, and is highly performant, creating machine images for multiple platforms in parallel. Packer does not replace configuration management like Chef or Puppet. In fact, when building images, Packer is able to use tools like Chef or Puppet to install software onto the image.
[Vagrant](https://www.vagrantup.com/) is a tool for building and managing virtual machine environments in a single workflow. With an easy-to-use workflow and focus on automation, Vagrant lowers development environment setup time, increases production parity, and makes the "works on my machine" excuse a relic of the past. It provides easy to configure, reproducible, and portable work environments built on top of industry-standard technology and controlled by a single consistent workflow to help maximize the productivity and flexibility of you and your team.
### Password Management
[Back to the Top](#table-of-contents)
[Bitwarden](https://bitwarden.com/host/) is a free and open-source password management service that stores sensitive information such as website credentials in an encrypted vault.
[Bitwarden Server](https://github.com/bitwarden/server) is a project contains the APIs, database, and other core infrastructure items needed for the "backend" of all bitwarden client applications. Checkout [Bitwarden's self-hosted release repository](https://github.com/bitwarden/self-host).
[Vaultwarden](https://github.com/dani-garcia/vaultwarden) is an unofficial Bitwarden compatible server written in Rust, formerly known as bitwarden_rs.
[AuthPass.app](https://authpass.app/) is an Open-Source Password Manager for mobile and desktop that is Keepass 2.x (kdbx 3.x) compatible.
[pass](https://www.passwordstore.org/) is an open-source unix-based password utilitiy with various [gui clients](https://www.passwordstore.org/#other)
### Network Tools
[Back to the Top](#table-of-contents)
[MQTT](https://mqtt.org/) is an [OASIS standard](https://www.oasis-open.org/standards/) messaging protocol for the Internet of Things (IoT). It is designed as an extremely lightweight publish/subscribe messaging transport that is ideal for connecting remote devices with a small code footprint and minimal network bandwidth.
[Mongoose](https://github.com/cesanta/mongoose) is a networking library for C/C++. It implements event-driven non-blocking APIs for TCP, UDP, HTTP, WebSocket, MQTT. It is designed for connecting devices and bringing them online.
[Eclipse Mosquitto](https://github.com/eclipse/mosquitto) is an open source implementation of a server for version 5.0, 3.1.1, and 3.1 of the [MQTT](https://mqtt.org/) protocol.
[Ejabberd](https://ejabberd.im/) is an open-source, robust, scalable and extensible realtime platform built using [Erlang/OTP](https://www.erlang.org/), that includes [XMPP](https://xmpp.org/) Server, [MQTT](https://mqtt.org/) Broker and [SIP](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Session_Initiation_Protocol) Service.
[LibreSpeed](https://librespeed.org/) is a network speed test tool that can be run on your LAN or hosted in the cloud.
[SmokePing](https://oss.oetiker.ch/smokeping/) is a deluxe latency measurement tool. It can measure, store and display latency, latency distribution and packet loss. It uses RRDtool to maintain a longterm data-store and to draw pretty graphs, giving up to the minute information on the state of each network connection.
[Nginx proxy manager (NPM)](https://nginxproxymanager.com/) is a reverse proxy management system running on Docker. It's easy to set up and does not require users to know how to work with Nginx servers or SSL certificates.
[Netdata](https://github.com/netdata/netdata) is high-fidelity infrastructure monitoring and troubleshooting, real-time monitoring Agent collects thousands of metrics from systems, hardware, containers, and applications with zero configuration. It runs permanently on all your physical/virtual servers, containers, cloud deployments, and edge/IoT devices, and is perfectly safe to install on your systems mid-incident without any preparation.
[Pi-hole](https://pi-hole.net/) is a [DNS sinkhole](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/DNS_Sinkhole) that protects your devices from unwanted content, without installing any client-side software, intended for use on a private network. It is designed for use on embedded devices with network capability, such as the Raspberry Pi, but it can be used on other machines running Linux and cloud implementations.
[AdGuard Home](https://github.com/AdguardTeam/AdGuardHome) is a DNS relay station with ad/tracker/other blocking, IP address redirections, and DNS-over-HTTPS.
[NetBird](https://netbird.io/) is an open-source VPN management platform built on top of WireGuard® making it easy to create secure private networks for your organization or home.
[Supabase](https://github.com/supabase/supabase) is an open source Firebase alternative. It is building the features of Firebase using enterprise-grade open source tools.
[Plik](https://github.com/root-gg/plik) is a scalable & friendly temporary file upload system (Wetransfer like) in golang.
[Restify](https://github.com/restify/node-restify) is a framework, utilizing [connect](https://github.com/senchalabs/connect) style middleware for building REST APIs.
[Traefik](https://traefik.io/traefik/) is an open source Edge Router that makes publishing your services a fun and easy experience. It receives requests on behalf of your system and finds out which components are responsible for handling them. What sets Traefik apart, besides its many features, is that it automatically discovers the right configuration for your services.
[DuckDNS](https://www.duckdns.org/) is a free service that allows you to bind your own favorite subdomain under ```duckdns.org``` to the public IP address in use from your router, even though such address is dynamically allocated by your internet service provider and therefore changes over time.
[Trust-DNS](https://github.com/bluejekyll/trust-dns) is a Rust based DNS client, server, and Resolver, built to be safe and secure from the ground up.
[Hugo](https://github.com/gohugoio/hugo) is a static HTML and CSS website generator written in Go. It is optimized for speed, ease of use, and configurability. Hugo takes a directory with content and templates and renders them into a full HTML website.
[sshuttle](https://github.com/sshuttle/sshuttle) is a transparent proxy server that works as a poor man's VPN that forwards connection over ssh. It works with Linux and MacOS and supports DNS tunneling.
[NetHopper](https://www.nethopper.io/) is a Multi-Cloud Application Network as a Service. The easiest way to visualize, connect, secure, protect, and monitor microservices across any cluster, site, cloud, or network.
[Cypress](https://cypress.io/) is a tool that makes it fast, easy and reliable testing for anything that runs in a browser.
[Kimchi](https://github.com/kimchi-project/kimchi) is an HTML5 based management tool for KVM. It is designed to make it as easy as possible to get started with KVM and create your first guest.
[ION](https://github.com/pion/ion) is a distributed real-time communication system, the goal is to chat anydevice, anytime, anywhere.
[FreeRDP](https://github.com/FreeRDP/FreeRDP) is a free remote desktop protocol library and clients.
[Pimox](https://github.com/pimox/pimox7) is a port of Proxmox to the Raspberry Pi allowing you to build a Proxmox cluster of Rapberry Pi's or even a hybrid cluster of Pis and x86 hardware.
[PiKVM](https://github.com/pikvm/pikvm) is a very simple and fully functional Raspberry Pi-based KVM over IP.
[Firezone](https://firezone.dev/) is a self-hosted WireGuard®-based VPN server and Linux firewall.
### Monitoring
[Back to the Top](#table-of-contents)
[Proxmox Mail Gateway](https://www.proxmox.com/en/proxmox-mail-gateway) is an open-source email security solution protecting your mail server against all email threats from the moment they emerge.
[M2MLabs MainSpring](http://www.m2mlabs.com/) is an application framework for building machine-to-machine applications like vehicle tracking or machine remote monitoring. In such applications typically a remote device equipped with sensors (e.g. gps, temperature, pressure) and actors communicates with a server application that is running the device communication protocol, device configuration, storage of data sent by the devices as well as the application business logic and the presentation layer.
[VictoriaMetrics](https://victoriametrics.com/) is a fast and scalable open source time series database and monitoring solution which exists in a Single and in a cluster version. It is compatible with Prometheus pull model and supports a [wide variety of ingestion protocols](https://docs.victoriametrics.com/#prominent-features): Influx, Graphite, Prometheus remote_write, Prometheus exposion format, OpenTSDB put message, JSON line format, Arbitrary CSV data, native binary formant, DataDog agent or DogStatsD; as way as many ways to query data via PromQL or [MetricsQL](https://docs.victoriametrics.com/MetricsQL.html) from Grafana or own [VMUI](https://docs.victoriametrics.com/Single-server-VictoriaMetrics.html#vmui).
[InfluxDB](https://www.influxdata.com) is an open source time series database, purpose-built by InfluxData for monitoring metrics and events, provides real-time visibility into stacks, sensors, and systems. Use InfluxDB to capture, analyze, and store millions of points per second, meet demanding SLA's, and chart a path to automation.
[Grafana](https://grafana.com/oss/grafana/) is a tool that allows you to query, visualize, alert on and understand your metrics no matter where they are stored.
[Prometheus](https://prometheus.io/) is a free software application used for event monitoring and alerting. It records real-time metrics in a time series database (allowing for high dimensionality) built using a HTTP pull model, with flexible queries and real-time alerting.
[Loki](https://grafana.com/oss/loki/) is a horizontally-scalable, highly-available, multi-tenant log aggregation system inspired by Prometheus. It is designed to be very cost effective and easy to operate. It does not index the contents of the logs, but rather a set of labels for each log stream.
[Thanos](https://thanos.io/) is a set of components that can be composed into a highly available metric system with unlimited storage capacity, which can be added seamlessly on top of existing Prometheus deployments.
[Wyze](https://wyze.com/) is a great security and monitoring application to live stream HD video from the security cameras from anywhere in the world.
[Uptime Kuma](https://uptime.kuma.pet/) is a fancy self-hosted monitoring tool.
[Gatus](https://gatus.io/) is a developer-oriented health dashboard that gives you the ability to monitor your services using HTTP, ICMP, TCP, and even DNS queries as well as evaluate the result of said queries by using a list of conditions on values like the status code, the response time, the certificate expiration, the body and many others.
[Upptime](https://upptime.js.org) is the open-source uptime monitor and status page, powered entirely by GitHub Actions, Issues, and Pages.
[HertzBeat](https://github.com/dromara/hertzbeat) is an open-source, real-time monitoring system with custom-monitor and agentless. It supports web service, database, os, middleware and more.
[Ciao](https://github.com/brotandgames/ciao) is a tool that checks HTTP(S) URL endpoints for a HTTP status code (or errors on the lower TCP stack) and sends a notification on status change via E-Mail or Webhooks.
[Server](https://gotify.net/) is a simple server for sending and receiving messages in real-time per WebSocket.
[Ngxtop](https://github.com/lebinh/ngxtop) is a real-time metrics for nginx server (and others).
[Blocky](https://github.com/0xERR0R/blocky) is a fast and lightweight DNS proxy as ad-blocker for local network with many features
[Dashy](https://dashy.to/) is a self-hostable personal dashboard built for you. Includes status-checking, widgets, themes, icon packs, a UI editor and tons more.
[Netdata](https://github.com/netdata/netdata) is high-fidelity infrastructure monitoring and troubleshooting, real-time monitoring Agent collects thousands of metrics from systems, hardware, containers, and applications with zero configuration. It runs permanently on all your physical/virtual servers, containers, cloud deployments, and edge/IoT devices, and is perfectly safe to install on your systems mid-incident without any preparation.
[Restic](https://restic.net/) is a modern backup program that can back up your files: from Linux, BSD, Mac and Windows. To many different storage types, including self-hosted and online services. easily, being a single executable that you can run without a server or complex setup. effectively, only transferring the parts that actually changed in the files you back up.
[Autorestic](https://github.com/cupcakearmy/autorestic) is a wrapper around the amazing restic. While being amazing the restic cli can be a bit overwhelming and difficult to manage if you have many different locations that you want to backup to multiple locations.
[MinIO](https://min.io/) is a high performance object storage tool that provides the world's fastest object storage server. With READ/WRITE speeds of 325 GiB/s and 165 GiB/s on standard hardware with default parity (EC:4), object storage can operate as the primary storage tier for a diverse set of workloads ranging from Spark, Presto, TensorFlow.
[Greyhole](https://www.greyhole.net/) is a tool that uses Samba to create a storage pool of all your available hard drives (whatever their size, however they are connected), and allows you to create redundant copies of the files you store, in order to prevent data loss when part of your hardware fails.
[Falcon LogScale](https://www.crowdstrike.com/products/observability/falcon-logscale/) is purpose-built to help any organization achieve the benefits of large-scale logging and analysis. Falcon LogScale has virtually no latency, even at ingest volumes of 1PB(Petabyte) per day.
[Googerteller](https://github.com/berthubert/googerteller) is a tool that makes an audible sound any time your computer sends a packet to a Google tracker or a Google service, which excludes Google Cloud users.
[DeviceHive](https://www.devicehive.com) is a free, highly scalable open-source IoT platform for data collection, processing and analysis, visualization, and device management with the broad range of integration options.
[Distributed Services Architecture (DSA)](https://github.com/IOT-DSA) is an open source IoT platform that facilitates device inter-communication, logic and applications at every layer of the Internet of Things infrastructure. The objective is to unify the disparate devices, services and applications into a structured and adaptable real-time data model.
[IoTivity](https://iotivity.org) is an open source software framework enabling seamless device-to-device connectivity to address the emerging needs of the Internet of Things.
[Eclipse IoT Project](https://projects.eclipse.org/projects/iot) provides open source technology that will be used to build IoT solutions for industry and consumers.
### Communications
[Back to the Top](#table-of-contents)
[Matrix](https://matrix.org/) is a tool that gives you simple HTTP APIs and SDKs (iOS, Android, Web) to create chatrooms, direct chats and chat bots, complete with end-to-end encryption, file transfer, synchronised conversation history, formatted messages, read receipts and more.
[Element](https://element.io/) is a Matrix web client built using the [Matrix React SDK](https://github.com/matrix-org/matrix-react-sdk).
[Mattermost](https://mattermost.com/) is a secure, open source platform for communication, collaboration, and workflow orchestration across tools and teams.
[Telegram](https://telegram.org/) is a cross-platform, cloud-based instant messaging service. It has an open API and source code free for everyone. Telegram also provides end-to-end encrypted video calling, VoIP, file sharing and several other features.
[Expanse](https://github.com/jc9108/expanse) is a fully selfhosted multi-user web app for externally storing Reddit items (saved, created, upvoted, downvoted, hidden) to bypass Reddit's 1000-item listing limits.
[Mailroute](https://mailroute.net/) is a great tool that provides the best email filtering & security( CMMC, NIST 800-171, DFARS, DISA, HIPPA). It protects your inbox, stop spam, viruses, ransomware, security threats & more with email filtering services. With an easy setup on Office 365, Google & more.
[Docker Mailserver](https://github.com/docker-mailserver/docker-mailserver) is a production-ready fullstack but simple mail server (SMTP, IMAP, LDAP, Antispam, Antivirus, etc.) running inside a container. Only configuration files, no SQL database.
[iRedMail](https://www.iredmail.org/) is a self-hosted email server.
[iRedMail Easy](https://www.iredmail.org/easy.html) is a web-based deployment platform, it offers an easy to use web interface to help you deploy iRedMail server, keep your server up to date, also get fast and professional technical support from iRedMail team.
[Spider Email Archiver](https://spiderd.io/) is an On-Premises Email Archiving Software.
[MailCow](https://github.com/mailcow/mailcow-dockerized) is a self-hosted email server.
[Nextcloud Talk](https://nextcloud.com/talk/) is a on-premises, private audio/video conferencing and text chat through browser and mobile interfaces with integrated screen sharing and SIP integration.
[Poste.io Email Server](https://poste.io/) is self-hosted SMTP + IMAP + POP3 + Antispam + Antivirus Web administration + Web email. It is easy setup with a [DNS guide]((https://poste.io/doc/configuring-dns)) for protect from spam.
### Business Management
[Back to the Top](#table-of-contents)
[Nextcloud](http://nextcloud.com/) is a suite of enterprise client-server software for creating and using file hosting services. It offers an on-premise Universal File Access and sync platform with powerful collaboration capabilities and desktop, mobile and web interfaces.
[Odoo](https://www.odoo.com/) is a suite of open source business apps that cover all your company needs: CRM, eCommerce, accounting, inventory, point of sale, project management, etc.
[Eden Workplace](https://www.edenworkplace.com/products) is a complete workplace management platform that lets you achieve more. Desk Booking Software to make desk reservations easier for your team, including assigning permanent and hybrid desks, providing wayfinding solutions for employees.
[Matomo](https://matomo.org/) is an ethical alternative where you won't make privacy sacrifices or compromise your site. Matomo is the Google Analytics alternative that protects your data and your customer's privacy.
[Plausible Analytics](https://plausible.io/) is a simple, lightweight (< 1 KB), open-source and privacy-friendly alternative to Google Analytics. It doesn’t use cookies and is fully compliant with GDPR, CCPA and PECR. You can self-host Plausible or have us run it for you in the Cloud.
[Mailroute](https://mailroute.net/) is a great tool that provides the best email filtering & security( CMMC, NIST 800-171, DFARS, DISA, HIPPA). It protects your inbox, stop spam, viruses, ransomware, security threats & more with email filtering services. With an easy setup on Office 365, Google & more.
[InvoicePlane](https://www.invoiceplane.com/) is a self-hosted open source application for managing your quotes, invoices, clients and payments.
### Collaboration & Synchronization
[Back to the Top](#table-of-contents)
[Syncthing](https://syncthing.net/) is a continuous file synchronization program. It synchronizes files between two or more computers in real time.
[Synology](https://www.synology.com/) is a tool that allows you to easily access and manage files in your Synology Drive on the go. Apart from common file types, such as documents, images, videos and music, you can also open Synology Office document, spreadsheets and slides in the user-friendly viewer provided by Drive.
[Nextcloud](http://nextcloud.com/) is a suite of client-server software for creating and using file hosting services. It offers an on-premise Universal File Access and sync platform with powerful collaboration capabilities and desktop, mobile and web interfaces.
[FileRun](https://hub.docker.com/r/filerun/filerun) is a self-hosted Google Drive alternative. It is a full featured web based file manager with an easy to use user interface.
[FileBrowser](https://hub.docker.com/r/filebrowser/filebrowser) provides a file managing interface within a specified directory and it can be used to upload, delete, preview, rename and edit your files. It allows the creation of multiple users and each user can have its own directory.
[Rsync](https://rsync.samba.org/) is a utility in the command line which enables users to transfer and synchronize files efficiently between a computer and an external hard drive in the entire connected network.
[Warpinator](https://github.com/linuxmint/warpinator) is a free, open-source tool for sending and receiving files between computers that are on the same network.
[FileZilla Client](https://filezilla-project.org/) is a fast and reliable cross-platform FTP, FTPS and SFTP client with lots of useful features and an intuitive graphical user interface.
[Dragit](https://github.com/sireliah/dragit) is an application for intuitive file sharing between devices. It's useful for when you want to send file from one computer to another with minimal effort. Dragit automatically detects devices in the local network with help of mDNS protocol and allows you to send file immediately.
[WinFsp](https://github.com/winfsp/winfsp) is a set of software components for Windows computers that allows the creation of user mode file systems. In this sense it is similar to FUSE (Filesystem in Userspace), which provides the same functionality on UNIX-like computers.
[SSHFS-Win](https://github.com/winfsp/sshfs-win) is a minimal port of SSHFS to Windows. Looking under the hood it uses Cygwin for the POSIX environment and WinFsp for the FUSE (Filesystem in Userspace) functionality.
[RiftShare](https://riftshare.app) is a cross platform (Windows, MacOS, Linux) file sharing tool that supports fully encrypted transfers both on the local network and off network using a simple passphrase. RiftShare uses [magic-wormhole](https://github.com/magic-wormhole/magic-wormhole) under the hood and is compatible with other magic-wormhole clients. It is also fully open source and licensed under the GPLv3.
[Usermode FTP Server](https://gitlab.com/ergoithz/umftpd) is a tool that let's you start an FTP server as user and transfer files with any FTP client. Allowing you to access your files directly with many file browsers' builtin FTP support: Windows File Explorer, Thunar, Gnome Files, Dolphin and many more.
### Encryption
[Back to the Top](#table-of-contents)
[VeraCrypt](https://www.veracrypt.fr/code/VeraCrypt/) is free open-source disk encryption software for Windows, Mac OS X and Linux. The file encryption, data encryption performed by VeraCrypt is real-time (on-the-fly), automatic, transparent, needs very little memory, and does not involve temporary unencrypted files.
[AxCrypt](https://axcrypt.net/) is an inexpensive and effective encryption tool for Windows, macOS, iOS, and Android.
[AESCrypt](https://www.aescrypt.com/) is an advanced file encryption utility that integrates with the Windows shell or runs from the Linux command prompt to provide a simple, yet powerful, tool for encrypting files using the Advanced Encryption Standard (AES). It is available for Windows, MacOS, and Linux.
[Linux Unified Key Setup (LUKS)](https://www.redhat.com/sysadmin/disk-encryption-luks) is a disk encryption specification created by Clemens Fruhwirth in 2004 and was originally intended for Linux. It uses device mapper crypt ( dm-crypt) as a kernel module to handle encryption on the block device level.
[GNU Privacy Guard (GnuPG)](https://gnupg.org/) is a complete and free implementation of the OpenPGP standard as defined by RFC4880 (also known as PGP ). It allows you to encrypt and sign your data and communications; it features a versatile key management system, along with access modules for all kinds of public key directories.
[Pretty Good Privacy (PGP)](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pretty_Good_Privacy) is an encryption program that provides cryptographic privacy and authentication for data communication. It's used for signing, encrypting, and decrypting texts, e-mails, files, directories, and whole disk partitions and to increase the security of e-mail communications.
**How Encryption Keys work**

* **Symmetric** is a data encryption method whereby the same private key is used to encode and decode information.
* **Asymmetric** is a data encryption method that allows users to encrypt information using shared keys. For example, if you need to send a message across the internet, but you don't want anyone but the intended recipient to see what you've written.
**Types of Encryption**
* **Triple DES (Triple Data Encryption Algorithm)** is a symmetric-key block cipher, which applies the DES cipher algorithm three times to each data block(contains 64 bits of data).
* **AES (Advanced Encryption Standard)** is an algorithm that encrypts and decrypts data in blocks of 128 bits. It can do this using 128-bit, 192-bit, or 256-bit keys.
* **RSA (Rivest–Shamir–Adleman)** is a type of public-key cryptography used for secure data transmission of e-mail and other digital transactions over the Internet.
* **Twofish** is a symmetric key block cipher with a block size of 128 bits and key sizes up to 256 bits. It is an advanced version of Blowfish encryption.
* **Format Preserving Encryption (FPE)** is a valid encryption algorithm to be used for compliance with NIST standards. It is mostly used in on-premise encryption and tokenization solutions.
**Application Level Encryption**
* **Hashes** is a function that converts an input of letters and numbers into an encrypted output of a fixed length. For example, algorithms such as [MD5 (Message Digest 5)](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/MD5) or [SHA (Secure Hash Algorithm)](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Secure_hash_algorithms).
* **Digital Certificates** is a file that verifies the identity of a device or user and enables encrypted connections. A digital signature is a hashing approach that uses a numeric string to provide authenticity and validate identity. Digital certificates are typically issued by a **certificate authority (CA)**, which is a trusted third-party entity that issues digital certificates for use by other parties.
### Backups
[Back to the Top](#table-of-contents)
[Proxmox Backup Server](https://www.proxmox.com/en/proxmox-backup-server) is an enterprise backup solution for backing up and restoring VMs, containers, and physical hosts. The open-source solution supports incremental backups, deduplication, Zstandard compression, and authenticated encryption.
[Borgmatic](https://github.com/modem7/docker-borgmatic) is a simple, configuration-driven backup software for servers and workstations. It protects your files with client-side encryption. Backup your databases too. Monitor it all with integrated third-party services.
[Vorta](https://vorta.borgbase.com/) is a backup client for macOS and Linux desktops. It integrates the mighty Borg Backup with your favorite desktop environment to protect your data from disk failure, ransomware and theft.
[UrBackup](https://www.urbackup.org/) is an easy to setup Open Source client/server backup system, that through a combination of image and file backups accomplishes both data safety and a fast restoration time. File and image backups are made while the system is running without interrupting current processes. Available for Windows, macOS, and Linux.
[Kopia](https://kopia.io/) is a user-friendly desktop app for Windows, macOS, and Linux which allows you to create snapshots, define policies, and restore files quickly with Fast and Encrypted Backups.
### Home Server
[Back to the Top](#table-of-contents)
[Home Assistant](https://www.home-assistant.io/) is an open source home automation that puts local control and privacy first. Home Assistant is powered by a worldwide community of tinkerers and DIY enthusiasts that runs great on Raspberry Pi.
[Homebridge](https://homebridge.io/) is a software framework that allows you to integrate with smart home devices that do not natively support [HomeKit](https://www.apple.com/shop/accessories/all/homekit). There are over 2,000 Homebridge plugins supporting thousands of different smart accessories.
[Homebridge UI](https://github.com/oznu/homebridge-config-ui-x) is a tool that provides an easy to use interface to manage your Homebridge plugins, configuration and accessories.
- Install and configure Homebridge plugins.
- Monitor your Homebridge server via a fully customisable widget-based dashboard.
- View and control Homebridge accessories.
- Backup and Restore your Homebridge instance.
[ESPHome](https://esphome.io/) is a system to control your ESP8266/ESP32 by simple yet powerful configuration files and control them remotely through Home Automation systems.
[Shelly Cloud](https://shelly.cloud/) is a Smart home control tool that has been perfected and provides precise monitoring of your Shelly devices no matter where you are. Shelly devices are compatible with Alexa, Google Home, Android, and iOS.
[Zigbee](https://csa-iot.org/all-solutions/zigbee/) is the full-stack, secure, reliable, and market-proven solution used by a majority of large smart home ecosystem providers, such as Amazon's Echo Plus, Samsung SmartThings, Signify (Philips Hue), and more.
[openHAB](https://github.com/openhab) is a cross-platform software with the aim to integrate all kinds of Smart Home technologies, devices, etc.
[Z-Wave](https://www.z-wave.com/) is the leading wireless communications protocol behind many of the secure, trusted brands that are working to make everyone's home smarter and safer.
[Homey](https://homey.app/) is an applciation to control, automate and monitor your entire smart home from your phone, tablet or desktop.
[Caddy](https://caddyserver.com/) is the only web server to use HTTPS automatically and by default. Caddy obtains and renews TLS certificates for your sites automatically.
[Bazarr](https://hub.docker.com/r/linuxserver/bazarr) is a companion application to Sonarr and Radarr. It can manage and download subtitles based on your requirements. You define your preferences by TV show or movie and Bazarr takes care of everything for you.
[Sonarr](https://github.com/Sonarr/Sonarr) is a PVR for Usenet and BitTorrent users. It can monitor multiple RSS feeds for new episodes of your favorite shows and will grab, sort and rename them.
[Homarr](https://github.com/ajnart/homarr) is a customizable browser's home page to interact with your homeserver's Docker containers (e.g. Sonarr/Radarr)
[Rustdesk](https://rustdesk.com/) is an open source virtual/remote desktop infrastructure for everyone. Display and control your PC (Windows, macOS, and Linux) and Android devices.
[TinyPilot](https://tinypilotkvm.com/) is a tool that enables KVM over IP letting you control any computer remotely.
[PM2](https://github.com/Unitech/pm2) is a production process manager for Node.js applications with a built-in load balancer. It allows you to keep applications alive forever, to reload them without downtime and to facilitate common system admin tasks.
[authentik](https://github.com/goauthentik/authentik) is an open-source Identity Provider focused on flexibility and versatility. You can use authentik in an existing environment to add support for new protocols. authentik is also a great solution for implementing signup/recovery/etc in your application, so you don't have to deal with it.
[ESPHome Remote](https://github.com/landonr/esphome-remote) IS a WI-FI smart home remote with display that runs on ESPHome. It uses Lilygo T-Display or M5Stack Fire.
[Tdarr](https://tdarr.io/) is a distributed transcode automation application using FFmpeg/HandBrake + Audio/Video library analytics + video health checking (Windows, macOS, Linux & Docker). A common use for Tdarr is to simply convert video files from h264 to h265 (hevc), saving 40%-50% in size.
[QNAP Switch System (QSS)](https://www.qnap.com/) is a configuration interface for QNAP's managed switch series. Enable management functions such as link aggregation, VLAN, and RSTP, to take care of your network topology with ease.
[ASUSTOR](https://www.asustor.com/) is a subsidiary of ASUS and a leading provider of network attached storage (NAS). It specializes in the development and integration of storage, backup, multimedia, video surveillance and mobile applications for home and enterprise users.
[Seafile](https://www.seafile.com/) is an open-source, cross-platform file-hosting software system. Seafile organize files into libraries stored on a central server. Each library can be synced into any desktop computer(Windows, Mac and Linux) and mobile devices through apps.
[SnapRAID](http://www.snapraid.it/) is a folder-based backup tool that behaves like a software or hardware RAID5/6 disk raid, but is not a disk raid itself. There is no realtime recovery, free space between disks cannot be combined and manual excution of backup is needed.
[FreeNAS](https://www.truenas.com/freenas/) is an Open Source Storage Platform and supports sharing across Windows, Apple, and UNIX-like systems. This includes ZFS (high storage capacities and integrates file systems and volume management into a single piece of software). It supports UPS, CIFS/SMB, FTP, NFS, RSYNC, SSH, AFP, Unison, UPnP, Webserver, iSCSI protocols, local and MS AD authentication, and disk enctyption.
[Gladys Assistant](https://github.com/gladysassistant/gladys) is a privacy-first, open-source home assistant and runs great on Raspberry Pi.
[Audiobookshelf](https://github.com/advplyr/audiobookshelf) is a self-hosted audiobook and podcast server.
[Mistborn](https://gitlab.com/cyber5k/mistborn) is a secure platform for easily standing up and managing your own cloud services: including firewall, ad-blocking, and multi-factor WireGuard VPN access.
### Media Server
[Back to the Top](#table-of-contents)
[Overseerr](https://overseerr.dev/) is a free and open source software application for managing requests for your media library. It integrates with your existing services, such as [Sonarr](https://sonarr.tv/), [Radarr](https://radarr.video/), and [Plex](https://www.plex.tv/).
[Jellyfin](https://jellyfin.org/) is a Free Software Media System that puts you in control of managing and streaming your media. It is an alternative to the proprietary Emby and Plex, to provide media from a dedicated server to end-user devices via multiple apps.
[Emby](https://emby.media/) is a home media server built on top of other popular open source technologies such as Service Stack, jQuery, jQuery mobile, and Mono. It features a REST-based API with built-in documention to facilitate client development.
[OpenMediaVault](https://www.openmediavault.org/) is a next generation network attached storage (NAS) solution based on Debian Linux. It contains services like SSH, (S)FTP, SMB/CIFS, AFS, UPnP media server, DAAP media server, RSync, BitTorrent client and many more.
[Plex media server](https://www.plex.tv/) is a application that gives you the power to add, access and share all the entertainment that matters to you, on almost any device. With 50,000+ on demand titles and hundreds of channels of live TV, plus your own personal media collection, using one powerful app.
[Infuse](https://firecore.com/) is a Video Player for iOS, Apple TV, and Mac. It plays every video file ever created to avoid wasting hours converting and transcoding files.
[InfuseSync](https://github.com/firecore/InfuseSync) is a plugin for Emby and Jellyfin media servers that tracks all media changes to decrease sync times with Infuse clients.
[AirSonic](https://hub.docker.com/r/airsonic/airsonic) is a free, web-based media streamer, providing ubiquitous access to your music.
[TubeSync](https://github.com/meeb/tubesync) is a PVR (personal video recorder) for YouTube. Or, like Sonarr but for YouTube (with a built-in download client). It is designed to synchronize channels and playlists from YouTube to local directories and update your media server once media is downloaded.
[Castopod](https://code.castopod.org/adaures/castopod) is an open-source hosting platform made for podcasters who want engage and interact with their audience.
[RuneAudio](https://www.runeaudio.com/) is a free and open source software that turns embedded hardware into Hi-Fi music players.
[Volumio (The Audiophile Music Player)](https://volumio.com/) is a very powerful and convenient music aggregator, now Volumio can also be used with great results in all sorts of different situations.
[Snapcast](https://github.com/badaix/snapcast) is a multiroom client-server audio player, where all clients are time synchronized with the server to play perfectly synced audio. It's not a standalone player, but an extension that turns your existing audio player into a Sonos-like multiroom solution.
[SonoBus](https://sonobus.net) is an easy to use application for streaming high-quality, low-latency peer-to-peer audio between devices over the internet or a local network.
### Video and Audio Processing
[Back to the Top](#table-of-contents)
[Intel® Quick Sync Video](https://www.intel.com/content/www/us/en/architecture-and-technology/quick-sync-video/quick-sync-video-general.html) is a tools that uses the dedicated media processing capabilities of Intel® Graphics Technology to decode and encode fast, enabling the processor to complete other tasks and improving system responsiveness.
[Intel® QuickAssist Technology (Intel® QAT)](https://www.intel.com/content/www/us/en/architecture-and-technology/intel-quick-assist-technology-overview.html) is a scalable, flexible, and extendable way to accelerate data encryption/decryption and compression for applications from networking to enterprise, cloud to storage, and content delivery to database.
[FFmpeg](https://ffmpeg.org) is a leading multimedia framework that can decode, encode, transcode, mux, demux, stream, filter and play pretty much anything that humans and machines have created. It supports the most obscure ancient formats up to the cutting edge ones on multiple platforms such as Windows, macOS, and Linux.
[FFmpeg.guide](https://ffmpeg.guide/) is a simple GUI tool to create complex FFmpeg filtergraphs quickly and correctly, without having to mess with the cumbersome filter syntax.
[HandBrake](https://handbrake.fr/) is a tool for transcoding video from almost any format with a selection of widely supported codecs. It is supported on Window, macOS, and Linux.
[Tdarr](https://github.com/HaveAGitGat/Tdarr) is a cross-platform conditional based transcoding application for automating media library transcode/remux management in order to process your media files as required. It can set rules for the required codecs, containers, languages etc that your media should have which helps keeps things organized and can increase compatability with your devices. A common use for Tdarr is to simply convert video files from h264 to h265 (hevc), saving 40%-50% in size.
[SRS](https://github.com/ossrs/srs) is a simple, high efficiency and realtime video server, supports RTMP, WebRTC, HLS, HTTP-FLV, SRT and GB28181.
**Video/Audio Standards**
[AAC(Advanced Audio Coding)](https://mpeg.chiariglione.org/) is an audio coding standard for lossy digital audio compression. It's endorsed by ISO and IEC as MPEG-2 and MPEG-4 standards for video streams.
[H.264(AVC)](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/H.264/MPEG-4_AVC) is a video compression standard based on block-oriented and motion-compensated integer-DCT coding that defines multiple profiles (tools) and levels (max bitrates and resolutions) with support up to 8K.
[H.265(HEVC)](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/High_Efficiency_Video_Coding) is a video compression standard that is the successor to H.264(AVC). It offers a 25% to 50% better data compression at the same level of video quality, or improved video quality at the same bit-rate.
[HTTP Live Streaming (HLS)](https://developer.apple.com/streaming/) is a communications protocol developed by Apple that sends live and on‐demand audio and video to iPhone, iPad, Mac, Apple Watch, Apple TV, and PC.
[Dynamic Adaptive Streaming over HTTP (DASH)](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/HTML/DASH_Adaptive_Streaming_for_HTML_5_Video) is an adaptive streaming protocol that allows for a video stream to switch between bit rates on the basis of network performance, in order to keep a video playing.
[OpenMAX™](https://www.khronos.org/openmax/) is a cross-platform API that provides comprehensive streaming media codec and application portability by enabling accelerated multimedia components to be developed, integrated and programmed across multiple operating systems and silicon platforms.
[GStreamer](https://gstreamer.freedesktop.org/) is a library for constructing graphs of media-handling components. The applications it supports range from simple Ogg/Vorbis playback, audio/video streaming to complex audio (mixing) and video (non-linear editing) processing. Applications can take advantage of advances in codec and filter technology transparently.
[Media Source Extensions (MSE)](https://www.w3.org/TR/media-source/) is a [W3C specification](https://github.com/w3c/media-source) that allows JavaScript to send byte streams to media codecs within Web browsers that support HTML5 video and audio. Also, this allows the implementation of client-side prefetching and buffering code for streaming media entirely in JavaScript.
[WebRTC](https://webrtc.org/) is an open-source project that adds real-time communication capabilities to your application that works on top of an open standard. It supports video, voice, and generic data to be sent between peers, allowing developers to build powerful voice- and video-communication solutions.
### Podcasting
[Back to the Top](#table-of-contents)
[Castopod](https://code.castopod.org/adaures/castopod) is an open-source hosting platform made for podcasters who want engage and interact with their audience.
[Audiobookshelf](https://www.audiobookshelf.org/) is a self-hosted audiobook and podcast server.
[Podverse](https://podverse.fm/) is creating an open source podcast app for iOS, Android, F-Droid, and Web.
[Alby](https://getalby.com/) is a Bitcoin Lightning App for your Browser.
[Alby wallet API](https://blog.getalby.com/introducing-the-alby-wallet-api/) is an implemented OAuth an open standard that apps use to provide client applications with secure delegated access. Thus Podverse users create an Alby wallet account or use their existing Alby account to grant specific access rights to their Alby wallet.
[AntennaPod](https://antennapod.org/) is a podcast player that is completely open. The app is open-source and you can subscribe to any RSS feed. AntennaPod is built by volunteers without commercial interest, so it respects your privacy while giving you full control.
[Podgrab](https://github.com/akhilrex/podgrab) is a self-hosted podcast manager/downloader/archiver tool to download podcast episodes as soon as they become live with an integrated player.
[Podify](https://github.com/podify-org/podify) is a self-hosted service that allows you to download videos and audio from any source supported by youtube-dl, sort the downloads into feeds, and subscribe to these feeds using your favorite podcast app.
[dir2cast](https://github.com/ben-xo/dir2cast/) is designed to turn a directory of MP3s into a podcast - automatically. Perfect for, say, radio shows - upload the MP3s to a folder, and use dir2cast.php as your PodCast URL.
### AudioBooks
[Back to the Top](#table-of-contents)
[Audioserve](https://github.com/izderadicka/audioserve) is a simple personal server to serve audio files from directories. Intended primarily for audio books, but anything with decent directories structure will do. Focus here is on simplicity and minimalist design.
[Audiobookshelf](https://www.audiobookshelf.org/) is a self-hosted audiobook and podcast server.
[Jellyfin Bookshelf Plugin](https://github.com/jellyfin/jellyfin-plugin-bookshelf)
### Maps
[Back to the Top](#table-of-contents)
[MapTiler Server](https://www.maptiler.com/server/self-host-satellite-maps/) is a self-hosted Aerial and satellite imagery maps of the entire world from your own server or laptop.
[KelperJs](http://keplerjs.io/) is a open source full-stack geosocial network platform.
[OpenStreetMap(OSM)](https://www.openstreetmap.org/) is a map of the world, created by people like you and free to use under an open license. Hosting is supported by UCL, Fastly, Bytemark Hosting, and other partners.
[uMap](https://github.com/umap-project/umap) is a tool that lets you create maps with OpenStreetMap layers in a minute and embed them in your site.
### Bookmarks
[Back to the Top](#table-of-contents)
[Linkding](https://github.com/sissbruecker/linkding/) is a simple bookmark service that you can host yourself. It's designed be to be minimal, fast, and easy to set up using Docker.
[LinkAce](https://www.linkace.org/) is a self-hosted bookmark archive to collect links of your favorite websites.
[Eagle](https://eagle.cool/) is a tool to collect, search and organize your design files in a logical way and all in one place.
[Shlink](https://shlink.io/) is a self-hosted URL shortener that keeps control over all your shortened URLs, by serving them under your own domains, using this simple yet powerful tool.
[Pinry](https://docs.getpinry.com/) is a tiling image board system for people who want to save, tag, and share images, videos and webpages in an easy to skim through format.
[Shaark](https://github.com/MarceauKa/shaark) is a self-hosted platform to keep and share your content: web links, posts, passwords and pictures.
### Photos
[Back to the Top](#table-of-contents)
[PhotoPrism®](https://docs.photoprism.app/license/docs/) is an AI-powered app for browsing, organizing & sharing your photo collection. It makes use of the latest technologies to tag and find pictures automatically without getting in your way. You can run it at home, on a private server, or in the cloud.
[Immich](https://immich.app/) is a high performance self-hosted photo and video backup solution directly from your mobile phone.
[Piwigo](https://piwigo.org/) is a full featured, self-hosted, and open source photo gallery application for the web. It comes with more than 200 templates, plugins, and configurations that let you personalize how your photos are presented. It allows users to upload photos from digiKam, Shotwell, Lightroom or mobile applications. Lastly, users can create galleries and give viewing permissions to their clients. They can download individual photos or whole albums, post comments, give ratings, mark photos as favorites, and perform searches.
[PhotoSync](https://www.photosync-app.com/home.html) is a service to wirelessly transfer, backup & share photos/videos to your computer, NAS, other phones and popular cloud/photo services. It's available for Windows, MacOS, Linux, Android, and iOS.
[Lychee](https://lycheeorg.github.io/) is a great looking and easy-to-use photo-management-system you can run on your server, to manage and share photos.
[Photoview](https://photoview.github.io/) is a simple and user-friendly photo gallery that's made for photographers and aims to provide an easy and fast way to navigate directories, with thousands of high-resolution photos.
[Gimme-iPhotos](https://github.com/Zebradil/Gimme-iPhotos) is a tool uses [pyicloud](https://github.com/picklepete/pyicloud) to synchronize photos and videos from iCloud to your local machine.
[PyiCloud](https://github.com/picklepete/pyicloud) is a module which allows pythonistas to interact with iCloud webservices. It's powered by the fantastic [requests](https://github.com/kennethreitz/requests) HTTP library.
[Chevereto](https://hub.docker.com/r/linuxserver/chevereto) is an image hosting software that allows you to create a beautiful and full-featured image hosting website on your own server.
[Got Your Back (GYB)](https://github.com/GAM-team/got-your-back) is a command line tool for backing up your Gmail messages to your computer using Gmail's API over HTTPS.
### Note-Taking
[Back to the Top](#table-of-contents)
[Joplin](https://joplinapp.org/) is an open source note-taking app that you can securely access from any device.
[HedgeDoc](https://hedgedoc.org/) is an open-source, web-based, self-hosted, collaborative markdown editor.
[Turtl](https://turtlapp.com/) is a secure, collaborative notebook for bookmarks or passwords, files or shopping lists.
[TiddlyWiki](https://tiddlywiki.com/) is a single-file mode wiki application for todo lists, effective project management tool and of course writing drafts and notes. It has extensions for all the major browsers.
[Milanote](https://milanote.com/) is a tool for organizing creative projects into beautiful visual boards.
[Laverna](https://laverna.cc/) is a note taking application with Markdown editor and encryption support. Consider it like open source alternative to Evernote.
[Zettlr](https://www.zettlr.com/) is an open-source Markdown editor for the 21st century.
[Carnet](https://www.getcarnet.app/) is a complete open source note taking app. It has extensions for all the major browsers.
### Gaming
[Back to the Top](#table-of-contents)
[Cartridge](https://github.com/unclebacon-live/cartridge) is a self-hosted game library made with Laravel + Vue.js.
**Cartridge Features**
- Scan for ROM files and match with IGDB game information
- Serve ROM download links alongside game details
- Manage access to library with user creation and permissions (WIP)
- Allow users to request games (Planned)
- Play select ROMs in-browser using JS emulators (Planned)
- Track played and favorite games (even ones that aren't available for download) (Planned)
[Moonlight Game Streaming](https://moonlight-stream.org/) is a program that let you stream from your PC games over the Internet with no configuration required. Stream from almost any device, whether you're in another room or miles away from your gaming rig. [Sunshine](https://github.com/LizardByte/Sunshine) is a **Game stream host for Moonlight** that is a self-hosted, low latency, cloud gaming solution with support for AMD, Intel, and NVIDIA GPUs. It is an open source implementation of NVIDIA's GameStream.

[Chiaki](https://git.sr.ht/~thestr4ng3r/chiaki) is a Free and Open Source Software Client for PlayStation 4 and PlayStation 5 Remote Play for Linux, FreeBSD, OpenBSD, Android, macOS, Windows, Nintendo Switch and potentially even more platforms.
#### Game Emulators
[EmuDeck](https://www.emudeck.com/) is a tool that takes care of everything for your retrogaming needs from RetroArch Configuration, Bezels, Gamepad Configuration for GameCube, Wii, Citra, SNES, etc. EmuDeck will even install EmulationStation Desktop Edition and carry over all their custom configurations and no need to configure ROM paths or anything.
[EmulationStation Desktop Edition (ES-DE)](https://www.es-de.org/) is a frontend application for browsing and launching games from your multi-platform game collection. It's available for Unix/Linux, macOS(M1 & Intel) and Windows.
[RetroPie](https://retropie.org.uk/) is a frontend for emulators that allows you to turn your Raspberry Pi, ODroid C1/C2, or PC into a retro-gaming machine. It builds upon Raspbian, [EmulationStation](https://github.com/Aloshi/EmulationStation), RetroArch and many other projects to enable you to play your favourite Arcade, home-console, and classic PC games with the minimum set-up.

[RetroArch](https://www.retroarch.com/) is a frontend for emulators, game engines and media players. It enables you to run classic games on a wide range of computers and consoles through its slick graphical interface. Settings are also unified so configuration is done once and for all. [RetroArch Flatpak](https://flathub.org/apps/details/org.libretro.RetroArch)
[Cartridge](https://github.com/unclebacon-live/cartridge) is a self-hosted game library made with Laravel + Vue.js.
**Cartridge Features**
- Scan for ROM files and match with IGDB game information
- Serve ROM download links alongside game details
- Manage access to library with user creation and permissions (WIP)
- Allow users to request games (Planned)
- Play select ROMs in-browser using JS emulators (Planned)
- Track played and favorite games (even ones that aren't available for download) (Planned)

Cartridge UI
[Dolphin](https://dolphin-emu.org) is an emulator for two recent Nintendo video game consoles: the GameCube and the Wii. It allows PC gamers to enjoy games for these two consoles in full HD (1080p) with several enhancements: compatibility with all PC controllers, turbo speed, networked multiplayer, and even more.
[Citra](https://citra-emu.org/) is an open-source emulator for the Nintendo 3DS capable of playing many of your favorite games.
[yuzu](https://yuzu-emu.org) is an experimental open-source emulator for the Nintendo Switch from the creators of Citra.[
[m64p](https://m64p.github.io/) is a Nintendo 64 Emulator. It uses mupen64plus-gui, a brand new mupen64plus frontend written in Qt5. It supports all of the things you’d expect from a frontend (savestate management, pausing, screenshots).
[DeSmuME](https://desmume.org/) is a Nintendo DS emulator.
[Snes9x](https://www.snes9x.com/) is a portable, freeware Super Nintendo Entertainment System (SNES) emulator.
[bsnes](https://github.com/bsnes-emu/bsnes) is a Super Nintendo (SNES) emulator focused on performance, features, and ease of use.
[mGBA](https://mgba.io/) is a new emulator for running Game Boy Advance games. It aims to be faster and more accurate than many existing Game Boy Advance emulators, as well as adding features that other emulators lack.
[DOSBox](https://www.dosbox.com/) is an open-source DOS emulator which primarily focuses on running DOS Games.
[DOSBox Staging](https://github.com/dosbox-staging/dosbox-staging) is a full x86 CPU emulator (independent of host architecture), capable of running DOS programs that require real or protected mode.
[Flycast](https://github.com/flyinghead/flycast) is a multi-platform Sega Dreamcast, Naomi and Atomiswave emulator derived from reicast.
[PCSX2](https://pcsx2.net/) is a PlayStation 2 'emulator', a free program that tries to replicate the PlayStation 2 console to enable you to play PS2 games on your PC.
[RPCS3](https://rpcs3.net/) is an experimental open-source Sony PlayStation 3 emulator and debugger written in C++ for Windows and Linux. RPCS3 started development in May of 2011 by its founders DH and Hykem. The emulator is currently capable of running over 1800 commercial titles powered by Vulkan and OpenGL.
[MAME](https://www.mamedev.org/) is a Arcade Machine Emulator.
[xemu](https://xemu.app/) is an original Xbox emulator.
[Xenia](https://github.com/xenia-project/xenia) is an Xbox 360 Emulator.
**Also checkout these subreddits for more great Game Emulators recommendations**
- [r/emulation](https://www.reddit.com/r/emulation/)
- [r/emulations](https://www.reddit.com/r/emulators/)
- [r/RetroArch](https://www.reddit.com/r/RetroArch/)
- [r/RetroPie](https://www.reddit.com/r/RetroPie/)
- [r/DolphinEmulator](https://www.reddit.com/r/DolphinEmulator/)
- [r/Citra](https://www.reddit.com/r/Citra/)
- [r/cemu](https://www.reddit.com/r/cemu/)
- [r/yuzu](https://www.reddit.com/r/yuzu/)
- [r/OpenEmu](https://www.reddit.com/r/OpenEmu/)
- [r/MAME](https://www.reddit.com/r/MAME/)
- [r/EmuDev](https://www.reddit.com/r/EmuDev/)
- [r/Roms](https://www.reddit.com/r/Roms/)
### Foundations/Projects
[Back to the Top](#table-of-contents)
[Matter](https://buildwithmatter.com/) is an open standard for smart home technology that lets your device work with any Matter-certified ecosystem using a single protocol. Matter comes from the [Connectivity Standards Alliance](https://csa-iot.org/), an organization of hundreds of companies(Amazon, Apple, Google, Comcast, Zigbee Alliance, and Connectivity Standards Alliance (CSA) creating products for the smart home.
[Open Source Hardware Association (OSHWA)](https://www.oshwa.org) is a non-profit organization that advocates for open-source hardware. It aims to act as a hub of open source hardware activity of all types while actively cooperating with other initiatives such as the TAPR Open Hardware License, open-source development groups at CERN, and the Open Source Initiative (OSI).
[The Open Connectivity Foundation](https://openconnectivity.org) is dedicated to ensuring secure interoperability for consumers, businesses and industries by delivering a standard communications platform, a bridging specification, an open source implementation and a certification program allowing devices to communicate regardless of form factor, operating system, service provider, transport technology or ecosystem.
[Raspberry Pi Foundation](https://www.raspberrypi.org/about/) is a UK-based charity with the mission to enable young people to realise their full potential through the power of computing and digital technologies.
[OpenSSF(Open Source Security Foundation)](https://openssf.org/) is a cross-industry forum for a collaborative effort to improve open source software security.
[OpenJS Foundation](https://openjsf.org/) is the premier home for critical open source JavaScript projects, including Appium, Dojo, jQuery, Node.js, and webpack, and 27 more.
[EdgeX Foundry](https://www.edgexfoundry.org) is a vendor-neutral project under the Linux Foundation. The initiative is aligned around a common goal: the simplification and standardization of the foundation for edge computing architectures in the Industrial IoT market, while still allowing the ecosystem to add significant value.
[Eclipse Foundation](https://www.eclipse.org) provides our global community of individuals and organizations with a mature, scalable and commercially-friendly environment for open source software collaboration and innovation.
### System Hardware
[Back to the Top](table-of-contents)
* [Refurbished Servers on Amazon](https://www.amazon.com/refurbished-servers/s?k=refurbished+servers&rh=p_36%3A10000-60000&qid=1667083059&rnid=386442011&ref=sr_nr_p_36_2)
* [Network Switches & Hubs on ebay](https://www.ebay.com/b/Enterprise-Network-Switches-Hubs/182091/bn_887002)
* [Server Monkey](https://www.servermonkey.com/servers.html)
* [The Server Store](https://www.theserverstore.com/)
#### CPUs
**Intel Processors(x86)**
[Back to the Top](table-of-contents)

I recommend using Intel CPUs no older than the second generation of the Intel Core processors (Core i7, i5, i3) AKA **Sandy Bridge(Jan. 2011)** for those that want to utilize [Intel® Quick Sync Video](https://www.intel.com/content/www/us/en/architecture-and-technology/quick-sync-video/quick-sync-video-general.html). Though, if you're concerned about power efficiency(~5W idle) I would recommend 7th Generation or newer.
Also, I recommend using **[Intel® QuickAssist Technology (Intel® QAT)](https://www.intel.com/content/www/us/en/architecture-and-technology/intel-quick-assist-technology-overview.html)** a scalable, flexible, and extendable way to accelerate data encryption/decryption and compression for applications from networking to enterprise, cloud to storage, and content delivery to database. Available in 3rd Gen Intel® Xeon® Scalable Processors and Intel Atom® Processor C Series/P Series.
* [Intel Celeron Processor N Series](https://ark.intel.com/content/www/us/en/ark/products/series/87282/intel-celeron-processor-n-series.html)
* [Intel Atom Series](https://ark.intel.com/content/www/us/en/ark.html#@PanelLabel29035)
* [Intel Pentium](https://ark.intel.com/content/www/us/en/ark.html#@PanelLabel29862)
* [Intel i3](https://ark.intel.com/content/www/us/en/ark.html#@PanelLabel122139)
* [Intel i5](https://ark.intel.com/content/www/us/en/ark.html#@PanelLabel122139)
* [Intel i7](https://ark.intel.com/content/www/us/en/ark.html#@PanelLabel122139)
* [Intel Xeon](https://ark.intel.com/content/www/us/en/ark.html#@PanelLabel595)
**AMD Processors(x86)**
[Back to the Top](table-of-contents)

* [AMD Athlon](https://www.amd.com/en/processors/athlon-pro)
* [AMD Ryzen G-Series](https://cpuarchive.com/CPU/AMD/Ryzen)
* [AMD Ryzen 3](https://cpuarchive.com/CPU/AMD/Ryzen)
* [AMD Ryzen 5](https://cpuarchive.com/CPU/AMD/Ryzen)
* [AMD Ryzen 7](https://cpuarchive.com/CPU/AMD/Ryzen)
* [AMD Threadripper](https://www.amd.com/en/processors/threadripper-creators)
#### Devices
[Back to the Top](table-of-contents)
**Note: Will be adding more device soon!**
* [Raspberry Pi](https://github.com/mikeroyal/Self-Hosting-Guide#raspberry-pi)
* [Turing Pi 2](https://turingpi.com/)
* [Home Assistant Yellow](https://www.home-assistant.io/blog/2021/09/13/home-assistant-yellow/)
* [ZimaBoard](https://www.zimaboard.com/)
* [ODROID-H3 and H3+](https://ameridroid.com/products/odroid-h3)
* [Intel® NUC Mini PCs](https://www.intel.com/content/www/us/en/products/details/nuc.html)
* [Beelink mini PC](https://www.bee-link.com/)
* [M1 Mac Mini](https://www.apple.com/mac-mini/)
### Operating Systems
[Back to the Top](table-of-contents)
**Creating a bootable media device(USB/MicroSD card)**
[Rufus](https://rufus.ie/) is a utility that helps format and create bootable USB flash drives.

Rufus
**OR**
[Etcher](https://www.balena.io/etcher/) is an open source, cross-platform software that makes it easy to flash operating system images to a microSD card or USB device.

Etcher UI
**A List of Operating Systems that are great for either settig up a personal Home Server or a Enterprise Server for your Organization/Company.**
[Home Assistant OS](https://home-assistant.io/hassio/) is a container-based system for managing your Home Assistant Core installation and related applications. The system is controlled via Home Assistant which communicates with the Supervisor. The Supervisor provides an API to manage the installation. This includes changing network settings or installing and updating software.

Home Assistant OS
[Umbrel](https://umbrel.com/) is an OS for running a personal server in your home. It can Self-host open source apps like Nextcloud, Bitcoin node, and more.

Umbrel
[CasaOS](https://casaos.io/) is a simple, easy-to-use, elegant open-source Home Cloud system.

CasaOS
[Ubuntu](https://ubuntu.com/) is a modern open source operating system on Linux for the enterprise Server, Desktop, Cloud, and IoT developed by Canonical.
* [Ubuntu Server](https://ubuntu.com/download/server)
* [Ubuntu for ARM](https://ubuntu.com/download/server/arm)
* [Ubuntu for Raspberry Pi](https://ubuntu.com/raspberry-pi)
* [Ubuntu Flavours](https://www.ubuntu.com/download/flavours) is for those that prefer an alternative desktop environment such as [KDE Plasma Desktop](https://kubuntu.org/), [MATE](https://ubuntu-mate.org/), [Xfce](https://xubuntu.org/), [LXQt](https://lubuntu.me/), [Budgie](https://ubuntubudgie.org/), and [UKUI](https://www.ubuntukylin.com/) you can download a Flavour for your preferred desktop environment and use that to install Ubuntu, pre-configured for the desktop environment of your choice.

Ubuntu
[Debian](https://www.debian.org/) is an operating system and a distribution of Free Software. It is maintained and updated through the work of many users who volunteer their time and effort.

Debian 11
[Linux Mint](https://linuxmint.com/) is a modern, elegant, and comfortable open source operating system(based on Debian and Ubuntu), which is both powerful and easy to use for both new and advanced users. The flagsip version of Linux Mint uses the [Cinnamon desktop environment](https://cinnamon-spices.linuxmint.com/) similiar to Windows 7.

Linux Mint
[Linux Mint Debian Edition (LMDE)](https://www.linuxmint.com/download_lmde.php) uses [Debian Bullseye](https://www.debian.org/) as the base for a very stable and rock solid user experience with the Cinnamon desktop.

Linux Mint Debian Edition (LMDE)
**[Pop!_OS](https://pop.system76.com)** created by [System76](https://system76.com).

Pop!_OS
[Fedora Linux](https://getfedora.org/) is a polished, easy to use operating system for laptop & desktop computers, with a complete set of tools for developers and makers of all kinds. The OS serves as the foundation for which you can scale existing apps and roll out emerging technologies across bare-metal, virtual, container, and all types of cloud environments.
* [Fedora Spins](https://spins.fedoraproject.org/) is for those that prefer an alternative desktop environment such as KDE Plasma Desktop, MATE; or Xfce, you can download a spin for your preferred desktop environment and use that to install Fedora, pre-configured for the desktop environment of your choice.
* [Fedora Server](https://getfedora.org/) is a powerful, flexible operating system that includes the best and latest datacenter technologies. It puts you in control of all your infrastructure and services.
* [Fedora ARM](https://arm.fedoraproject.org/) is an initiative to bring versions of Fedora tailored for running on ARM-based systems.
* [Fedora Silverblue](https://silverblue.fedoraproject.org/) is a variant of the Fedora Workstation that uses rpm-ostree to provide an immutable OS image with reliable updates and easy rollbacks.
* [Fedora Kinoite](https://kinoite.fedoraproject.org/) is an immutable desktop operating system. It aims to be extremely stable and reliable. It also aims to be an excellent platform for developers and for those using container-focused workflows. Kinoite is a variant of the Fedora KDE Spin.
* [Fedora CoreOS](https://getfedora.org/coreos?stream=stable) is an automatically-updating, minimal operating system for running containerized workloads securely and at scale.

Fedora Linux
[CentOS Stream](https://www.centos.org/centos-stream/) is a continuously delivered distro(uses the Fedora OS base) that tracks just ahead of Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL) development, positioned as a midstream between Fedora Linux and RHEL.

CentOS Stream
[Red Hat® Enterprise Linux® (RHEL)](https://www.redhat.com/en/technologies/linux-platforms/enterprise-linux) the world's leading enterprise Linux platform. The OS serves as the foundation for which you can scale existing apps and roll out emerging technologies across bare-metal, virtual, container, and all types of cloud environments.

Red Hat Enterprise Linux Desktop
[SUSE](https://www.suse.com/) is a leading Linux OS most adaptable Linux operating system and the only open Kubernetes management platform thanks to their acquistion of [Rancher](https://rancher.com/). They also developer of [SUSE Linux Enterprise](https://www.suse.com/download/) and the primary sponsor of the community-supported [openSUSE Project](https://software.opensuse.org/), which develops the openSUSE Linux distribution.
* [openSUSE Leap](https://en.opensuse.org/Portal:Leap) is a brand new way of building openSUSE and is new type of a hybrid Linux distribution. Leap uses source from SUSE Linux Enterprise (SLE), which gives Leap a level of stability unmatched by other Linux distributions, and combines that with community developments to give users, developers and sysadmins the best stable Linux experience available.
* [openSUSE Tumbleweed](https://en.opensuse.org/Portal:Tumbleweed) is a pure rolling release version of openSUSE containing the latest "stable" versions of all software instead of relying on rigid periodic release cycles. The project does this for users that want the newest stable software.
* [openSUSE Kubic](https://get.opensuse.org/kubic/) is a multi-purpose Standalone & Kubernetes Container Operating System based on openSUSE MicroOS. Kubic uses kubeadm to provide an easy way of configuring a Kubernetes cluster across multiple machines, while our MicroOS base keeps your operating system updated automatically, with fully atomic rollbacks if required.
* [openSUSE MicroOS](https://get.opensuse.org/microos/) is a M icro Service OS providing Transactional (Atomic) Updates upon a read-only btrfs root filesystem. It's designed to host container workloads with automated administration & patching.


SUSE Linux Enterprise 12

openSUSE
[NixOS](https://nixos.org/) is a Linux distribution built on top of the [Nix package manager](https://nixos.wiki/wiki/Nix). It has tools dedicated to DevOps and deployment tasks. [NixOS Guide](https://github.com/mikeroyal/NixOS-Guide)
* [Nix Tour](https://nixcloud.io/tour/) is an interactive tour that uses the actual package manager to learn you the language by example, in the browser.
* [Nix](https://nixos.wiki/wiki/Nix) is a package manager and build system that parses reproducible build instructions specified in the [Nix Expression Language](https://nixos.wiki/wiki/Nix_Expression_Language), is a pure functional language with lazy evaluation. Nix expressions are pure functions taking dependencies as arguments and producing derivation specifying a reproducible build environment for the package. Nix stores the results of the build in unique addresses specified by a hash of the complete dependency tree, creating an immutable package store that allows for atomic upgrades, rollbacks and concurrent installation of different versions of a package, essentially eliminating [dependency hell](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Dependency_hell).
* [Nix Expression Language](https://nixos.wiki/wiki/Nix_Expression_Language) is a pure, lazy, functional language. Purity means that operations in the language don't have side-effects (for instance, there is no variable assignment). The language is not a full-featured, general purpose language. Its main job is to describe packages, compositions of packages, and the variability within packages.
* [Nixpkgs](https://nixos.wiki/wiki/Nixpkgs) is the largest repository of [Nix](https://nixos.wiki/wiki/Nix) packages(over 80,000 packages) and [NixOS](https://nixos.wiki/wiki/NixOS) modules. The repository is [hosted on GitHub](https://github.com/nixos/nixpkgs) and maintained by the community, with official backing from the [NixOS Foundation](https://nixos.org/). Additionally, checkout [Language-specific package helpers](https://nixos.wiki/wiki/Language-specific_package_helpers) and [Alternative Package Sets](https://nixos.wiki/wiki/Alternative_Package_Sets).
* [NixOS Packages Search](https://search.nixos.org/packages) is a tool for searching through NixOS packages.

NixOS Packages Search

NixOS Desktop with the new Calamares Installer

NixOS with the Plasma Desktop
### Storage
[Back to the Top](https://github.com/mikeroyal/Self-Hosting-Guide#table-of-contents)
- [Western Digital Hard Drives Storage size range 2TB up to 20TB](https://www.westerndigital.com/c/internal-drives.0_TB-4_TB.11_TB-20_TB.5_TB-10_TB.hard_drives)
- [Seagate Hard Drives Storage size range 2TB up to 18TB](https://www.seagate.com/internal-hard-drives/hdd/)
- [Hard Drives Storage size range 2TB up to 20TB from Bestbuy](https://www.bestbuy.com/site/searchpage.jsp?id=pcat17071&qp=harddrivesizerange_facet%3DStorage%20Capacity~2TB%20-%203TB%5Eharddrivesizerange_facet%3DStorage%20Capacity~4TB%20-%207TB%5Eharddrivesizerange_facet%3DStorage%20Capacity~8TB%20-%2011TB%5Eharddrivesizerange_facet%3DStorage%20Capacity~12TB%20or%20More%5Einternalorexternal_facet%3DInternal%20Or%20External~Internal&st=hard+drive)
- [Hard Drives Storage size range 1TB up to 20TB on Newegg](https://www.newegg.com/p/pl?d=hard+drives&N=600003298%20600003311%20600003316%20600003299%20600543907%20600003300%20601331745%20600083978%20600217643%20600486069%20600490667%20600376735%20601192404%20601398066%20601355746%20601334339%20601322010%20600376738%20600003341%20600003347%20100167523)
- [Hard Drives Storage size range 1TB up to 18TB on Amazon](https://www.amazon.com/s?k=hard+drives&i=computers&rh=n%3A1254762011%2Cp_n_feature_two_browse-bin%3A5446812011%7C5446813011%7C5446815011%7C5446816011%7C7817230011%2Cp_n_feature_keywords_six_browse-bin%3A6158683011&s=review-rank&dc&qid=1653712565&rnid=562234011&ref=sr_st_review-rank)
**Useful Tools for Storage Management**
[Scrutiny](https://github.com/AnalogJ/scrutiny) is a WebUI for smartd Hard Drive S.M.A.R.T Monitoring, Historical Trends & Real World Failure Thresholds.
[DUA (Disk Usage Analyzer)](https://lib.rs/crates/dua-cli) is a tool to conveniently learn about the usage of disk space of a given directory. It's parallel by default and will max out your SSD, providing relevant information as fast as possible. Optionally delete superfluous data, and do so more quickly than rm.
[Dirstat-rs](https://github.com/scullionw/dirstat-rs) is a fast, cross-platform disk usage CLI, similar to [Windirstat](https://windirstat.net/).
[Dutree](https://github.com/nachoparker/dutree) is a tool to analyze file system usage written in Rust.
### File systems
[Back to the Top](https://github.com/mikeroyal/Self-Hosting-Guide#table-of-contents)
* [FSArchiver](https://www.fsarchiver.org/) is a system tool that allows you to save the contents of a file system to a compressed archive file. The file system can be restored on a partition which has a different size and it can be restored on a different file system.
[GlusterFS](https://www.gluster.org/) is a free and open source scalable network filesystem. Gluster is a scalable network filesystem. Using common off-the-shelf hardware, you can create large, distributed storage solutions for media streaming, data analysis, and other data- and bandwidth-intensive tasks.
[Ceph](https://ceph.io/) is a software-defined storage solution designed to address the object, block, and file storage needs of data centers adopting open source as the new norm for high-growth block storage, object stores and data lakes. Ceph provides enterprise scalable storage while keeping [CAPEX](https://corporatefinanceinstitute.com/resources/knowledge/modeling/how-to-calculate-capex-formula/) and [OPEX](https://www.investopedia.com/terms/o/operating_expense.asp) costs in line with underlying bulk commodity disk prices.
[Hadoop Distributed File System (HDFS)](https://www.ibm.com/analytics/hadoop/hdfs) is a distributed file system that handles large data sets running on commodity hardware. It is used to scale a single Apache Hadoop cluster to hundreds (and even thousands) of nodes. HDFS is one of the major components of Apache Hadoop, the others being [MapReduce](https://www.ibm.com/analytics/hadoop/mapreduce) and [YARN](https://hadoop.apache.org/docs/current/hadoop-yarn/hadoop-yarn-site/YARN.html).
[ZFS](https://docs.oracle.com/cd/E19253-01/819-5461/zfsover-2/) is an enterprise-ready open source file system and volume manager with unprecedented flexibility and an uncompromising commitment to data integrity.
[OpenZFS](https://openzfs.org/wiki/Main_Page ) is an open-source storage platform. It includes the functionality of both traditional file systems and volume manager. It has many advanced features including:
- Protection against data corruption.
- Integrity checking for both data and metadata.
- Continuous integrity verification and automatic "self-healing" repair.
[Btrfs](https://btrfs.wiki.kernel.org/index.php/Main_Page) is a modern copy on write (CoW) filesystem for Linux aimed at implementing advanced features while also focusing on fault tolerance, repair and easy administration. Its main features and benefits are:
- Snapshots which do not make the full copy of files
- RAID - support for software-based RAID 0, RAID 1, RAID 10
- Self-healing - checksums for data and metadata, automatic detection of silent data corruptions
[MergerFS](https://github.com/trapexit/mergerfs) is a union filesystem geared towards simplifying storage and management of files across numerous commodity storage devices. It is similar to mhddfs, unionfs, and aufs.
**MergerFS Features**
- Configurable behaviors / file placement
- Ability to add or remove filesystems at will
- Resistance to individual filesystem failure
- Support for extended attributes (xattrs)
- Support for file attributes (chattr)
- Runtime configurable (via xattrs)
- Works with heterogeneous filesystem types
- Moving of file when filesystem runs out of space while writing
- Ignore read-only filesystems when creating files
- Turn read-only files into symlinks to underlying file
- Hard link copy-on-write / CoW
- Support for POSIX ACLs
[Proxmox Cluster File System (PMXCFS)](https://pve.proxmox.com/wiki/Cluster_Manager) is a File System used to transparently distribute the cluster configuration to all cluster nodes.
[UnionFS](https://unionfs.filesystems.org/) is a filesystem service for Linux, FreeBSD and NetBSD which implements a union mount for other file systems. It allows files and directories of separate file systems, known as branches, to be transparently overlaid, forming a single coherent file system.
[OverlayFS](https://www.kernel.org/doc/html/latest/filesystems/overlayfs.html) is a modern union filesystem that is similar to [AUFS](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Aufs), but faster and with a simpler implementation. It's typically used on systems running on embed devices, like OpenWRT, where is useful to preserve a basic set of configurations and at the same time allowing the user to perform modifications.
[Bcachefs](https://bcachefs.org/) is an advanced new filesystem for Linux, with an emphasis on reliability and robustness and the complete set of features one would expect from a modern filesystem. Scalability has been tested to 50+ TB, will eventually scale far higher.
[Squashfs](https://www.kernel.org/doc/html/latest/filesystems/squashfs.html) is a compressed read-only filesystem for Linux. It uses zlib, lz4, lzo, or xz compression to compress files, inodes and directories. Inodes in the system are very small and all blocks are packed to minimize data overhead.
[Apple File System (APFS)](https://support.apple.com/guide/disk-utility/file-system-formats-available-in-disk-utility-dsku19ed921c/mac) is the default file system for Mac computers using macOS 10.13 or later, features strong encryption, space sharing, snapshots, fast directory sizing, and improved file system fundamentals.
[NTFS(New Technology File System)](https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/windows-server/storage/file-server/ntfs-overview) is the primary file system for recent versions of Windows and Windows Server—provides a full set of features including security descriptors, encryption, disk quotas, and rich metadata, and can be used with Cluster Shared Volumes (CSV) to provide continuously available volumes that can be accessed simultaneously from multiple nodes of a failover cluster.
[exFAT(Extended File Allocation Table )](https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/win32/fileio/exfat-specification) is the file system that was the successor to FAT32 in the FAT family of file systems. It was optimized for flash memory such as USB flash drives and SD cards.
### Books
[Back to the Top](https://github.com/mikeroyal/Self-Hosting-Guide#table-of-contents)
- [Self-hosted Cookbook](https://github.com/tborychowski/self-hosted-cookbook) is a cookbook, for docker-compose based recipes, for self-hosted applications and services.
- [Geek's Cookbook](https://github.com/geek-cookbook/geek-cookbook) is a collection of guides for establishing your own highly-available "private cloud" and using it to run self-hosted services such as GitLab, Plex, NextCloud, etc.
- [Database Books(PDFs)](https://github.com/miollek/Free-Database-Books)
### Podcasts
[Back to the Top](https://github.com/mikeroyal/Self-Hosting-Guide#table-of-contents)
- [Self-Hosted Podcast](https://selfhosted.show/) is a chat show between Chris and Alex two long-time "self-hosters" who share their lessons and take you along for the journey as they learn new ones.
- [Self-Hosted SRE(Site Reality Engineer) Podcast](https://sshsre.fireside.fm/) is a feed to say thank you to our Self-Hosted Site Reality Engineers!
### YouTube Channels
[Back to the Top](https://github.com/mikeroyal/Self-Hosting-Guide#table-of-contents)
- [Jeff Geerling](https://www.youtube.com/c/JeffGeerling)
- [Level1Techs](https://www.youtube.com/c/Level1Techs)
- [Open Source is Awesome](https://www.youtube.com/c/AwesomeOpenSource)
- [Self-Hosted Show by Jupiter Broadcasting](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=XBhhVHVQ148&list=PLUW3LUwQvegxit4XMxUNW3qrRFmgP_aaT)
- [Techno Tim](https://www.youtube.com/c/TechnoTimLive)
- [Raid Owl](https://www.youtube.com/c/RaidOwl)
- [NextCloud](https://www.youtube.com/c/Nextcloud)
- [Raspberry Pi](https://www.youtube.com/c/raspberrypi)
- [Wolfgang's Channel](https://www.youtube.com/c/WolfgangsChannel)
- [Pro Tech Show](https://www.youtube.com/c/ProTechShow)
- [Geeked](https://www.youtube.com/c/GeekedTV)
- [The Tinker Dad](https://www.youtube.com/c/TheTinkerDad)
- [DB Tech](https://www.youtube.com/c/DBTechYT)
- [The Digital Life](https://www.youtube.com/c/TheDigitalLifeTech)
- [censiCLICK](https://www.youtube.com/c/censiCLICK)
- [Home Network Geek](https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCCniXOLmZ85FHN8c8K_c0LA/featured)
### Tutorials & Resources
[Back to the Top](https://github.com/mikeroyal/Self-Hosting-Guide#table-of-contents)
- [Awesome-SelfHosted](https://github.com/awesome-selfhosted/awesome-selfhosted) is a directory of free software solutions and web applications which can be hosted locally.
- [Personal Security Checklist](https://github.com/Lissy93/personal-security-checklist) is a curated checklist of 300+ tips for protecting digital security and privacy in 2022.
- [Awesome Privacy](https://github.com/Lissy93/awesome-privacy) is acurated list of privacy & security-focused software and services.
- [Perfect Media Server](https://perfectmediaserver.com/) is a project aim is to share knowledge and information about building an open-source media server. It was created by [Alex Kretzschmar AKA ironicbadger](https://github.com/ironicbadger).
- [/r/Selfhosted Official Wiki](https://wiki.r-selfhosted.com/getting-started/how-to-self-host/)
- [How I fell into the self-hosting rabbit hole in 2021](https://www.windowscentral.com/self-hosting-2021)
- [The (hardware) key to making phishing defense seamless with Cloudflare Zero Trust and Yubico](https://blog.cloudflare.com/making-phishing-defense-seamless-cloudflare-yubico/)
- [Deploy Your Self-Hosted Mattermost Server](https://mattermost.com/deploy/)
- [Monitor your Internet with a Raspberry Pi by Jeff Geerling](https://www.jeffgeerling.com/blog/2021/monitor-your-internet-raspberry-pi)
- [NextCloud Migration Guide](https://nextcloud.com/migration/)
- [GitLab self-managed subscription](https://docs.gitlab.com/ee/subscriptions/self_managed/)
- [Proxmox VE Training Courses](https://www.proxmox.com/en/training)
- [Self-Hosted GitLab with CodeFlow](https://www.getcodeflow.com/self-hosted-gitlab.html)
- [Self-host Appsmith in Just a Few Minutes on Digital Ocean AppSmith](https://www.appsmith.com/blog/self-host-appsmith-in-just-a-few-minutes-on-digital-ocean)
- [Linode Guides & Tutorials](https://www.linode.com/docs/guides/)
- [Linode Beginner's Guide](https://www.linode.com/docs/guides/linode-beginners-guide/)
- [Access a Pi-hole or Raspberry Pi from anywhere | Tailscale](https://tailscale.com/kb/1114/pi-hole/)
- [Tailscale on Kubernetes | Tailscale](https://tailscale.com/kb/1185/kubernetes/)
- [Tailscale on Proxmox host | Tailscale](https://tailscale.com/kb/1133/proxmox/)
- [Configuring Linux DNS | Tailscale](https://tailscale.com/kb/1188/linux-dns/)
- [Run a private Minecraft server with Tailscale | Tailscale](https://tailscale.com/kb/1137/minecraft/)
- [Set up a dogcam with Tailscale, Raspberry Pi, and Motion | Tailscale](https://tailscale.com/kb/1076/dogcam/)
- [Azure Self-hosted gateway overview](https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/api-management/self-hosted-gateway-overview)
- [Create and configure a self-hosted integration runtime for Azure Data Factory and Synapse pipelines](https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/data-factory/create-self-hosted-integration-runtime?tabs=data-factory)
- [Run a self-hosted agent in Docker - Azure Pipelines | Microsoft Docs](https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/devops/pipelines/agents/docker)
- [Azure DevOps Self Hosted](https://github.com/Azure/DevOps-Self-Hosted)
### Subreddits
[Back to the Top](https://github.com/mikeroyal/Self-Hosting-Guide#table-of-contents)
- [r/Selfhosted](https://www.reddit.com/r/selfhosted/)
- [r/Webhosting](https://www.reddit.com/r/webhosting/)
- [r/NextCloud](https://www.reddit.com/r/NextCloud/)
- [r/HomeServer](https://www.reddit.com/r/HomeServer/)
- [r/Homeassistant](https://www.reddit.com/r/homeassistant/)
- [r/Homebridge](https://www.reddit.com/r/homebridge/)
- [r/HomeKit](https://www.reddit.com/r/HomeKit/)
- [r/SmartThings](https://www.reddit.com/r/SmartThings/)
- [r/Proxmox](https://www.reddit.com/r/Proxmox/)
- [r/Tailscale](https://www.reddit.com/r/Tailscale/)
- [r/WireGuard](https://www.reddit.com/r/WireGuard/)
- [r/Adguard](https://www.reddit.com/r/Adguard/)
- [r/Pihole](https://www.reddit.com/r/pihole/)
- [r/Raspberry_pi](https://www.reddit.com/r/raspberry_pi/)
- [r/RASPBERRY_PI_PROJECTS](https://www.reddit.com/r/RASPBERRY_PI_PROJECTS/)
- [r/RetroPie](https://www.reddit.com/r/RetroPie/)
- [r/Arduino](https://www.reddit.com/r/arduino/)
- [r/ArduinoProjects](https://www.reddit.com/r/ArduinoProjects/)
- [r/Opensource](https://www.reddit.com/r/opensource/)
- [r/Devops](https://www.reddit.com/r/devops/)
- [r/Kubernetes](https://www.reddit.com/r/kubernetes/)
- [r/Docker](https://www.reddit.com/r/docker/)
- [r/Portainer](https://www.reddit.com/r/portainer/)
- [r/Ansible](https://www.reddit.com/r/ansible/)
- [r/Terraform](https://www.reddit.com/r/Terraform/)
- [r/CloudFlare](https://www.reddit.com/r/CloudFlare/)
- [r/Homeautomation](https://www.reddit.com/r/homeautomation/)
- [r/HomeNetworking](https://www.reddit.com/r/HomeNetworking/)
- [r/Homelab](https://www.reddit.com/r/homelab/)
- [r/Synology](https://www.reddit.com/r/synology/)
- [r/unRAID](https://www.reddit.com/r/unRAID/)
- [r/QNAP](https://www.reddit.com/r/qnap/)
- [r/OpenWrt](https://www.reddit.com/r/openwrt/)
- [r/Smarthome](https://www.reddit.com/r/smarthome/)
- [r/TpLink](https://www.reddit.com/r/TpLink/)
- [r/DataHoarder](https://www.reddit.com/r/DataHoarder/)
- [r/ZFS](https://www.reddit.com/r/zfs/)
- [r/PFSENSE](https://www.reddit.com/r/PFSENSE/)
- [r/OpenMediaVault](https://www.reddit.com/r/OpenMediaVault/)
# WireGuard
[Back to the Top](#table-of-contents)

### What is WireGuard?
[Back to the Top](#table-of-contents)
[WireGuard®](https://www.wireguard.com/) is a straight-forward, fast and modern VPN that utilizes state-of-the-art cryptography. It aims to be faster, simpler, leaner, and more useful than IPsec while avoiding the massive headache. WireGuard is designed as a general-purpose VPN for running on embedded interfaces and super computers alike, fit for many circumstances. Initially released for the Linux kernel, it is now cross-platform (Windows, macOS, BSD, iOS, Android) and widely deployable.

### What is Tailscale?
[Back to the Top](#table-of-contents)
[Tailscale](https://github.com/tailscale) is a WireGuard-based app that makes secure, private networks easy for teams of any scale. It works like an [overlay network](https://tailscale.com/blog/how-tailscale-works/) between the computers of your networks using all kinds of [NAT traversal sorcery](https://tailscale.com/blog/how-nat-traversal-works/).
* [Tailscale Terraform Provider](https://github.com/tailscale/terraform-provider-tailscale)
* [Tailscale Docker extension](https://github.com/tailscale/docker-extension)
* [Tailscale Synology](https://github.com/tailscale/tailscale-synology)

How NAT Traversal works on a Home router. Credit: [Tailscale](https://tailscale.com/blog/how-nat-traversal-works/).
[Headscale](https://github.com/juanfont/headscale) is an open source, self-hosted implementation of the Tailscale coordination server.
### What is Netmaker?
[Back to the Top](#table-of-contents)
[Netmaker](https://www.netmaker.org/) is a tool that enables you to create relays, gateways, full VPN meshes, and even zero trust networks. It's fully configurable to let you maximize the power of Wireguard.

NetMaker Architecture. Credit: [Netmaker](https://netmaker.readthedocs.io/en/v0.7.2/index.html).
### WireGuard Tools
[Back to the Top](#table-of-contents)
[Wiretrustee](https://wiretrustee.com/) is a WireGuard®-based mesh network that connects your devices into a single private network.
[Wireguard Manager](https://github.com/complexorganizations/wireguard-manager) is a tool that enables you to build your own vpn under a minute.
[Tailscale](https://github.com/tailscale) is a WireGuard-based app that makes secure, private networks easy for teams of any scale. It works like an [overlay network](https://tailscale.com/blog/how-tailscale-works/) between the computers of your networks using all kinds of [NAT traversal sorcery](https://tailscale.com/blog/how-nat-traversal-works/).
[Headscale](https://github.com/juanfont/headscale) is an open source, self-hosted implementation of the Tailscale coordination server.
[Firezone](https://firezone.dev/) is a self-hosted WireGuard®-based VPN server and Linux firewall.
[NetBird](https://netbird.io/) is an open-source VPN management platform built on top of WireGuard® making it easy to create secure private networks for your organization or home.
[Mistborn](https://gitlab.com/cyber5k/mistborn) is a secure platform for easily standing up and managing your own cloud services: including firewall, ad-blocking, and multi-factor WireGuard VPN access.
[Mistborn CLI](https://gitlab.com/cyber5k/mistborn-cli) is a Command-line interface for [Mistborn](https://gitlab.com/cyber5k/mistborn).
[BoringTun](https://github.com/cloudflare/boringtun) is an implementation of the WireGuard® protocol designed for portability and speed. It's successfully deployed on millions of [iOS](https://apps.apple.com/us/app/1-1-1-1-faster-internet/id1423538627) and [Android](https://play.google.com/store/apps/details?id=com.cloudflare.onedotonedotonedotone&hl=en_US) consumer devices as well as thousands of Cloudflare Linux servers.
[PiVPN](https://pivpn.io/) is the simplest VPN installer, designed for [Raspberry Pi](https://www.raspberrypi.com).
[Algo VPN](https://github.com/trailofbits/algo) is a set of Ansible scripts that simplify the setup of a personal WireGuard and IPsec VPN. It uses the most secure defaults available and works with common cloud providers.
[Pro Custodibus](https://www.procustodibus.com/features/) is a tool for managing WireGuard with a variety of business VPN (Virtual Private Network) use cases, such as site-to-site connectivity, secure remote access from anywhere, secure access to the cloud (Amazon Web Services, Google Cloud Platform, Microsoft Azure, etc), and more.
[Drago](https://seashell.github.io/drago) is a flexible configuration manager for WireGuard designed to make it simple to configure secure network overlays spanning heterogeneous nodes distributed across different clouds and physical locations. Drago is in active development, and we welcome contributions from the open-source community.
[Netmaker](https://netmaker.org/) is a tool that helps connect any computers together over a secure, fast, private network, and manage multiple networks from a central server.
[Kilo](https://github.com/squat/kilo) is a multi-cloud network overlay built on WireGuard and designed for Kubernetes. Kilo connects nodes in a cluster by providing an encrypted layer 3 network that can span across data centers and public clouds. The Pod network created by Kilo is always fully connected, even when the nodes are in different networks or behind NAT. By allowing pools of nodes in different locations to communicate securely, Kilo enables the operation of multi-cloud clusters. Kilo's design allows clients to VPN to a cluster in order to securely access services running on the cluster.
[Subspace](https://github.com/subspacecloud/subspace) is a simple WireGuard VPN server GUI.
[WG UI](https://github.com/EmbarkStudios/wg-ui) is a basic, self-contained management service for WireGuard with a self-serve web UI.
[WireHole](https://github.com/IAmStoxe/wirehole) is a combination of WireGuard, PiHole, and Unbound in a docker-compose project with the intent of enabling users to quickly and easily create and deploy a personally managed full or split-tunnel WireGuard VPN with ad blocking capabilities (via Pihole), and DNS caching with additional privacy options (via Unbound).
[Gluetun](https://github.com/qdm12/gluetun) is a lightwieght VPN client in a thin Docker container for multiple VPN providers, written in Go, and uses OpenVPN or Wireguard, DNS over TLS, with a few proxy servers built-in.
[Ethr](https://github.com/microsoft/ethr) is a cross platform network performance measurement tool written in golang. The goal of this project is to provide a native tool for comprehensive network performance measurements of bandwidth, connections/s, packets/s, latency, loss & jitter, across multiple protocols such as TCP, UDP, HTTP, HTTPS, and across multiple platforms such as Windows, Linux and other Unix systems.
### Setting up WireGuard with PiVPN
[Back to the Top](#table-of-contents)

**Installing PiVPN:**
```sudo apt install curl -y```
```curl -L https://install.pivpn.io | bash```








### Setting up WireGuard on Unraid
[Back to the Top](#table-of-contents)

Select Apps, then search for WireGuard and install **Wireguard-Easy**.


VPN manager
Almost all of the settings can stay as default, however, there are a few that we will modify.
* Set the WG_HOST variable to be the IP address of your Unraid server.
* If you’d like to modify the WireGuard port (51820), you can do that here.
* Change the default Web GUI password.

### Setting up WireGuard on pfSense
[Back to the Top](#table-of-contents)

When looking at how to set up WireGuard on pfSense, the first thing that we need to do is install the package. Follow the instructions below to install the WireGuard package on pfSense.

* Open the Package Manager and search for WireGuard, then Install the latest version of the package.

* After the package has installed, select VPN then WireGuard and under the Tunnels section, select Add Tunnel.
* In the Tunnel Configuration, set the Description as WireGuard, the Listen Port as 51820, then Generate private and public keys.
* Copy the Public Key. We will need this for our client configuration.
* Create the tunnel, then select Settings, and ensure that Enable WireGuard is selected. Then Save and Apply.


### Setting up WireGuard on OpenWRT
[Back to the Top](#table-of-contents)

**Quick Links:**
* [WireGuard route all traffic through wireguard tunnel](https://openwrt.org/docs/guide-user/services/vpn/wireguard/all-traffic-through-wireguard)
* [Automated WireGuard Server and Multi-client](https://openwrt.org/docs/guide-user/services/vpn/wireguard/automated)
* [WireGuard basics](https://openwrt.org/docs/guide-user/services/vpn/wireguard/basics)
* [WireGuard client](https://openwrt.org/docs/guide-user/services/vpn/wireguard/client)
* [WireGuard extras](https://openwrt.org/docs/guide-user/services/vpn/wireguard/extras)
* [WireGuard performance](https://openwrt.org/docs/guide-user/services/vpn/wireguard/performance)
* [WireGuard Road-Warrior Configuration](https://openwrt.org/docs/guide-user/services/vpn/wireguard/road-warrior)
* [WireGuard](https://openwrt.org/docs/guide-user/services/vpn/wireguard/start)
* [WireGuard server](https://openwrt.org/docs/guide-user/services/vpn/wireguard/server)
* [WireGuard peers](https://openwrt.org/docs/guide-user/services/vpn/wireguard/serverclient)
* [Automated WireGuard site-to-site VPN configuration](https://openwrt.org/docs/guide-user/services/vpn/wireguard/site-to-site)
In your router’s webUI, navigate to System - Software, click Update lists:
In the Filter field, type WireGuard, locate and install the **wireguard, wireguard-tools, kmod-wireguard, and luci-app-wireguard packages.** **Note: The wireguard package is included in version 22.02.**

**Generate WireGuard keypair**
SSH into your router as ‘root’ ([OpenWrt Wiki](https://openwrt.org/docs/guide-quick-start/sshadministration)):
```ssh root@192.168.1.1```
Generate WireGuard keys:
```wg genkey | tee privatekey | wg pubkey > publickey```
```chmod 600 privatekey```
Note your Private & Public keys, you will need them later:
```cat privatekey```
``` cat publickey```
**Creating an Interface**
Navigate to Network - Interface,
Click the Add new interface... button and enter the following configuration:
* Name - give it any name
* Protocol - WireGuard VPN
Create interface
In the General Settings tab:
* Bring up on boot - Checked
* Private Key - copy and paste the generated previously Private key
* IP Address - enter the WireGuard IP Address obtained in the Client Area ending with /32, e.g. 172.27.124.169/32
**Add a Firewall zone**
Navigate to Network - Firewall
Click the Add button and enter the following configuration:
* Name - Give it any name
* Input - Reject
* Output - Accept
* Forward - Reject
* Masquerading - Checked
* MSS clamping - Checked
* Covered networks - select the previously created VPN tunnel interface
* Allow forward to destination zones - Unspecified
* Allow forward from source zones - lan

**DNS**
Navigate to Network - Interfaces
Click on the Edit button next to the WAN interface
In the Advanced Settings tab, uncheck the Use DNS servers advertised by peer and specify one of the following DNS servers in the Use custom DNS servers field:
* 172.16.0.1 = regular DNS with no blocking
* 10.0.254.2 = standard AntiTracker to block advertising and malware domains
* 10.0.254.3 = Hardcore Mode AntiTracker to also block Google and Facebook domains

Click the Save button.
**Last Steps**
* A device reboot is not required, though it may be useful to confirm that everything behaves as expected.
* Run a leak test at [https://www.dnsleaktest.com](https://www.dnsleaktest.com/) via one of the internal network clients attached to your OpenWRT router.
### Setting up WireGuard on Home Assistant
[Back to the Top](#table-of-contents)

**Install Wireguard Add-on in Home Assistant**
* Next, open up Home Assistant. Go to Supervisor > Add-on store, and search for WireGuard.
* Click the WireGuard addon, and the click Install.

**Configure Wireguard Settings**
After installing WireGuard, do not start it yet. We need to configure a few options first.
* Click the Configuration tab at the very top.
* There are **two blocks of code here: server and peers.** The server section is the WireGuard server info, and the peers section is where you’d add new devices that will connect to your VPN.
**Server Configuration**
* **Host:** add the subdomain you just created. (vpn.mydomain.com)
* **Addresses:** If your internal network is using the 192.168.x.x or 10.x.x.x range, you can leave the default IP addresses WireGuard has provided. (see note above)
* **DNS:** Set to your router’s internal IP address (**Open CMD > ipconfig /all > Under DNS servers**)
If you have Adguard or PiHole installed, you can use the IP address of those instead. This will allow you to block ads even when connected to the WireGuard VPN.
**Peers Configuration**
This is where you’ll create WireGuard configuration files for each of the devices you want to connect to WireGuard with. For this example, I’m using my phone and leaving ```allowed_ips``` and ```client_allowed_ips``` as is. If you adding multiple devices, then you’ll need to copy the entire block of code starting at name, give it a different name, and add the next available IP address (For example: 172.27.66.4)
Click **Save** once finished.
Then, go back to the Info tab and click **Start**.

**Port Forward**
The next step is to forward port 51820 from your Home Assistant server through your router. Unfortunately, there are so many different types of routers, each with different steps to port forward. The important thing to note is that you’ll be **port forwarding 51820(wireguard port)** from the internal IP of your Home Assistant instance (for example: 192.168.68.24) and choosing the **UDP protocol only**.
**Download Wireguard app on mobile device**
Download the WireGuard app from the [Apple App Store](https://apps.apple.com/us/app/wireguard/id1441195209) or [Google Play Store](https://play.google.com/store/apps/details?id=com.wireguard.android&hl=en_US&gl=US). You will need it for the next step.
If all goes well, you can click into the new tunnel connection from within the app. If you see data flowing under the Transfer section, that means you are good to go.
**Improving Security**
Once you have everything setup and working correctly, you should read through the [WireGuard Addon docs](https://github.com/hassio-addons/addon-wireguard/blob/main/wireguard/DOCS.md) to setup up ```allowed_ips``` and ```client_allowed_ips``` to further secure your VPN instance. There’s also some other helpful options you can configure such as log level, but these are all optional.
# Nextcloud
[Back to the Top](https://github.com/mikeroyal/Self-Hosting-Guide#table-of-contents)

[Nextcloud](https://nextcloud.com) is an industry-leading, on-premises content collaboration platform for file sync & share and communication server. It is fully open source and you can host it yourself or pay a company to do it for you. Also checkout the following links below:
- [Nextcloud App Store](https://apps.nextcloud.com)
- [Nextcloud GitHub](https://github.com/nextcloud)
- [Nextcloud Developer Program](https://nextcloud.com/developer)

Nexcloud login screen
[Nextcloud Hub](https://nextcloud.com/hub/) is a tool that allows you to share and collaborate on documents, send and receive email, manage your calendar and have video chats without data leaks. As fully on-premises solution, Nextcloud Hub provides the benefits of online collaboration without the compliance and security risks.

Nexcloud Hub
[Nextcloud Desktop Client](https://nextcloud.com/install/#install-clients) is a tool to synchronize files from Nextcloud Server with your computer.
[Nextcloud Deck](https://apps.nextcloud.com/apps/deck) is a kanban style organization tool aimed at personal planning and project organization for teams integrated with Nextcloud.
[Nextcloud Files](https://nextcloud.com/files/) is a tool tool that allows your employees have easy access to their files, photos and documents to work and can share and collaborate with team members, customers and partners. So IT knows nobody besides those they shared with has access to those files.
[Nextcloud Talk](https://nextcloud.com/talk/) is a tool that protects your communication better than other team collaboration platforms like Microsoft Teams or Slack, making sure your data stays on your servers. It also goes further than other encrypted communication technologies by keeping even metadata from leaking.
[Nextcloud Home](https://nextcloud.com/athome/) is a tool that allows you store your documents, calendar, contacts and photos on your server at home, at one of at one Nextcloud's providers or in a data center you trust.
[Nextcloud Enterprise](https://nextcloud.com/enterprise/) is a service that gives professional organizations software optimized and tested for mission critical environments.
[Nextcloud Outlook Integration](https://nextcloud.com/outlook/) is a tool that automatically upload files to replace large attachments or integrate Calendars and Contacts in Microsoft Outlook.
[Collabora Online in Nextcloud](https://nextcloud.com/collaboraonline/) is a powerful LibreOffice-based online office suite with collaborative editing, which supports all major document, spreadsheet and presentation file formats and works in all modern browsers.
[ONLYOFFICE integration in Nextcloud](https://nextcloud.com/onlyoffice/) is a service that empowers your users to collaborate on office documents with team members in real time. It has compatibility with Microsoft Office formats means perfect documents, every time.
[Nextcloud VM(virtual machine appliance)](https://download.nextcloudvm.com/) is a set of carefully crafted family of [*nix](https://bit.ly/2UaCC7b) scripts, which interactively guide you through a quality-controlled installation of a Nextcloud instance for Home/SME Server and scripts for Raspberry Pi 4. It is Community developed and maintained.
# Raspberry Pi
[Back to the Top](https://github.com/mikeroyal/Self-Hosting-Guide#table-of-contents)

## Models of Raspberry Pi boards
[Back to the Top](https://github.com/mikeroyal/Self-Hosting-Guide#table-of-contents)
**Raspberry Pi 4 Model B**

[Check out the Raspberry Pi 4](https://www.raspberrypi.org/products/raspberry-pi-4-model-b/)
**Raspberry Pi 4 Model B Hardware Specifications**
- Broadcom BCM2711, Quad core Cortex-A72 (ARM v8) 64-bit SoC @ 1.5GHz
- 2GB, 4GB or 8GB LPDDR4-3200 SDRAM (depending on model)
- 2.4 GHz and 5.0 GHz IEEE 802.11ac wireless
- Bluetooth 5.0, BLE
- Gigabit Ethernet
- 2 USB 3.0 ports; 2 USB 2.0 ports.
- Raspberry Pi standard 40 pin GPIO header (fully backwards compatible with previous Pi boards)
- 2 × micro-HDMI ports (up to 4kp60 supported)
- OpenGL ES 3.0 graphics
**Raspberry Pi 400 Personal Computer Kit**

[Check out the Raspberry Pi 400 Personal Computer Kit](https://www.raspberrypi.org/products/raspberry-pi-400/)
**Raspberry Pi 400 Hardware Specifications**
- Broadcom BCM2711, Quad core Cortex-A72 (ARM v8) 64-bit SoC @ 1.8GHz
- 4GB LPDDR4-3200 SDRAM
- 2.4 GHz and 5.0 GHz IEEE 802.11ac wireless
- Bluetooth 5.0, BLE
- Gigabit Ethernet
- 2 USB 3.0 ports; 2 USB 2.0 ports.
- Raspberry Pi standard 40 pin GPIO header
- 2 × micro-HDMI ports (up to 4kp60 supported)
- OpenGL ES 3.0 graphics
**Raspberry Pi Pico Microcontroller**

[Check out the Raspberry Pi Pico](https://www.raspberrypi.org/products/raspberry-pi-pico/)
**Raspberry Pi Pico Hardware Specifications**
- RP2040 microcontroller chip designed by Raspberry Pi in the UK
- Dual-core Arm Cortex-M0+ processor, flexible clock running up to 133 MHz
- 264KB on-chip SRAM
- 2MB on-board QSPI Flash
- 26 multifunction GPIO pins, including 3 analogue inputs
- 2 × UART, 2 × SPI controllers, 2 × I2C controllers, 16 × PWM channels
- 1 × USB 1.1 controller and PHY, with host and device support
- 8 × Programmable I/O (PIO) state machines for custom peripheral support
- Castellated module allows soldering direct to carrier boards
- Drag-and-drop programming using mass storage over USB
- Low-power sleep and dormant modes
- Accurate on-chip clock
- Temperature sensor
- Accelerated integer and floating-point libraries on-chip
**Raspberry Pi OS. The default Operating System for every Raspberry Pi device**
[Check out Raspberry Pi OS](https://www.raspberrypi.org/software/operating-systems/)
 ## Raspberry Pi Learning Resources
[Back to the Top](https://github.com/mikeroyal/Self-Hosting-Guide#table-of-contents)
[Raspberry Pi](https://www.raspberrypi.org/) is an ARM powered single board computer(SBC) that is the size of a credit card and costs around $35.
[Raspberry Pi Foundation](https://www.raspberrypi.org/about/) is a UK-based charity that works to put the power of computing and digital making into the hands of people all over the world.
[Getting Started with Raspberry Pi Projects](https://projects.raspberrypi.org/)
[Online learning for the Raspberry Pi](https://www.raspberrypi.org/training/online/)
[Raspberry Pi Training Program](https://www.raspberrypi.org/training/)
[Raspberry Pi Online Courses on Udemy](https://www.udemy.com/topic/raspberry-pi/)
[Raspberry Pi Online Courses on Coursera](https://www.coursera.org/courses?languages=en&query=raspberry%20pi)
[The Raspberry Pi Platform and Python Programming course on Coursera](https://www.coursera.org/learn/raspberry-pi-platform)
[Learning Raspberry Pi with Online Courses on edX](https://www.edx.org/learn/raspberry-pi)
[Raspberry Pi Online Training Courses on LinkedIn Learning](https://www.linkedin.com/learning/topics/raspberry-pi)
[Getting Started with Raspberry Pi course on FutureLearn](https://www.futurelearn.com/courses/getting-started-with-your-raspberry-pi)
[Home Assistant on Raspberry Pi](https://www.home-assistant.io/getting-started/)
[PiSwitch: Build your own Nintendo Switch-style console](https://magpi.raspberrypi.org/articles/piswitch-nintendo-switch-console)
## Raspberry Pi Operating Systems
[Back to the Top](https://github.com/mikeroyal/Self-Hosting-Guide#table-of-contents)
[Raspberry Pi OS](https://www.raspberrypi.org/software/operating-systems/)
[Hass.io(Home Assistant OS)](https://www.home-assistant.io/hassio/installation/)
[OmniROM(Android 11) based on ASOP](https://forum.xda-developers.com/t/omnirom-android-r-11-for-pi-4.4183121/)
[Manjaro Linux ARM](https://manjaro.org/download/#ARM)
[Arch Linux ARM](https://archlinuxarm.org/platforms/armv8/broadcom/raspberry-pi-4)
[Ubuntu MATE for Raspberry Pi](https://ubuntu-mate.org/ports/raspberry-pi/)
[Ubuntu Desktop for Raspberry Pi](https://ubuntu.com/raspberry-pi)
[Ubuntu Core on a Raspberry Pi](https://ubuntu.com/download/raspberry-pi-core)
[Ubuntu Server for ARM](https://ubuntu.com/download/server/arm)
[Fedora ARM](https://arm.fedoraproject.org)
[Kali Linux for the Raspberry Pi](https://www.kali.org/docs/arm/kali-linux-raspberry-pi/)
[Twister OS](https://twisteros.com/)
[TitusPi](https://github.com/ChrisTitusTech/TitusPi)
[RetroArch](https://www.retroarch.com/?page=platforms)
[RetroPie](https://retropie.org.uk/)
[LibreELEC](https://libreelec.tv/)
[OSMC](https://osmc.tv)
[RISC OS](https://www.riscosopen.org/content/)
[DietPi](https://github.com/MichaIng/DietPi)
[Windows 10 IoT Core](https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/iot-core/windows-iot-core)
## Raspberry Pi Tools
[Back to the Top](#table-of-contents)
[Raspberry Pi Imager](https://www.raspberrypi.org/software/) is the quick and easy way to install Raspberry Pi OS and other operating systems to a microSD card, ready to use with your Raspberry Pi.
[Raspberry Pi Locator](https://rpilocator.com/) is a website to track Raspberry Pi 4 model B, Compute Module 4, Pi Zero 2 W, and Pico availability across multiple retailers in different countries.
[Raspberry Pi Network Install (Beta)](https://www.raspberrypi.com/documentation/computers/getting-started.html#installing-over-the-network-beta) is a feature can be used to start the Raspberry Pi Imager application directly on a Raspberry Pi 4, or a Raspberry Pi 400, by downloading it from the internet using an Ethernet cable. The Raspberry Pi Imager application, which will run in memory on your Raspberry Pi, can then be used to flash the operating system onto a blank SD Card or USB disk, just like normal.
[Raspberry Pi Bootloader](https://www.raspberrypi.com/documentation/computers/raspberry-pi.html#updating-the-bootloader) is a feature, which is now available in beta, that utilize an **EEPROM(Electrically Erasable Programmable Read-Only Memory)** to store the system’s bootloader. This EEPROM is persistent storage that is located on the Pi’s mainboard. The advantage of using the EEPROM instead is that the Raspberry Pi 4 can perform tasks without needing any storage to be attached.
[Etcher](https://www.balena.io/etcher/) is an open source, cross-platform software that makes it easy to flash operating system images to a microSD card or USB device.
[Home Assistant](https://www.home-assistant.io/) is an open source home automation that puts local control and privacy first. Home Assistant is powered by a worldwide community of tinkerers and DIY enthusiasts that runs great on Raspberry Pi.
[Gladys Assistant](https://github.com/gladysassistant/gladys) is a privacy-first, open-source home assistant and runs great on Raspberry Pi.
[Kodi for Raspberry Pi](https://kodi.tv/download/853) is a free and open source media player application developed by the XBMC/Kodi Foundation.
[Pi-hole](https://pi-hole.net/) is a [DNS sinkhole](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/DNS_Sinkhole) that protects your devices from unwanted content, without installing any client-side software, intended for use on a private network. It is designed for use on embedded devices with network capability, such as the Raspberry Pi, but it can be used on other machines running Linux and cloud implementations.
[PiKVM](https://github.com/pikvm/pikvm) is a very simple and fully functional Raspberry Pi-based KVM over IP.
[PiShrink](https://github.com/Drewsif/PiShrink) is a bash script that automatically shrink a pi image that will then resize to the max size of the SD card on boot.
[RPiPlay](https://github.com/FD-/RPiPlay) is an open-source implementation of an AirPlay mirroring server for the Raspberry Pi that supports iOS 9 and later.
[Gpiozero](https://github.com/gpiozero/gpiozero) is a simple interface to GPIO(General-Purpose Input/Output) devices with the Raspberry Pi.
[Balena Sound](https://sound.balenalabs.io/) is a single or multi-room streamer for an existing audio device using a Raspberry Pi! It supports Bluetooth, Airplay and Spotify Connect.
[OpenBalena](https://balena.io/open) is a platform to deploy and manage connected devices.
### Home Assistant
[Back to the Top](#table-of-contents)
## Raspberry Pi Learning Resources
[Back to the Top](https://github.com/mikeroyal/Self-Hosting-Guide#table-of-contents)
[Raspberry Pi](https://www.raspberrypi.org/) is an ARM powered single board computer(SBC) that is the size of a credit card and costs around $35.
[Raspberry Pi Foundation](https://www.raspberrypi.org/about/) is a UK-based charity that works to put the power of computing and digital making into the hands of people all over the world.
[Getting Started with Raspberry Pi Projects](https://projects.raspberrypi.org/)
[Online learning for the Raspberry Pi](https://www.raspberrypi.org/training/online/)
[Raspberry Pi Training Program](https://www.raspberrypi.org/training/)
[Raspberry Pi Online Courses on Udemy](https://www.udemy.com/topic/raspberry-pi/)
[Raspberry Pi Online Courses on Coursera](https://www.coursera.org/courses?languages=en&query=raspberry%20pi)
[The Raspberry Pi Platform and Python Programming course on Coursera](https://www.coursera.org/learn/raspberry-pi-platform)
[Learning Raspberry Pi with Online Courses on edX](https://www.edx.org/learn/raspberry-pi)
[Raspberry Pi Online Training Courses on LinkedIn Learning](https://www.linkedin.com/learning/topics/raspberry-pi)
[Getting Started with Raspberry Pi course on FutureLearn](https://www.futurelearn.com/courses/getting-started-with-your-raspberry-pi)
[Home Assistant on Raspberry Pi](https://www.home-assistant.io/getting-started/)
[PiSwitch: Build your own Nintendo Switch-style console](https://magpi.raspberrypi.org/articles/piswitch-nintendo-switch-console)
## Raspberry Pi Operating Systems
[Back to the Top](https://github.com/mikeroyal/Self-Hosting-Guide#table-of-contents)
[Raspberry Pi OS](https://www.raspberrypi.org/software/operating-systems/)
[Hass.io(Home Assistant OS)](https://www.home-assistant.io/hassio/installation/)
[OmniROM(Android 11) based on ASOP](https://forum.xda-developers.com/t/omnirom-android-r-11-for-pi-4.4183121/)
[Manjaro Linux ARM](https://manjaro.org/download/#ARM)
[Arch Linux ARM](https://archlinuxarm.org/platforms/armv8/broadcom/raspberry-pi-4)
[Ubuntu MATE for Raspberry Pi](https://ubuntu-mate.org/ports/raspberry-pi/)
[Ubuntu Desktop for Raspberry Pi](https://ubuntu.com/raspberry-pi)
[Ubuntu Core on a Raspberry Pi](https://ubuntu.com/download/raspberry-pi-core)
[Ubuntu Server for ARM](https://ubuntu.com/download/server/arm)
[Fedora ARM](https://arm.fedoraproject.org)
[Kali Linux for the Raspberry Pi](https://www.kali.org/docs/arm/kali-linux-raspberry-pi/)
[Twister OS](https://twisteros.com/)
[TitusPi](https://github.com/ChrisTitusTech/TitusPi)
[RetroArch](https://www.retroarch.com/?page=platforms)
[RetroPie](https://retropie.org.uk/)
[LibreELEC](https://libreelec.tv/)
[OSMC](https://osmc.tv)
[RISC OS](https://www.riscosopen.org/content/)
[DietPi](https://github.com/MichaIng/DietPi)
[Windows 10 IoT Core](https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/iot-core/windows-iot-core)
## Raspberry Pi Tools
[Back to the Top](#table-of-contents)
[Raspberry Pi Imager](https://www.raspberrypi.org/software/) is the quick and easy way to install Raspberry Pi OS and other operating systems to a microSD card, ready to use with your Raspberry Pi.
[Raspberry Pi Locator](https://rpilocator.com/) is a website to track Raspberry Pi 4 model B, Compute Module 4, Pi Zero 2 W, and Pico availability across multiple retailers in different countries.
[Raspberry Pi Network Install (Beta)](https://www.raspberrypi.com/documentation/computers/getting-started.html#installing-over-the-network-beta) is a feature can be used to start the Raspberry Pi Imager application directly on a Raspberry Pi 4, or a Raspberry Pi 400, by downloading it from the internet using an Ethernet cable. The Raspberry Pi Imager application, which will run in memory on your Raspberry Pi, can then be used to flash the operating system onto a blank SD Card or USB disk, just like normal.
[Raspberry Pi Bootloader](https://www.raspberrypi.com/documentation/computers/raspberry-pi.html#updating-the-bootloader) is a feature, which is now available in beta, that utilize an **EEPROM(Electrically Erasable Programmable Read-Only Memory)** to store the system’s bootloader. This EEPROM is persistent storage that is located on the Pi’s mainboard. The advantage of using the EEPROM instead is that the Raspberry Pi 4 can perform tasks without needing any storage to be attached.
[Etcher](https://www.balena.io/etcher/) is an open source, cross-platform software that makes it easy to flash operating system images to a microSD card or USB device.
[Home Assistant](https://www.home-assistant.io/) is an open source home automation that puts local control and privacy first. Home Assistant is powered by a worldwide community of tinkerers and DIY enthusiasts that runs great on Raspberry Pi.
[Gladys Assistant](https://github.com/gladysassistant/gladys) is a privacy-first, open-source home assistant and runs great on Raspberry Pi.
[Kodi for Raspberry Pi](https://kodi.tv/download/853) is a free and open source media player application developed by the XBMC/Kodi Foundation.
[Pi-hole](https://pi-hole.net/) is a [DNS sinkhole](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/DNS_Sinkhole) that protects your devices from unwanted content, without installing any client-side software, intended for use on a private network. It is designed for use on embedded devices with network capability, such as the Raspberry Pi, but it can be used on other machines running Linux and cloud implementations.
[PiKVM](https://github.com/pikvm/pikvm) is a very simple and fully functional Raspberry Pi-based KVM over IP.
[PiShrink](https://github.com/Drewsif/PiShrink) is a bash script that automatically shrink a pi image that will then resize to the max size of the SD card on boot.
[RPiPlay](https://github.com/FD-/RPiPlay) is an open-source implementation of an AirPlay mirroring server for the Raspberry Pi that supports iOS 9 and later.
[Gpiozero](https://github.com/gpiozero/gpiozero) is a simple interface to GPIO(General-Purpose Input/Output) devices with the Raspberry Pi.
[Balena Sound](https://sound.balenalabs.io/) is a single or multi-room streamer for an existing audio device using a Raspberry Pi! It supports Bluetooth, Airplay and Spotify Connect.
[OpenBalena](https://balena.io/open) is a platform to deploy and manage connected devices.
### Home Assistant
[Back to the Top](#table-of-contents)

[Home Assistant](https://home-assistant.io/hassio/) is a container-based system for managing your Home Assistant Core installation and related applications. The system is controlled via Home Assistant which communicates with the Supervisor. The Supervisor provides an API to manage the installation. This includes changing network settings or installing and updating software.
**Quick Links**
- [Getting Started with Home Assistant](https://home-assistant.io/getting-started)
- [Home Assistant for Raspberry Pi](https://www.home-assistant.io/installation/raspberrypi/)
- [Installing Home Assistant OS using Proxmox 7](https://github.com/Kanga-Who/home-assistant/blob/master/Home%20Assistant%20with%20Proxmox%20installation.md)
[Home Assistant Frontend](https://demo.home-assistant.io/) is a frontend for Home Assistant.
#### Tools to write the HA image to your boot media(microSD card or USB device)
[Raspberry Pi Imager](https://www.raspberrypi.org/software/) is the quick and easy way to install Raspberry Pi OS and other operating systems to a microSD card, ready to use with your Raspberry Pi.

[Etcher](https://www.balena.io/etcher/) is an open source, cross-platform software that makes it easy to flash operating system images to a microSD card or USB device.

### Home Assistant integrations

Home Assistant integrations. Credit: [Home Assistant](https://www.home-assistant.io/integrations/)
[ESPHome](https://esphome.io/) is a system to control your ESP8266/ESP32 by simple yet powerful configuration files and control them remotely through Home Automation systems.
[Shelly Cloud](https://shelly.cloud/) is a Smart home control tool that has been perfected and provides precise monitoring of your Shelly devices no matter where you are. Shelly devices are compatible with Alexa, Google Home, Android, and iOS.
[Plex media server](https://www.plex.tv/) is a application that gives you the power to add, access and share all the entertainment that matters to you, on almost any device. With 50,000+ on demand titles and hundreds of channels of live TV, plus your own personal media collection, using one powerful app.
[Amazon Alexa](https://alexa.amazon.com/) is a smart virtual assistant software to manage Alexa-enabled devices, control music playback, view shopping lists on the go, keep track of upcoming reminders, check on active timers and much more.
[Google Assistant](https://assistant.google.com/) is a smart virtual assistant software on mobile and home automation devices.
[Apple HomeKit](https://www.apple.com/shop/accessories/all/homekit) is a software framework that enables your app to coordinate and control home automation accessories from multiple vendors to present a coherent, user-focused interface. Using HomeKit, your app can: Discover HomeKit-compatible automation accessories and add them to a persistent, cross-device home configuration database.
[Samsung SmartThings](https://www.smartthings.com/) is a sofwtare frmaeowrk that you can connect, monitor and control multiple smart home devices quicker and easier. Connect your Samsung smart TVs, smart appliances, smart speakers and brands like Ring, Nest and Philips Hue all from one app.
[Ecobee](https://www.ecobee.com) is a home automation company in Canada that makes thermostats for residential and commercial use.
[Lutron Caséta](https://www.lutron.com/en-US/Products/Pages/SingleRoomControls/CasetaWireless/Overview.aspx) is a smart lighting control system that is a great solution for giving any client smart lighting control. It was purposely built to work in homes of all ages and it works with older wiring as well as new.
[Philips Hue](https://www.philips-hue.com) is a smart lighting system. The smart lights, Hue Bridge, and smart controls will forever change the way you experience light.
[Sonos](https://www.sonos.com) is the wireless home sound system that fills as many rooms as you want with great-sounding music, movies, and TV.
[MQTT](https://mqtt.org/) is an [OASIS standard](https://www.oasis-open.org/standards/) messaging protocol for the Internet of Things (IoT). It is designed as an extremely lightweight publish/subscribe messaging transport that is ideal for connecting remote devices with a small code footprint and minimal network bandwidth.
[Zigbee](https://csa-iot.org/all-solutions/zigbee/) is the full-stack, secure, reliable, and market-proven solution used by a majority of large smart home ecosystem providers, such as Amazon's Echo Plus, Samsung SmartThings, Signify (Philips Hue), and more.
[openHAB](https://github.com/openhab) is a cross-platform software with the aim to integrate all kinds of Smart Home technologies, devices, etc.
[Z-Wave](https://www.z-wave.com/) is the leading wireless communications protocol behind many of the secure, trusted brands that are working to make everyone's home smarter and safer.
[Zwavejs2Mqtt](https://zwave-js.github.io/zwavejs2mqtt/) is a fully configurable Zwave to MQTT Gateway and Control Panel Web UI.
[Z-Wave JS Server](https://github.com/zwave-js/zwave-js-server) is a small server wrapper around Z-Wave JS to access it via a WebSocket.
[Z-Wave JS Config DB Browser](https://devices.zwave-js.io/) is the official device configuration reference to find out if your device is supported. Currently supports 387 brands, spanning at least 2075 device configurations.
### Homebridge
[Back to the Top](#table-of-contents)

[Homebridge](https://homebridge.io/) is a software frameowrk that allows you to integrate with smart home devices that do not natively support [HomeKit](https://www.apple.com/shop/accessories/all/homekit). There are over 2,000 Homebridge plugins supporting thousands of different smart accessories.
- [Official Homebridge Raspberry Pi Image](https://github.com/homebridge/homebridge-raspbian-image/wiki/Getting-Started)
- [Setup Homebridge on a Raspberry Pi (Raspbian)](https://github.com/homebridge/homebridge/wiki/Install-Homebridge-on-Raspbian)
- [Setup Homebridge on Debian or Ubuntu](https://github.com/homebridge/homebridge/wiki/Install-Homebridge-on-Debian-or-Ubuntu-Linux)
- [Setup Homebridge on Red Hat, CentOS Stream or Fedora](https://github.com/homebridge/homebridge/wiki/Install-Homebridge-on-Red-Hat%2C-CentOS-or-Fedora-Linux)
- [Setup Homebridge on Docker (Linux)](https://github.com/homebridge/homebridge/wiki/Install-Homebridge-on-Docker)
#### Tools to write the Homebridge image to your boot media(microSD card or USB device)
[Raspberry Pi Imager](https://www.raspberrypi.org/software/) is the quick and easy way to install Raspberry Pi OS and other operating systems to a microSD card, ready to use with your Raspberry Pi.

[Etcher](https://www.balena.io/etcher/) is an open source, cross-platform software that makes it easy to flash operating system images to a microSD card or USB device.

[Homebridge UI](https://github.com/oznu/homebridge-config-ui-x) is a tool that provides an easy to use interface to manage your Homebridge plugins, configuration and accessories.
- Install and configure Homebridge plugins.
- Monitor your Homebridge server via a fully customisable widget-based dashboard.
- View and control Homebridge accessories.
- Backup and Restore your Homebridge instance.

Homebridge UI
### ESPHome
[Back to the Top](#table-of-contents)

[ESPHome](https://esphome.io/) is a system to control your ESP8266/ESP32 by simple yet powerful configuration files and control them remotely through Home Automation systems.
#### Quick Links
- [ESP Web Tools](https://esphome.github.io/esp-web-tools/)
- [Installing ESPHome Manually | ESPHome](https://esphome.io/guides/installing_esphome.html)
- [Getting Started with the ESPHome Command Line](https://esphome.io/guides/getting_started_command_line.html)
- [Getting Started with ESPHome and Home Assistant](https://esphome.io/guides/getting_started_hassio.html)
- [ESPHome on the Raspberry Pi Pico! | Jeff Geerling](https://www.jeffgeerling.com/blog/2022/esphome-on-raspberry-pi-pico)
- [How to Start on Raspberry Pi Home Automation | ESPHome](https://www.instructables.com/How-to-Start-on-Raspberry-Pi-Home-Automation-ESPHo/)
- [ESPHome Setup | Integrating Home Assistant with Adafruit IO](https://learn.adafruit.com/integrating-adafruit-io-with-home-assistant/esphome-setup)
### Install ESPHome using Home Assistant
In [Home Assistant](https://www.home-assistant.io/integrations/esphome/) go to:
**Configuration > Add-ons, Backups & Supervisor > Add-on Store (button in the lower right corner) or click on the My Home Assistant Link below:**
Open your Home Assistant instance and show the Supervisor add-on store.
[](https://my.home-assistant.io/redirect/config_flow_start?domain=esphome)
- Next, search for ESPHome, click on the result and then click on the Install button.

- When the installation is finished, the Install button will be replaced with Start button – click on it to start the ESPHome add-on.

- Wait a few seconds for the ESPHome to start and then click on the Open Web UI button.

### Install ESPHome using Docker
- First thing is to pull the [ESPHome Docker image from Docker Hub](https://hub.docker.com/u/esphome) (Online).
```docker pull esphome/esphome```
- Then, start the ESPHome wizard. This wizard will ask you about your device type, your device name, your WiFi credentials and finally will generate a yaml file containing all of the configurations for you.
```docker run --rm -v "${PWD}":/config -it esphome/esphome wizard stl.yaml```
- Now, connect your ESP device to the device where Docker is running (either using an USB cable or Serial-To-USB adapter) and if you are on Linux type the following command :
```dmesg | grep ttyUSB```
- Put your device in programming mode (if needed) and execute the next command to install the ESPHome on the device connected to the /dev/ttyUSB1 using the configuration stored in stl.yaml file
```docker run --rm -v "${PWD}":/config --device=/dev/ttyUSB1 -it esphome/esphome run stl.yaml```
### Install ESPHome using Python
- If you are on macOS or Linux check if Python 3.8 or later is installed by executing the command.
```python3 --version```
- If you are on macOS, you need to install wheel and esphome packages by using the following command.
```pip3 install wheel esphome```
- If you are on Linux, you have to install esphome package by using the following command.
```pip3 install --user esphome```
- If you are on macOS or Linux you can start the ESPHome wizard using the following command.
```esphome wizard stl-python.yaml```
- Finally, connect your ESP device to your Computer (using USB cable or Serial-To-usb adapter) and put it in programming mode (if needed). Then, Install ESPHome using the configuration in the stl-python.yaml file.
```esphome run stl-python.yaml```
### Turning Raspberry Pi into a Router
[Back to the Top](#table-of-contents)
#### Software
[OpenWrt Project](https://openwrt.org/) is a Linux operating system targeting embedded devices. Instead of trying to create a single, static firmware, OpenWrt provides a fully writable filesystem with package management. It's primarily used on embedded devices to route network traffic.
* [OpenWrt Wiki - Raspberry Pi setup](https://openwrt.org/toh/raspberry_pi_foundation/raspberry_pi)
**Download the appropriate OpenWrt image for your Raspberry PI by going to the link above.**
### Tools to write the Operating System (OS) image to your boot media(microSD card)
[Raspberry Pi Imager](https://www.raspberrypi.org/software/) is the quick and easy way to install Raspberry Pi OS and other operating systems to a microSD card, ready to use with your Raspberry Pi.

#### Hardware
[Raspberry Pi Router Board for CM4 module (Cost: $55 USD)](https://www.seeedstudio.com/CM4-Router-Board-p-5211.html) is an expansion board based on the Raspberry Pi Compute Module 4. It brings Raspberry Pi CM4 two full-speed gigabit network ports and offers better performance, lower CPU usage, and higher stability for a long time work compared with a USB network card. It's compatible with [Raspberry Pi OS](https://www.raspberrypi.com/software/operating-systems/), [Ubuntu Server](https://ubuntu.com/download/raspberry-pi) and other Raspberry Pi systems.

Raspberry Pi Router Board for CM4 module
**Technical Specs:**
* Compatible Module: Raspberry Pi Compute Module 4 series.
* BCM2711 4 core @ 1.5GHz Cortex-A72.
* Support standard Raspberry Pi HAT interface.
* Support POE HAT to supply power to the board.
* Support POE HAT for external power supply.
* Full-speed dual gigabit network interface.
* Master-slave dual USB2.0 interface.
* Micro SD card slot, used to support non-eMMC version of CM4.
* Standard HDMI video output interface.
* 0.91 inch IIC OLED display.
* 5V DC fan interface(Support controlling via PWM signal).
* Ethernet: high-performance Gigabit ethernet controller RTL8111E chip, JXD 2111x G2406s chip as isolation transformer.
* Port0: Compute Module 4 Built-In.
* Port1: PCI Express 1000BASE-T NIC.
* GPIO: 40-Pin GPIO compatible with Raspberry Pi.
### Setting Watchdog Timer (WDT) on Raspberry Pi
[Back to the Top](#table-of-contents)
[Watchdog Timer (WDT)](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Watchdog_timer) is a timer that monitors microcontroller (MCU) programs to see if they are out of control or have stopped operating.
### Installing and enabling WDT service
To enable watchdog you have to change the boot parameters by adding **dtparam=watchdog=on** in **/boot/config.txt** using a text editor such as nano, vim, gedit, etc.. Also, install watchdog package and enable it to start at startup. Also, make sure to restart your Raspberry Pi for these settings to take effect.
```pi@raspberrypi:~ $ sudo apt install watchdog```
```pi@raspberrypi:~ $sudo systemctl enable watchdog```
### Configure WDT service
Configuration file for watchdog can be found in **/etc/watchdog.conf**.
```
max-load-1 = 24
watchdog-device = /dev/watchdog
realtime = yes
priority = 1
```
**To start the WTD service:**
```pi@raspberrypi:~ $ sudo systemctl start watchdog```
**Check watchdog status:**
```pi@raspberrypi:~ $ sudo systemctl status watchdog```
**To stop the service:**
```pi@raspberrypi:~ $ sudo systemctl stop watchdog```
## Raspberry Pi Upgrades
[Back to the Top](https://github.com/mikeroyal/Self-Hosting-Guide#table-of-contents)
[Raspberry Pi Cases from Pi-Shop US](https://www.pishop.us/product-category/raspberry-pi/pi-cases/)

[Raspberry Pi Cases from The Pi Hut](https://thepihut.com/collections/raspberry-pi-cases)
[X825 expansion board](https://www.amazon.com/Geekworm-Raspberry-Storage-Expansion-Compatible/dp/B07VXF2HJG) provides a complete storage solution for newest Raspberry Pi 4 Model B, it supports up to 4TB 2.5-inch SATA hard disk drives (HDD) / solid-state drive (SSD).
[Sabrent M.2 SSD [NGFF] to USB 3.0 / SATA III 2.5-Inch Aluminum Enclosure Adapter](https://www.amazon.com/Sabrent-2-5-Inch-Aluminum-Enclosure-EC-M2CU/dp/B07924J5NT/ref=sr_1_10?crid=28O2JRHO9DE4G&dchild=1&keywords=m.2+to+usb+3.0+adapter&qid=1616632834&sprefix=m.2+to+usb,aps,236&sr=8-10)

[Samsung 970 EVO 250GB - NVMe PCIe M.2 2280 SSD](https://www.amazon.com/dp/B07BN5FJZQ/ref=twister_B08KGF1DPF?_encoding=UTF8&psc=1)

[Western Digital 1TB WD Blue SN550 NVMe Internal SSD](https://www.amazon.com/dp/B07YFF8879/ref=twister_B082KVPKQ5?_encoding=UTF8&psc=1)

[SAMSUNG T5 Portable SSD](https://www.amazon.com/Samsung-500GB-Portable-Solid-State/dp/B074WZJ4MF/ref=sr_1_4?crid=343DRDX8SJJV6&dchild=1&keywords=samsung+t5+portable+ssd&qid=1616632092&sprefix=samsung+t5+portable,aps,374&sr=8-4)

[Samsung SSD 860 EVO 250GB mSATA Internal SSD](https://www.amazon.com/Samsung-250GB-mSATA-Internal-MZ-M6E250BW/dp/B07864YNTZ/ref=sr_1_8?crid=2KRBSPRQYUIOH&dchild=1&keywords=samsung+850+evo+msata&qid=1616632277&sprefix=samsung+850+evo+m,aps,233&sr=8-8)

[Samsung 850 EVO 120GB SSD mSATA](https://www.amazon.com/Samsung-850-120GB-mSATA-MZ-M5E120BW/dp/B00TGIVQ4G/ref=sr_1_9?crid=2KRBSPRQYUIOH&dchild=1&keywords=samsung+850+evo+msata&qid=1616632277&sprefix=samsung+850+evo+m,aps,233&sr=8-9)

# Grafana
[Back to the Top](https://github.com/mikeroyal/Self-Hosting-Guide#table-of-contents)

## Grafana Learning Resources
[Grafana](https://grafana.com/) is an analytics platform that enables you to query and visualize data, then create and share dashboards based on your visualizations. Easily visualize metrics, logs, and traces from multiple sources such as Prometheus, Loki, Elasticsearch, InfluxDB, Postgres, Fluentd, Fluentbit, Logstash and many more.
[Getting Started with Grafana](https://grafana.com/docs/)
[Grafana Community](https://community.grafana.com/)
[Grafana Professional Services Training | Grafana Labs](https://grafana.com/training/)
[Grafana Pro Training AWS | Grafana Labs](https://grafana.com/training/aws/)
[Grafana Tutorials](https://grafana.com/tutorials/)
[Top Grafana Courses on Udemy](https://www.udemy.com/topic/grafana/)
[Grafana Online Training Courses | LinkedIn Learning](https://www.linkedin.com/learning/topics/grafana)
[Grafana Training Courses - NobleProg](https://www.nobleprog.com/grafana-training)
[Setting Up Grafana to Visualize Our Metrics Course on Coursera](https://www.coursera.org/lecture/continuous-integration/setting-up-grafana-to-visualize-our-metrics-part-4-of-10-OOMzF)
## Grafana Tools
[Grafana Cloud ](https://grafana.com/products/cloud/) is a composable observability platform, integrating metrics, traces and logs with Grafana. Leverage the best open source observability software – including Prometheus, Loki, and Tempo – without the overhead of installing, maintaining, and scaling your observability stack.
**Grafana Cloud Integrations. Source: [Grafana](https://grafana.com/products/cloud/)**
[Grafana Enterprise](https://grafana.com/products/enterprise/) is a service that includes features that provide better scalability, collaboration, operations, and governance in a self-managed environment.
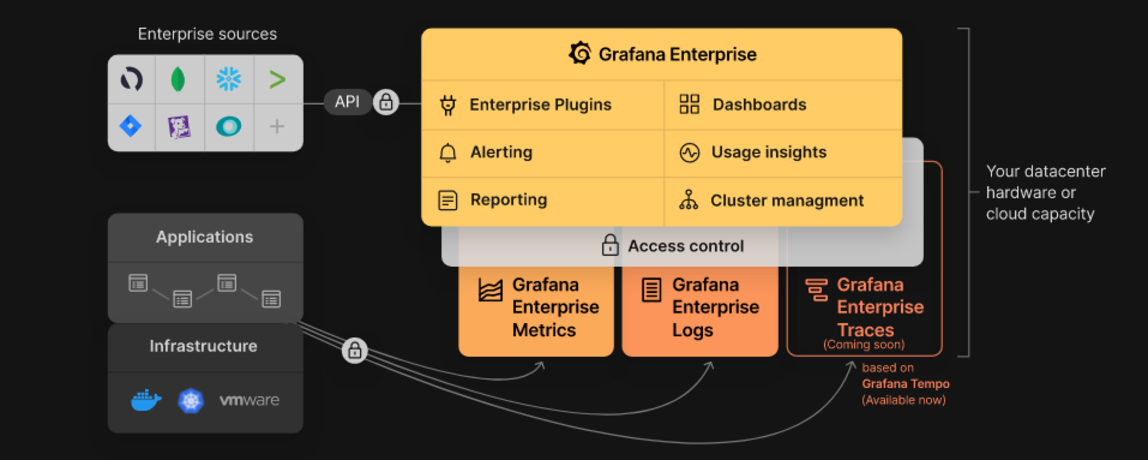
**Grafana Enterprise Stack. Source: [Grafana](https://grafana.com/products/enterprise/)**
[Grafana Tempo](https://grafana.com/oss/tempo/) is an open source high-scale distributed tarcing backend. Tempo is cost-efficient, requiring only object storage to operate, and is deeply integrated with Grafana, Loki, and Prometheus.
[Grafana MetricTank](https://grafana.com/oss/metrictank/) is a multi-tenant timeseries platform for Graphite developed by Grafana Labs. MetricTank provides high-availability(HA) and efficient long-term storage, retrieval, and processing for large-scale environments.
[Grafana Tanka](https://grafana.com/oss/tanka/) is a robust configuration utility for your [Kubernetes](https://kubernetes.io/) cluster, powered by the [Jsonnet](https://jsonnet.org/) language.
[Grafana Loki](https://grafana.com/oss/loki/) is a horizontally-scalable, highly-available(HA), multi-tenant log aggregation system inspired by Prometheus.
[Cortex](https://grafana.com/oss/cortex/) is a project that lets users query metrics from many Prometheusservers in a single place, without any gaps in the grpahs due to server failture. Also, Cortex lets you store Prometheus metrics for long term capacity planning and performance analysis.
[Graphite](https://grafana.com/oss/graphite/) is an open source monitoring system.
# Networking
[Back to the Top](https://github.com/mikeroyal/Self-Hosting-Guide#table-of-contents)

## Networking Tools & Concepts
[cURL](https://curl.se/) is a computer software project providing a library and command-line tool for transferring data using various network protocols(HTTP, HTTPS, FTP, FTPS, SCP, SFTP, TFTP, DICT, TELNET, LDAP LDAPS, MQTT, POP3, POP3S, RTMP, RTMPS, RTSP, SCP, SFTP, SMB, SMBS, SMTP or SMTPS). cURL is also used in cars, television sets, routers, printers, audio equipment, mobile phones, tablets, settop boxes, media players and is the Internet transfer engine for thousands of software applications in over ten billion installations.
[cURL Fuzzer](https://github.com/curl/curl-fuzzer) is a quality assurance testing for the curl project.
[DoH](https://github.com/curl/doh) is a stand-alone application for DoH (DNS-over-HTTPS) name resolves and lookups.
[Authelia](https://www.authelia.com/) is an open-source highly-available authentication server providing single sign-on capability and two-factor authentication to applications running behind [NGINX](https://nginx.org/en/).
[nginx(engine x)](https://nginx.org/en/) is an HTTP and reverse proxy server, a mail proxy server, and a generic TCP/UDP proxy server, originally written by Igor Sysoev.
[Proxmox Virtual Environment(VE)](https://www.proxmox.com/en/) is a complete open-source platform for enterprise virtualization. It inlcudes a built-in web interface that you can easily manage VMs and containers, software-defined storage and networking, high-availability clustering, and multiple out-of-the-box tools on a single solution.
[Wireshark](https://www.wireshark.org/) is a very popular network protocol analyzer that is commonly used for network troubleshooting, analysis, and communications protocol development. Learn more about the other useful [Wireshark Tools](https://wiki.wireshark.org/Tools) available.
[HTTPie](https://github.com/httpie/httpie) is a command-line HTTP client. Its goal is to make CLI interaction with web services as human-friendly as possible. HTTPie is designed for testing, debugging, and generally interacting with APIs & HTTP servers.
[HTTPStat](https://github.com/reorx/httpstat) is a tool that visualizes curl statistics in a simple layout.
[Wuzz](https://github.com/asciimoo/wuzz) is an interactive cli tool for HTTP inspection. It can be used to inspect/modify requests copied from the browser's network inspector with the "copy as cURL" feature.
[Websocat](https://github.com/vi/websocat) is a ommand-line client for WebSockets, like netcat (or curl) for ws:// with advanced socat-like functions.
• Connection: In networking, a connection refers to pieces of related information that are transferred through a network. This generally infers that a connection is built before the data transfer (by following the procedures laid out in a protocol) and then is deconstructed at the at the end of the data transfer.
• Packet: A packet is, generally speaking, the most basic unit that is transferred over a network. When communicating over a network, packets are the envelopes that carry your data (in pieces) from one end point to the other.
Packets have a header portion that contains information about the packet including the source and destination, timestamps, network hops. The main portion of a packet contains the actual data being transferred. It is sometimes called the body or the payload.
• Network Interface: A network interface can refer to any kind of software interface to networking hardware. For instance, if you have two network cards in your computer, you can control and configure each network interface associated with them individually.
A network interface may be associated with a physical device, or it may be a representation of a virtual interface. The "loop-back" device, which is a virtual interface to the local machine, is an example of this.
• LAN: LAN stands for "local area network". It refers to a network or a portion of a network that is not publicly accessible to the greater internet. A home or office network is an example of a LAN.
• WAN: WAN stands for "wide area network". It means a network that is much more extensive than a LAN. While WAN is the relevant term to use to describe large, dispersed networks in general, it is usually meant to mean the internet, as a whole.
If an interface is connected to the WAN, it is generally assumed that it is reachable through the internet.
• Protocol: A protocol is a set of rules and standards that basically define a language that devices can use to communicate. There are a great number of protocols in use extensively in networking, and they are often implemented in different layers.
Some low level protocols are TCP, UDP, IP, and ICMP. Some familiar examples of application layer protocols, built on these lower protocols, are HTTP (for accessing web content), SSH, TLS/SSL, and FTP.
• Port: A port is an address on a single machine that can be tied to a specific piece of software. It is not a physical interface or location, but it allows your server to be able to communicate using more than one application.
• Firewall: A firewall is a program that decides whether traffic coming into a server or going out should be allowed. A firewall usually works by creating rules for which type of traffic is acceptable on which ports. Generally, firewalls block ports that are not used by a specific application on a server.
• NAT: Network address translation is a way to translate requests that are incoming into a routing server to the relevant devices or servers that it knows about in the LAN. This is usually implemented in physical LANs as a way to route requests through one IP address to the necessary backend servers.
• VPN: Virtual private network is a means of connecting separate LANs through the internet, while maintaining privacy. This is used as a means of connecting remote systems as if they were on a local network, often for security reasons.
## Network Layers
While networking is often discussed in terms of topology in a horizontal way, between hosts, its implementation is layered in a vertical fashion throughout a computer or network. This means is that there are multiple technologies and protocols that are built on top of each other in order for communication to function more easily. Each successive, higher layer abstracts the raw data a little bit more, and makes it simpler to use for applications and users. It also allows you to leverage lower layers in new ways without having to invest the time and energy to develop the protocols and applications that handle those types of traffic.
As data is sent out of one machine, it begins at the top of the stack and filters downwards. At the lowest level, actual transmission to another machine takes place. At this point, the data travels back up through the layers of the other computer. Each layer has the ability to add its own "wrapper" around the data that it receives from the adjacent layer, which will help the layers that come after decide what to do with the data when it is passed off.
One method of talking about the different layers of network communication is the OSI model. OSI stands for Open Systems Interconnect.This model defines seven separate layers. The layers in this model are:
• Application: The application layer is the layer that the users and user-applications most often interact with. Network communication is discussed in terms of availability of resources, partners to communicate with, and data synchronization.
• Presentation: The presentation layer is responsible for mapping resources and creating context. It is used to translate lower level networking data into data that applications expect to see.
• Session: The session layer is a connection handler. It creates, maintains, and destroys connections between nodes in a persistent way.
• Transport: The transport layer is responsible for handing the layers above it a reliable connection. In this context, reliable refers to the ability to verify that a piece of data was received intact at the other end of the connection. This layer can resend information that has been dropped or corrupted and can acknowledge the receipt of data to remote computers.
• Network: The network layer is used to route data between different nodes on the network. It uses addresses to be able to tell which computer to send information to. This layer can also break apart larger messages into smaller chunks to be reassembled on the opposite end.
• Data Link: This layer is implemented as a method of establishing and maintaining reliable links between different nodes or devices on a network using existing physical connections.
• Physical: The physical layer is responsible for handling the actual physical devices that are used to make a connection. This layer involves the bare software that manages physical connections as well as the hardware itself (like Ethernet).
The TCP/IP model, more commonly known as the Internet protocol suite, is another layering model that is simpler and has been widely adopted.It defines the four separate layers, some of which overlap with the OSI model:
• Application: In this model, the application layer is responsible for creating and transmitting user data between applications. The applications can be on remote systems, and should appear to operate as if locally to the end user.
The communication takes place between peers network.
• Transport: The transport layer is responsible for communication between processes. This level of networking utilizes ports to address different services. It can build up unreliable or reliable connections depending on the type of protocol used.
• Internet: The internet layer is used to transport data from node to node in a network. This layer is aware of the endpoints of the connections, but does not worry about the actual connection needed to get from one place to another. IP addresses are defined in this layer as a way of reaching remote systems in an addressable manner.
• Link: The link layer implements the actual topology of the local network that allows the internet layer to present an addressable interface. It establishes connections between neighboring nodes to send data.
### Interfaces
**Interfaces** are networking communication points for your computer. Each interface is associated with a physical or virtual networking device. Typically, your server will have one configurable network interface for each Ethernet or wireless internet card you have. In addition, it will define a virtual network interface called the "loopback" or localhost interface. This is used as an interface to connect applications and processes on a single computer to other applications and processes. You can see this referenced as the "lo" interface in many tools.
## Network Protocols
Networking works by piggybacks on a number of different protocols on top of each other. In this way, one piece of data can be transmitted using multiple protocols encapsulated within one another.
**Media Access Control(MAC)** is a communications protocol that is used to distinguish specific devices. Each device is supposed to get a unique MAC address during the manufacturing process that differentiates it from every other device on the internet. Addressing hardware by the MAC address allows you to reference a device by a unique value even when the software on top may change the name for that specific device during operation. Media access control is one of the only protocols from the link layer that you are likely to interact with on a regular basis.
**The IP protocol** is one of the fundamental protocols that allow the internet to work. IP addresses are unique on each network and they allow machines to address each other across a network. It is implemented on the internet layer in the IP/TCP model. Networks can be linked together, but traffic must be routed when crossing network boundaries. This protocol assumes an unreliable network and multiple paths to the same destination that it can dynamically change between. There are a number of different implementations of the protocol. The most common implementation today is IPv4, although IPv6 is growing in popularity as an alternative due to the scarcity of IPv4 addresses available and improvements in the protocols capabilities.
**ICMP: internet control message protocol** is used to send messages between devices to indicate the availability or error conditions. These packets are used in a variety of network diagnostic tools, such as ping and traceroute. Usually ICMP packets are transmitted when a packet of a different kind meets some kind of a problem. Basically, they are used as a feedback mechanism for network communications.
**TCP: Transmission control protocol** is implemented in the transport layer of the IP/TCP model and is used to establish reliable connections. TCP is one of the protocols that encapsulates data into packets. It then transfers these to the remote end of the connection using the methods available on the lower layers. On the other end, it can check for errors, request certain pieces to be resent, and reassemble the information into one logical piece to send to the application layer. The protocol builds up a connection prior to data transfer using a system called a three-way handshake. This is a way for the two ends of the communication to acknowledge the request and agree upon a method of ensuring data reliability. After the data has been sent, the connection is torn down using a similar four-way handshake. TCP is the protocol of choice for many of the most popular uses for the internet, including WWW, FTP, SSH, and email. It is safe to say that the internet we know today would not be here without TCP.
**UDP: User datagram protocol** is a popular companion protocol to TCP and is also implemented in the transport layer. The fundamental difference between UDP and TCP is that UDP offers unreliable data transfer. It does not verify that data has been received on the other end of the connection. This might sound like a bad thing, and for many purposes, it is. However, it is also extremely important for some functions. It’s not required to wait for confirmation that the data was received and forced to resend data, UDP is much faster than TCP. It does not establish a connection with the remote host, it simply fires off the data to that host and doesn't care if it is accepted or not. Since UDP is a simple transaction, it is useful for simple communications like querying for network resources. It also doesn't maintain a state, which makes it great for transmitting data from one machine to many real-time clients. This makes it ideal for VOIP, games, and other applications that cannot afford delays.
**HTTP: Hypertext transfer protocol** is a protocol defined in the application layer that forms the basis for communication on the web. HTTP defines a number of functions that tell the remote system what you are requesting. For instance, GET, POST, and DELETE all interact with the requested data in a different way.
**FTP: File transfer protocol** is in the application layer and provides a way of transferring complete files from one host to another. It is inherently insecure, so it is not recommended for any externally facing network unless it is implemented as a public, download-only resource.
**DNS: Domain name system** is an application layer protocol used to provide a human-friendly naming mechanism for internet resources. It is what ties a domain name to an IP address and allows you to access sites by name in your browser.
**SSH: Secure shell** is an encrypted protocol implemented in the application layer that can be used to communicate with a remote server in a secure way. Many additional technologies are built around this protocol because of its end-to-end encryption and ubiquity. There are many other protocols that we haven't covered that are equally important. However, this should give you a good overview of some of the fundamental technologies that make the internet and networking possible.
[REST(REpresentational State Transfer)](https://www.codecademy.com/articles/what-is-rest) is an architectural style for providing standards between computer systems on the web, making it easier for systems to communicate with each other.
[JSON Web Token (JWT)](https://jwt.io) is a compact URL-safe means of representing claims to be transferred between two parties. The claims in a JWT are encoded as a JSON object that is digitally signed using JSON Web Signature (JWS).
[OAuth 2.0](https://oauth.net/2/) is an open source authorization framework that enables applications to obtain limited access to user accounts on an HTTP service, such as Amazon, Google, Facebook, Microsoft, Twitter GitHub, and DigitalOcean. It works by delegating user authentication to the service that hosts the user account, and authorizing third-party applications to access the user account.
# Docker
[Back to the Top](https://github.com/mikeroyal/Self-Hosting-Guide#table-of-contents)


**Container Architecture. Source: [Containerd.io](https://containerd.io)**
## Docker Learning Resources
[Docker Training Program](https://www.docker.com/dockercon/training)
[Docker Certified Associate (DCA) certification](https://training.mirantis.com/dca-certification-exam/)
[Docker Documentation | Docker Documentation](https://docs.docker.com/)
[The Docker Workshop](https://courses.packtpub.com/courses/docker)
[Docker Courses on Udemy](https://www.udemy.com/topic/docker/)
[Docker Courses on Coursera](https://www.coursera.org/courses?query=docker)
[Docker Courses on edX](https://www.edx.org/learn/docker)
[Docker Courses on Linkedin Learning](https://www.linkedin.com/learning/topics/docker)
## Docker Tools
[Docker](https://www.docker.com/) is an open platform for developing, shipping, and running applications. Docker enables you to separate your applications from your infrastructure so you can deliver software quickly working in collaboration with cloud, Linux, and Windows vendors, including Microsoft.
[Docker Enterprise](https://www.mirantis.com/software/docker/docker-enterprise/) is a subscription including software, supported and certified container platform for CentOS, Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL), Ubuntu, SUSE Linux Enterprise Server (SLES), Oracle Linux, and Windows Server 2016, as well as for cloud providers AWS and Azure. In [November 2019 Docker's Enterprise Platform business was acquired by Mirantis](https://www.mirantis.com/company/press-center/company-news/mirantis-acquires-docker-enterprise/).
[Docker Desktop](https://www.docker.com/products/docker-desktop) is an application for MacOS and Windows machines for the building and sharing of containerized applications and microservices. Docker Desktop delivers the speed, choice and security you need for designing and delivering containerized applications on your desktop. Docker Desktop includes Docker App, developer tools, Kubernetes and version synchronization to production Docker Engines.
[Docker Hub](https://hub.docker.com/) is the world's largest library and community for container images Browse over 100,000 container images from software vendors, open-source projects, and the community.
[Docker Compose](https://docs.docker.com/compose/) is a tool that was developed to help define and share multi-container applications. With Docker Compose, you can create a YAML file to define the services and with a single command, can spin everything up or tear it all down.
[Docker Swarm](https://docs.docker.com/engine/swarm/) is a Docker-native clustering system swarm is a simple tool which controls a cluster of Docker hosts and exposes it as a single "virtual" host.
[Dockerfile](https://docs.docker.com/engine/reference/builder/) is a text document that contains all the commands a user could call on the command line to assemble an image. Using docker build users can create an automated build that executes several command-line instructions in succession.
[Docker Containers](https://www.docker.com/resources/what-container) is a standard unit of software that packages up code and all its dependencies so the application runs quickly and reliably from one computing environment to another.
[Docker Engine](https://www.docker.com/products/container-runtime) is a container runtime that runs on various Linux (CentOS, Debian, Fedora, Oracle Linux, RHEL, SUSE, and Ubuntu) and Windows Server operating systems. Docker creates simple tooling and a universal packaging approach that bundles up all application dependencies inside a container which is then run on Docker Engine.
[Docker Images](https://docs.docker.com/engine/reference/commandline/images/) is a lightweight, standalone, executable package of software that includes everything needed to run an application: code, runtime, system tools, system libraries and settings. Images have intermediate layers that increase reusability, decrease disk usage, and speed up docker build by allowing each step to be cached. These intermediate layers are not shown by default. The SIZE is the cumulative space taken up by the image and all its parent images.
[Docker Network](https://docs.docker.com/engine/reference/commandline/network/) is a that displays detailed information on one or more networks.
[Docker Daemon](https://docs.docker.com/config/daemon/) is a service started by a system utility, not manually by a user. This makes it easier to automatically start Docker when the machine reboots. The command to start Docker depends on your operating system. Currently, it only runs on Linux because it depends on a number of Linux kernel features, but there are a few ways to run Docker on MacOS and Windows as well by configuring the operating system utilities.
[Docker Storage](https://docs.docker.com/storage/storagedriver/select-storage-driver/) is a driver controls how images and containers are stored and managed on your Docker host.
[Kitematic](https://kitematic.com/) is a simple application for managing Docker containers on Mac, Linux and Windows letting you control your app containers from a graphical user interface (GUI).
[Open Container Initiative](https://opencontainers.org/about/overview/) is an open governance structure for the express purpose of creating open industry standards around container formats and runtimes.
[Buildah](https://buildah.io/) is a command line tool to build Open Container Initiative (OCI) images. It can be used with Docker, Podman, Kubernetes.
[Podman](https://podman.io/) is a daemonless, open source, Linux native tool designed to make it easy to find, run, build, share and deploy applications using Open Containers Initiative (OCI) Containers and Container Images. Podman provides a command line interface (CLI) familiar to anyone who has used the Docker Container Engine.
[Containerd](https://containerd.io) is a daemon that manages the complete container lifecycle of its host system, from image transfer and storage to container execution and supervision to low-level storage to network attachments and beyond. It is available for Linux and Windows.
# Kubernetes
[Back to the Top](https://github.com/mikeroyal/Self-Hosting-Guide#table-of-contents)

## Kubernetes Learning Resources
[Kubernetes (K8s)](https://kubernetes.io/) is an open-source system for automating deployment, scaling, and management of containerized applications.
[Getting Kubernetes Certifications](https://training.linuxfoundation.org/certification/catalog/?_sft_technology=kubernetes)
[Getting started with Kubernetes on AWS](https://aws.amazon.com/kubernetes/)
[Kubernetes on Microsoft Azure](https://azure.microsoft.com/en-us/topic/what-is-kubernetes/)
[Intro to Azure Kubernetes Service](https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/aks/kubernetes-dashboard)
[Azure Red Hat OpenShift ](https://azure.microsoft.com/en-us/services/openshift/)
[Getting started with Google Cloud](https://cloud.google.com/learn/what-is-kubernetes)
[Getting started with Kubernetes on Red Hat](https://www.redhat.com/en/topics/containers/what-is-kubernetes)
[Getting started with Kubernetes on IBM](https://www.ibm.com/cloud/learn/kubernetes)
[Red Hat OpenShift on IBM Cloud](https://www.ibm.com/cloud/openshift)
[Enable OpenShift Virtualization on Red Hat OpenShift](https://developers.redhat.com/blog/2020/08/28/enable-openshift-virtualization-on-red-hat-openshift/)
[YAML basics in Kubernetes](https://developer.ibm.com/technologies/containers/tutorials/yaml-basics-and-usage-in-kubernetes/)
[Elastic Cloud on Kubernetes](https://www.elastic.co/elastic-cloud-kubernetes)
[Docker and Kubernetes](https://www.docker.com/products/kubernetes)
[Running Apache Spark on Kubernetes](http://spark.apache.org/docs/latest/running-on-kubernetes.html)
[Kubernetes Across VMware vRealize Automation](https://blogs.vmware.com/management/2019/06/kubernetes-across-vmware-cloud-automation-services.html)
[VMware Tanzu Kubernetes Grid](https://tanzu.vmware.com/kubernetes-grid)
[All the Ways VMware Tanzu Works with AWS](https://tanzu.vmware.com/content/blog/all-the-ways-vmware-tanzutm-works-with-aws)
[VMware Tanzu Education](https://tanzu.vmware.com/education)
[Using Ansible in a Cloud-Native Kubernetes Environment](https://www.ansible.com/blog/how-useful-is-ansible-in-a-cloud-native-kubernetes-environment)
[Managing Kubernetes (K8s) objects with Ansible](https://docs.ansible.com/ansible/latest/collections/community/kubernetes/k8s_module.html)
[Setting up a Kubernetes cluster using Vagrant and Ansible](https://kubernetes.io/blog/2019/03/15/kubernetes-setup-using-ansible-and-vagrant/)
[Running MongoDB with Kubernetes](https://www.mongodb.com/kubernetes)
[Kubernetes Fluentd](https://docs.fluentd.org/v/0.12/articles/kubernetes-fluentd)
[Understanding the new GitLab Kubernetes Agent](https://about.gitlab.com/blog/2020/09/22/introducing-the-gitlab-kubernetes-agent/)
[Intro Local Process with Kubernetes for Visual Studio 2019](https://devblogs.microsoft.com/visualstudio/introducing-local-process-with-kubernetes-for-visual-studio%E2%80%AF2019/)
[Kubernetes Contributors](https://www.kubernetes.dev/)
[KubeAcademy from VMware](https://kube.academy/)
[Kubernetes Tutorials from Pulumi](https://www.pulumi.com/docs/tutorials/kubernetes/)
[Kubernetes Playground by Katacoda](https://www.katacoda.com/courses/kubernetes/playground)
[Scalable Microservices with Kubernetes course from Udacity ](https://www.udacity.com/course/scalable-microservices-with-kubernetes--ud615)
## Kubernetes Tools, Frameworks, and Projects
[Open Container Initiative](https://opencontainers.org/about/overview/) is an open governance structure for the express purpose of creating open industry standards around container formats and runtimes.
[Buildah](https://buildah.io/) is a command line tool to build Open Container Initiative (OCI) images. It can be used with Docker, Podman, Kubernetes.
[Podman](https://podman.io/) is a daemonless, open source, Linux native tool designed to make it easy to find, run, build, share and deploy applications using Open Containers Initiative (OCI) Containers and Container Images. Podman provides a command line interface (CLI) familiar to anyone who has used the Docker Container Engine.
[Containerd](https://containerd.io) is a daemon that manages the complete container lifecycle of its host system, from image transfer and storage to container execution and supervision to low-level storage to network attachments and beyond. It is available for Linux and Windows.
[Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE)](https://cloud.google.com/kubernetes-engine/) is a managed, production-ready environment for running containerized applications.
[Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS)](https://azure.microsoft.com/en-us/services/kubernetes-service/) is serverless Kubernetes, with a integrated continuous integration and continuous delivery (CI/CD) experience, and enterprise-grade security and governance. Unite your development and operations teams on a single platform to rapidly build, deliver, and scale applications with confidence.
[Amazon EKS](https://docs.aws.amazon.com/eks/latest/userguide/what-is-eks.html) is a tool that runs Kubernetes control plane instances across multiple Availability Zones to ensure high availability.
[AWS Controllers for Kubernetes (ACK)](https://aws.amazon.com/blogs/containers/aws-controllers-for-kubernetes-ack/) is a new tool that lets you directly manage AWS services from Kubernetes. ACK makes it simple to build scalable and highly-available Kubernetes applications that utilize AWS services.
[Container Engine for Kubernetes (OKE)](https://www.oracle.com/cloud-native/container-engine-kubernetes/) is an Oracle-managed container orchestration service that can reduce the time and cost to build modern cloud native applications. Unlike most other vendors, Oracle Cloud Infrastructure provides Container Engine for Kubernetes as a free service that runs on higher-performance, lower-cost compute.
[Anthos](https://cloud.google.com/anthos/docs/concepts/overview) is a modern application management platform that provides a consistent development and operations experience for cloud and on-premises environments.
[Red Hat Openshift](https://www.openshift.com/) is a fully managed Kubernetes platform that provides a foundation for on-premises, hybrid, and multicloud deployments.
[OKD](https://okd.io/) is a community distribution of Kubernetes optimized for continuous application development and multi-tenant deployment. OKD adds developer and operations-centric tools on top of Kubernetes to enable rapid application development, easy deployment and scaling, and long-term lifecycle maintenance for small and large teams.
[Odo](https://odo.dev/) is a fast, iterative, and straightforward CLI tool for developers who write, build, and deploy applications on Kubernetes and OpenShift.
[Kata Operator](https://github.com/openshift/kata-operator) is an operator to perform lifecycle management (install/upgrade/uninstall) of [Kata Runtime](https://katacontainers.io/) on Openshift as well as Kubernetes cluster.
[Thanos](https://thanos.io/) is a set of components that can be composed into a highly available metric system with unlimited storage capacity, which can be added seamlessly on top of existing Prometheus deployments.
[OpenShift Hive](https://github.com/openshift/hive) is an operator which runs as a service on top of Kubernetes/OpenShift. The Hive service can be used to provision and perform initial configuration of OpenShift 4 clusters.
[Rook](https://rook.io/) is a tool that turns distributed storage systems into self-managing, self-scaling, self-healing storage services. It automates the tasks of a storage administrator: deployment, bootstrapping, configuration, provisioning, scaling, upgrading, migration, disaster recovery, monitoring, and resource management.
[VMware Tanzu](https://tanzu.vmware.com/tanzu) is a centralized management platform for consistently operating and securing your Kubernetes infrastructure and modern applications across multiple teams and private/public clouds.
[Kubespray](https://kubespray.io/) is a tool that combines Kubernetes and Ansible to easily install Kubernetes clusters that can be deployed on [AWS](https://github.com/kubernetes-sigs/kubespray/blob/master/docs/aws.md), GCE, [Azure](https://github.com/kubernetes-sigs/kubespray/blob/master/docs/azure.md), [OpenStack](https://github.com/kubernetes-sigs/kubespray/blob/master/docs/openstack.md), [vSphere](https://github.com/kubernetes-sigs/kubespray/blob/master/docs/vsphere.md), [Packet](https://github.com/kubernetes-sigs/kubespray/blob/master/docs/packet.md) (bare metal), Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (Experimental), or Baremetal.
[KubeInit](https://github.com/kubeinit/kubeinit) provides Ansible playbooks and roles for the deployment and configuration of multiple Kubernetes distributions.
[Rancher](https://rancher.com/) is a complete software stack for teams adopting containers. It addresses the operational and security challenges of managing multiple Kubernetes clusters, while providing DevOps teams with integrated tools for running containerized workloads.
[K3s](https://github.com/rancher/k3s) is a highly available, certified Kubernetes distribution designed for production workloads in unattended, resource-constrained, remote locations or inside IoT appliances.
[Helm](https://helm.sh/) is a Kubernetes Package Manager tool that makes it easier to install and manage Kubernetes applications.
[Knative](https://knative.dev/) is a Kubernetes-based platform to build, deploy, and manage modern serverless workloads. Knative takes care of the operational overhead details of networking, autoscaling (even to zero), and revision tracking.
[KubeFlow](https://www.kubeflow.org/) is a tool dedicated to making deployments of machine learning (ML) workflows on Kubernetes simple, portable and scalable.
[Etcd](https://etcd.io/) is a distributed key-value store that provides a reliable way to store data that needs to be accessed by a distributed system or cluster of machines. Etcd is used as the backend for service discovery and stores cluster state and configuration for Kubernetes.
[OpenEBS](https://openebs.io/) is a Kubernetes-based tool to create stateful applications using Container Attached Storage.
[Container Storage Interface (CSI)](https://www.architecting.it/blog/container-storage-interface/) is an API that lets container orchestration platforms like Kubernetes seamlessly communicate with stored data via a plug-in.
[MicroK8s](https://microk8s.io/) is a tool that delivers the full Kubernetes experience. In a Fully containerized deployment with compressed over-the-air updates for ultra-reliable operations. It is supported on Linux, Windows, and MacOS.
[Charmed Kubernetes](https://ubuntu.com/kubernetes/features) is a well integrated, turn-key, conformant Kubernetes platform, optimized for your multi-cloud environments developed by Canonical.
[Grafana Kubernetes App](https://grafana.com/grafana/plugins/grafana-kubernetes-app) is a toll that allows you to monitor your Kubernetes cluster's performance. It includes 4 dashboards, Cluster, Node, Pod/Container and Deployment. It allows for the automatic deployment of the required Prometheus exporters and a default scrape config to use with your in cluster Prometheus deployment.
[KubeEdge](https://kubeedge.io/en/) is an open source system for extending native containerized application orchestration capabilities to hosts at Edge.It is built upon kubernetes and provides fundamental infrastructure support for network, app. deployment and metadata synchronization between cloud and edge.
[Lens](https://k8slens.dev/) is the most powerful IDE for people who need to deal with Kubernetes clusters on a daily basis. It has support for MacOS, Windows and Linux operating systems.
[Flux CD](https://fluxcd.io/) is a tool that automatically ensures that the state of your Kubernetes cluster matches the configuration you've supplied in Git. It uses an operator in the cluster to trigger deployments inside Kubernetes, which means that you don't need a separate continuous delivery tool.
[Platform9 Managed Kubernetes (PMK)](https://platform9.com/managed-kubernetes/) is a Kubernetes as a service that ensures fully automated Day-2 operations with 99.9% SLA on any environment, whether in data-centers, public clouds, or at the edge.
# Ansible
[Back to the Top](https://github.com/mikeroyal/Self-Hosting-Guide#table-of-contents)

**[Mac Development Ansible Playbook by Jeff Geerling](https://github.com/geerlingguy/mac-dev-playbook)**
## Ansible Learning Resources
[Ansible](https://www.ansible.com/) is a simple IT automation engine that automates cloud provisioning, configuration management, application deployment, intra-service orchestration, and many other IT needs. It uses a very simple language (YAML, in the form of Ansible Playbooks) that allows you to describe your automation jobs in a way that approaches plain English. Anisble works on Linux (Red Hat EnterPrise Linux(RHEL) and Ubuntu) and Microsoft Windows.
[Red Hat Training for Ansible](https://www.ansible.com/products/training-certification)
[Top Ansible Courses Online from Udemy](https://www.udemy.com/topic/ansible/)
[Introduction to Ansible: The Fundamentals on Coursera](https://www.coursera.org/projects/ansible-fundamentals)
[Learning Ansible Fundamentals on Pluralsight](https://www.pluralsight.com/courses/ansible-fundamentals)
[Introducing Red Hat Ansible Automation Platform 2.1](https://www.ansible.com/blog/introducing-red-hat-ansible-automation-platform-2.1)
[Ansible Documentation](https://docs.ansible.com/ansible/latest/index.html)
[Ansible Galaxy User Guide](https://docs.ansible.com/ansible/latest/galaxy/user_guide.html)
[Ansible Use Cases](https://www.ansible.com/use-cases?hsLang=en-us)
[Ansible Integrations](https://www.ansible.com/integrations?hsLang=en-us)
[Ansible Collections Overview](https://github.com/ansible-collections/overview/blob/main/README.rst)
[Working with playbooks](https://docs.ansible.com/ansible/latest/user_guide/playbooks.html)
[Ansible for DevOps Examples by Jeff Geerling](https://github.com/geerlingguy/ansible-for-devops)
[Getting Started: Writing Your First Playbook - Ansible](https://www.ansible.com/blog/getting-started-writing-your-first-playbook)
[Working With Modules in Ansible](https://docs.ansible.com/ansible/latest/user_guide/modules.html)
[Ansible Best Practices: Roles & Modules](https://www.ansible.com/resources/webinars-training/ansible-best-practices-roles-modules)
[Working with command line tools for Ansible](https://docs.ansible.com/ansible/latest/user_guide/command_line_tools.html)
[Encrypting content with Ansible Vault](https://docs.ansible.com/ansible/latest/user_guide/vault.html)
[Using vault in playbooks with Ansible](https://docs.ansible.com/ansible/latest/user_guide/playbooks_vault.html)
[Using Ansible With Azure](https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/developer/ansible/overview)
[Configuring Ansible on an Azure VM](https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/developer/ansible/install-on-linux-vm)
[How to Use Ansible: An Ansible Cheat Sheet Guide from DigitalOcean](https://www.digitalocean.com/community/cheatsheets/how-to-use-ansible-cheat-sheet-guide)
[Intro to Ansible on Linode | Spatial Labs](https://spatial-labs.dev/posts/202101072328-intro-to-ansible-on-linode/)
## Ansible DevOps Tools Integration
[Ansible Automation Hub](https://www.ansible.com/products/automation-hub) is the official location to discover and download supported [collections](https://docs.ansible.com/ansible/latest/user_guide/collections_using.html#collections), included as part of an Ansible Automation Platform subscription. These content collections contain modules, plugins, roles, and playbooks in a downloadable package.
[Collections](https://docs.ansible.com/ansible/latest/user_guide/collections_using.html#collections) are a distribution format for Ansible content that can include playbooks, roles, modules, and plugins. As modules move from the core Ansible repository into collections, the module documentation will move to the [collections pages](https://docs.ansible.com/ansible/latest/collections/index.html#list-of-collections).
[Ansible Lint](https://ansible-lint.readthedocs.io/en/latest/) is a command-line tool for linting playbooks, roles and collections aimed towards any Ansible users. Its main goal is to promote proven practices, patterns and behaviors while avoiding common pitfalls that can easily lead to bugs or make code harder to maintain.
[Ansible cmdb](https://github.com/fboender/ansible-cmdb) is a tool that takes the output of Ansible’s fact gathering and converts it into a static HTML overview page containing system configuration information.
[Ansible Inventory Grapher](https://github.com/willthames/ansible-inventory-grapher) visually displays inventory inheritance hierarchies and at what level a variable is defined in inventory.
[Ansible Playbook Grapher](https://github.com/haidaraM/ansible-playbook-grapher) is a command line tool to create a graph representing your Ansible playbook tasks and roles.
[Ansible Shell](https://github.com/dominis/ansible-shell) is an interactive shell for Ansible with built-in tab completion for all the modules.
[Ansible Silo](https://github.com/groupon/ansible-silo) is a self-contained Ansible environment by [Docker](https://www.docker.com/).
[Ansigenome](https://github.com/nickjj/ansigenome) is a command line tool designed to help you manage your Ansible roles.
[ARA](https://github.com/openstack/ara) is a records Ansible playbook runs and makes the recorded data available and intuitive for users and systems by integrating with Ansible as a callback plugin.
[Capistrano](https://capistranorb.com/documentation/overview/what-is-capistrano/) is a remote server automation tool. It supports the scripting and execution of arbitrary tasks, and includes a set of sane-default deployment workflows.
[Fabric](https://www.fabfile.org) is a high level Python (2.7, 3.4+) library designed to execute shell commands remotely over SSH, yielding useful Python objects in return. It builds on top of [Invoke](https://www.pyinvoke.org) (subprocess command execution and command-line features) and [Paramiko](https://paramiko.org/) (SSH protocol implementation), extending their APIs to complement one another and provide additional functionality.
[ansible-role-wireguard](https://galaxy.ansible.com/githubixx/ansible_role_wireguard) is an Ansible role for installing WireGuard VPN. Supports Ubuntu, Debian, Archlinx, Fedora and CentOS Stream.
[wireguard_cloud_gateway](https://galaxy.ansible.com/consensus/wireguard_cloud_gateway) is an Ansible role for setting up Wireguard as a gateway VPN server for cloud networks.
[Red Hat OpenShift](https://www.openshift.com/) is focused on security at every level of the container stack and throughout the application lifecycle. It includes long-term, enterprise support from one of the leading Kubernetes contributors and open source software companies.
[OpenShift Hive](https://github.com/openshift/hive) is an operator which runs as a service on top of Kubernetes/OpenShift. The Hive service can be used to provision and perform initial configuration of OpenShift 4 clusters.
# Databases
[Back to the Top](https://github.com/mikeroyal/Self-Hosting-Guide#table-of-contents)


## SQL/NoSQL Learning Resources
[SQL](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/SQL) is a standard language for storing, manipulating and retrieving data in relational databases.
[NoSQL](https://www.ibm.com/cloud/blog/sql-vs-nosql) is a database that is interchangeably referred to as "nonrelational, or "non-SQL" to highlight that the database can handle huge volumes of rapidly changing, unstructured data in different ways than a relational (SQL-based) database with rows and tables.
[Transact-SQL(T-SQL)](https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/sql/t-sql/language-reference) is a Microsoft extension of SQL with all of the tools and applications communicating to a SQL database by sending T-SQL commands.
[Introduction to Transact-SQL](https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/learn/modules/introduction-to-transact-sql/)
[SQL Tutorial by W3Schools](https://www.w3schools.com/sql/)
[Learn SQL Skills Online from Coursera](https://www.coursera.org/courses?query=sql)
[SQL Courses Online from Udemy](https://www.udemy.com/topic/sql/)
[SQL Online Training Courses from LinkedIn Learning](https://www.linkedin.com/learning/topics/sql)
[Learn SQL For Free from Codecademy](https://www.codecademy.com/learn/learn-sql)
[GitLab's SQL Style Guide](https://about.gitlab.com/handbook/business-ops/data-team/platform/sql-style-guide/)
[OracleDB SQL Style Guide Basics](https://oracle.readthedocs.io/en/latest/sql/basics/style-guide.html)
[Tableau CRM: BI Software and Tools](https://www.salesforce.com/products/crm-analytics/overview/)
[Databases on AWS](https://aws.amazon.com/products/databases/)
[Best Practices and Recommendations for SQL Server Clustering in AWS EC2.](https://docs.aws.amazon.com/AWSEC2/latest/WindowsGuide/aws-sql-clustering.html)
[Connecting from Google Kubernetes Engine to a Cloud SQL instance.](https://cloud.google.com/sql/docs/mysql/connect-kubernetes-engine)
[Educational Microsoft Azure SQL resources](https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/sql/sql-server/educational-sql-resources?view=sql-server-ver15)
[MySQL Certifications](https://www.mysql.com/certification/)
[SQL vs. NoSQL Databases: What's the Difference?](https://www.ibm.com/cloud/blog/sql-vs-nosql)
[What is NoSQL?](https://aws.amazon.com/nosql/)
## SQL/NoSQL Tools and Databases
[Netdata](https://github.com/netdata/netdata) is high-fidelity infrastructure monitoring and troubleshooting, real-time monitoring Agent collects thousands of metrics from systems, hardware, containers, and applications with zero configuration. It runs permanently on all your physical/virtual servers, containers, cloud deployments, and edge/IoT devices, and is perfectly safe to install on your systems mid-incident without any preparation.
[Azure Data Studio](https://github.com/Microsoft/azuredatastudio) is an open source data management tool that enables working with SQL Server, Azure SQL DB and SQL DW from Windows, macOS and Linux.
[RStudio](https://rstudio.com/) is an integrated development environment for R and Python, with a console, syntax-highlighting editor that supports direct code execution, and tools for plotting, history, debugging and workspace management.
[MySQL](https://www.mysql.com/) is a fully managed database service to deploy cloud-native applications using the world's most popular open source database.
[PostgreSQL](https://www.postgresql.org/) is a powerful, open source object-relational database system with over 30 years of active development that has earned it a strong reputation for reliability, feature robustness, and performance.
[Amazon DynamoDB](https://aws.amazon.com/dynamodb/) is a key-value and document database that delivers single-digit millisecond performance at any scale. It is a fully managed, multiregion, multimaster, durable database with built-in security, backup and restore, and in-memory caching for internet-scale applications.
[Apache Cassandra™](https://cassandra.apache.org/) is an open source NoSQL distributed database trusted by thousands of companies for scalability and high availability without compromising performance. Cassandra provides linear scalability and proven fault-tolerance on commodity hardware or cloud infrastructure make it the perfect platform for mission-critical data.
[Apache HBase™](https://hbase.apache.org/) is an open-source, NoSQL, distributed big data store. It enables random, strictly consistent, real-time access to petabytes of data. HBase is very effective for handling large, sparse datasets. HBase serves as a direct input and output to the Apache MapReduce framework for Hadoop, and works with Apache Phoenix to enable SQL-like queries over HBase tables.
[Hadoop Distributed File System (HDFS)](https://www.ibm.com/analytics/hadoop/hdfs) is a distributed file system that handles large data sets running on commodity hardware. It is used to scale a single Apache Hadoop cluster to hundreds (and even thousands) of nodes. HDFS is one of the major components of Apache Hadoop, the others being [MapReduce](https://www.ibm.com/analytics/hadoop/mapreduce) and [YARN](https://hadoop.apache.org/docs/current/hadoop-yarn/hadoop-yarn-site/YARN.html).
[Apache Mesos](http://mesos.apache.org/) is a cluster manager that provides efficient resource isolation and sharing across distributed applications, or frameworks. It can run Hadoop, Jenkins, Spark, Aurora, and other frameworks on a dynamically shared pool of nodes.
[Apache Spark](https://spark.apache.org/) is a unified analytics engine for big data processing, with built-in modules for streaming, SQL, machine learning and graph processing.
[ElasticSearch](https://www.elastic.co/) is a search engine based on the Lucene library. It provides a distributed, multitenant-capable full-text search engine with an HTTP web interface and schema-free JSON documents. Elasticsearch is developed in Java.
[Logstash](https://www.elastic.co/products/logstash) is a tool for managing events and logs. When used generically, the term encompasses a larger system of log collection, processing, storage and searching activities.
[Kibana](https://www.elastic.co/products/kibana) is an open source data visualization plugin for Elasticsearch. It provides visualization capabilities on top of the content indexed on an Elasticsearch cluster. Users can create bar, line and scatter plots, or pie charts and maps on top of large volumes of data.
[Trino](https://trino.io/) is a Distributed SQL query engine for big data. It is able to tremendously speed up [ETL processes](https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/architecture/data-guide/relational-data/etl), allow them all to use standard SQL statement, and work with numerous data sources and targets all in the same system.
[Extract, transform, and load (ETL)](https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/architecture/data-guide/relational-data/etl) is a data pipeline used to collect data from various sources, transform the data according to business rules, and load it into a destination data store.
[Redis(REmote DIctionary Server)](https://redis.io/) is an open source (BSD licensed), in-memory data structure store, used as a database, cache, and message broker. It provides data structures such as strings, hashes, lists, sets, sorted sets with range queries, bitmaps, hyperloglogs, geospatial indexes, and streams.
[FoundationDB](https://www.foundationdb.org/) is an open source distributed database designed to handle large volumes of structured data across clusters of commodity servers. It organizes data as an ordered key-value store and employs ACID transactions for all operations. It is especially well-suited for read/write workloads but also has excellent performance for write-intensive workloads. FoundationDB was acquired by [Apple in 2015](https://techcrunch.com/2015/03/24/apple-acquires-durable-database-company-foundationdb/).
[IBM DB2](https://www.ibm.com/analytics/db2) is a collection of hybrid data management products offering a complete suite of AI-empowered capabilities designed to help you manage both structured and unstructured data on premises as well as in private and public cloud environments. Db2 is built on an intelligent common SQL engine designed for scalability and flexibility.
[MongoDB](https://www.mongodb.com/) is a document database meaning it stores data in JSON-like documents.
[OracleDB](https://www.oracle.com/database/) is a powerful fully managed database helps developers manage business-critical data with the highest availability, reliability, and security.
[MariaDB](https://mariadb.com/) is an enterprise open source database solution for modern, mission-critical applications.
[SQLite](https://sqlite.org/index.html) is a C-language library that implements a small, fast, self-contained, high-reliability, full-featured, SQL database engine.SQLite is the most used database engine in the world. SQLite is built into all mobile phones and most computers and comes bundled inside countless other applications that people use every day.
[SQLite Database Browser](https://sqlitebrowser.org/) is an open source SQL tool that allows users to create, design and edits SQLite database files. It lets users show a log of all the SQL commands that have been issued by them and by the application itself.
[InfluxDB](https://www.influxdata.com/) is an open source time series platform. This includes APIs for storing and querying data, processing it in the background for [ETL](https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/architecture/data-guide/relational-data/etl) or monitoring and alerting purposes, user dashboards, Internet of Things sensor data, and visualizing and exploring the data and more. It also has support for processing data from [Graphite](http://graphiteapp.org/).
[Atlas](https://github.com/Netflix/atlas) is an in-memory dimensional [time series database](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Time_series_database).
[CouchbaseDB](https://www.couchbase.com/) is an open source distributed [multi-model NoSQL document-oriented database](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Multi-model_database). It creates a key-value store with managed cache for sub-millisecond data operations, with purpose-built indexers for efficient queries and a powerful query engine for executing SQL queries.
[dbWatch](https://www.dbwatch.com/) is a complete database monitoring/management solution for SQL Server, Oracle, PostgreSQL, Sybase, MySQL and Azure. Designed for proactive management and automation of routine maintenance in large scale on-premise, hybrid/cloud database environments.
[Cosmos DB Profiler](https://hibernatingrhinos.com/products/cosmosdbprof) is a real-time visual debugger allowing a development team to gain valuable insight and perspective into their usage of Cosmos DB database. It identifies over a dozen suspicious behaviors from your application’s interaction with Cosmos DB.
[Adminer](https://www.adminer.org/) is an SQL management client tool for managing databases, tables, relations, indexes, users. Adminer has support for all the popular database management systems such as MySQL, MariaDB, PostgreSQL, SQLite, MS SQL, Oracle, Firebird, SimpleDB, Elasticsearch and MongoDB.
[DBeaver](https://dbeaver.io/) is an open source database tool for developers and database administrators. It offers supports for JDBC compliant databases such as MySQL, Oracle, IBM DB2, SQL Server, Firebird, SQLite, Sybase, Teradata, Firebird, Apache Hive, Phoenix, and Presto.
[DbVisualizer](https://dbvis.com/) is a SQL management tool that allows users to manage a wide range of databases such as Oracle, Sybase, SQL Server, MySQL, H3, and SQLite.
[AppDynamics Database](https://www.appdynamics.com/supported-technologies/database) is a management product for Microsoft SQL Server. With AppDynamics you can monitor and trend key performance metrics such as resource consumption, database objects, schema statistics and more, allowing you to proactively tune and fix issues in a High-Volume Production Environment.
[Toad](https://www.quest.com/toad/) is a SQL Server DBMS toolset developed by Quest. It increases productivity by using extensive automation, intuitive workflows, and built-in expertise. This SQL management tool resolve issues, manage change and promote the highest levels of code quality for both relational and non-relational databases.
[Lepide SQL Server](https://www.lepide.com/sql-storage-manager/) is an open source storage manager utility to analyse the performance of SQL Servers. It provides a complete overview of all configuration and permission changes being made to your SQL Server environment through an easy-to-use, graphical user interface.
[Sequel Pro](https://sequelpro.com/) is a fast MacOS database management tool for working with MySQL. This SQL management tool helpful for interacting with your database by easily to adding new databases, new tables, and new rows.
# Telco 5G
[Back to the Top](https://github.com/mikeroyal/Self-Hosting-Guide#table-of-contents)
 **VMware Cloud First Approach. Source: [VMware](https://www.vmware.com/products/telco-cloud-automation.html).**
**VMware Cloud First Approach. Source: [VMware](https://www.vmware.com/products/telco-cloud-automation.html).**
 **VMware Telco Cloud Automation Components. Source: [VMware](https://www.vmware.com/products/telco-cloud-automation.html).**
## Telco Learning Resources
[HPE(Hewlett Packard Enterprise) Telco Blueprints overview](https://techhub.hpe.com/eginfolib/servers/docs/Telco/Blueprints/infocenter/index.html#GUID-9906A227-C1FB-4FD5-A3C3-F3B72EC81CAB.html)
[Network Functions Virtualization Infrastructure (NFVI) by Cisco](https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/solutions/service-provider/network-functions-virtualization-nfv-infrastructure/index.html)
[Introduction to vCloud NFV Telco Edge from VMware](https://docs.vmware.com/en/VMware-vCloud-NFV-OpenStack-Edition/3.1/vloud-nfv-edge-reference-arch-31/GUID-744C45F1-A8D5-4523-9E5E-EAF6336EE3A0.html)
[VMware Telco Cloud Automation(TCA) Architecture Overview](https://docs.vmware.com/en/VMware-Telco-Cloud-Platform-5G-Edition/1.0/telco-cloud-platform-5G-edition-reference-architecture/GUID-C19566B3-F42D-4351-BA55-DE70D55FB0DD.html)
[5G Telco Cloud from VMware](https://telco.vmware.com/)
[Maturing OpenStack Together To Solve Telco Needs from Red Hat](https://www.redhat.com/cms/managed-files/4.Nokia%20CloudBand%20&%20Red%20Hat%20-%20Maturing%20Openstack%20together%20to%20solve%20Telco%20needs%20Ehud%20Malik,%20Senior%20PLM,%20Nokia%20CloudBand.pdf)
[Red Hat telco ecosystem program](https://connect.redhat.com/en/programs/telco-ecosystem)
[OpenStack for Telcos by Canonical](https://ubuntu.com/blog/openstack-for-telcos-by-canonical)
[Open source NFV platform for 5G from Ubuntu](https://ubuntu.com/telco)
[Understanding 5G Technology from Verizon](https://www.verizon.com/5g/)
[Verizon and Unity partner to enable 5G & MEC gaming and enterprise applications](https://www.verizon.com/about/news/verizon-unity-partner-5g-mec-gaming-enterprise)
[Understanding 5G Technology from Intel](https://www.intel.com/content/www/us/en/wireless-network/what-is-5g.html)
[Understanding 5G Technology from Qualcomm](https://www.qualcomm.com/invention/5g/what-is-5g)
[Telco Acceleration with Xilinx](https://www.xilinx.com/applications/wired-wireless/telco.html)
[VIMs on OSM Public Wiki](https://osm.etsi.org/wikipub/index.php/VIMs)
[Amazon EC2 Overview and Networking Introduction for Telecom Companies](https://docs.aws.amazon.com/whitepapers/latest/ec2-networking-for-telecom/ec2-networking-for-telecom.pdf)
[Citrix Certified Associate – Networking(CCA-N)](http://training.citrix.com/cms/index.php/certification/networking/)
[Citrix Certified Professional – Virtualization(CCP-V)](https://www.globalknowledge.com/us-en/training/certification-prep/brands/citrix/section/virtualization/citrix-certified-professional-virtualization-ccp-v/)
[CCNP Routing and Switching](https://learningnetwork.cisco.com/s/ccnp-enterprise)
[Certified Information Security Manager(CISM)](https://www.isaca.org/credentialing/cism)
[Wireshark Certified Network Analyst (WCNA)](https://www.wiresharktraining.com/certification.html)
[Juniper Networks Certification Program Enterprise (JNCP)](https://www.juniper.net/us/en/training/certification/)
[Cloud Native Computing Foundation Training and Certification Program](https://www.cncf.io/certification/training/)
## Tools
[Open Stack](https://www.openstack.org/) is an open source cloud platform, deployed as infrastructure-as-a-service (IaaS) to orchestrate data center operations on bare metal, private cloud hardware, public cloud resources, or both (hybrid/multi-cloud architecture). OpenStack includes advance use of virtualization & SDN for network traffic optimization to handle the core cloud-computing services of compute, networking, storage, identity, and image services.
[StarlingX](https://www.starlingx.io/) is a complete cloud infrastructure software stack for the edge used by the most demanding applications in industrial IOT, telecom, video delivery and other ultra-low latency use cases.
[Airship](https://www.airshipit.org/) is a collection of open source tools for automating cloud provisioning and management. Airship provides a declarative framework for defining and managing the life cycle of open infrastructure tools and the underlying hardware.
[Network functions virtualization (NFV)](https://www.vmware.com/topics/glossary/content/network-functions-virtualization-nfv) is the replacement of network appliance hardware with virtual machines. The virtual machines use a hypervisor to run networking software and processes such as routing and load balancing. NFV allows for the separation of communication services from dedicated hardware, such as routers and firewalls. This separation means network operations can provide new services dynamically and without installing new hardware. Deploying network components with network functions virtualization only takes hours compared to months like with traditional networking solutions.
[Software Defined Networking (SDN)](https://www.vmware.com/topics/glossary/content/software-defined-networking) is an approach to networking that uses software-based controllers or application programming interfaces (APIs) to communicate with underlying hardware infrastructure and direct traffic on a network. This model differs from that of traditional networks, which use dedicated hardware devices (routers and switches) to control network traffic.
[Virtualized Infrastructure Manager (VIM)](https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/net_mgmt/network_function_virtualization_Infrastructure/3_2_2/install_guide/Cisco_VIM_Install_Guide_3_2_2/Cisco_VIM_Install_Guide_3_2_2_chapter_00.html) is a service delivery and reduce costs with high performance lifecycle management Manage the full lifecycle of the software and hardware comprising your NFV infrastructure (NFVI), and maintaining a live inventory and allocation plan of both physical and virtual resources.
[Management and Orchestration(MANO)](https://www.etsi.org/technologies/open-source-mano) is an ETSI-hosted initiative to develop an Open Source NFV Management and Orchestration (MANO) software stack aligned with ETSI NFV. Two of the key components of the ETSI NFV architectural framework are the NFV Orchestrator and VNF Manager, known as NFV MANO.
[Magma](https://www.magmacore.org/) is an open source software platform that gives network operators an open, flexible and extendable mobile core network solution. Their mission is to connect the world to a faster network by enabling service providers to build cost-effective and extensible carrier-grade networks. Magma is 3GPP generation (2G, 3G, 4G or upcoming 5G networks) and access network agnostic (cellular or WiFi). It can flexibly support a radio access network with minimal development and deployment effort.
[OpenRAN](https://open-ran.org/) is an intelligent Radio Access Network(RAN) integrated on general purpose platforms with open interface between software defined functions. Open RANecosystem enables enormous flexibility and interoperability with a complete openess to multi-vendor deployments.
[Open vSwitch(OVS)](https://www.openvswitch.org/)is an open source production quality, multilayer virtual switch licensed under the open source Apache 2.0 license. It is designed to enable massive network automation through programmatic extension, while still supporting standard management interfaces and protocols (NetFlow, sFlow, IPFIX, RSPAN, CLI, LACP, 802.1ag).
[Edge](https://www.ibm.com/cloud/what-is-edge-computing) is a distributed computing framework that brings enterprise applications closer to data sources such as IoT devices or local edge servers. This proximity to data at its source can deliver strong business benefits, including faster insights, improved response times and better bandwidth availability.
[Multi-access edge computing (MEC)](https://www.etsi.org/technologies/multi-access-edge-computing) is an Industry Specification Group (ISG) within ETSI to create a standardized, open environment which will allow the efficient and seamless integration of applications from vendors, service providers, and third-parties across multi-vendor Multi-access Edge Computing platforms.
[Virtualized network functions(VNFs)](https://www.juniper.net/documentation/en_US/cso4.1/topics/concept/nsd-vnf-overview.html) is a software application used in a Network Functions Virtualization (NFV) implementation that has well defined interfaces, and provides one or more component networking functions in a defined way. For example, a security VNF provides Network Address Translation (NAT) and firewall component functions.
[Cloud-Native Network Functions(CNF)](https://www.cncf.io/announcements/2020/11/18/cloud-native-network-functions-conformance-launched-by-cncf/) is a network function designed and implemented to run inside containers. CNFs inherit all the cloud native architectural and operational principles including Kubernetes(K8s) lifecycle management, agility, resilience, and observability.
[Physical Network Function(PNF)](https://www.mpirical.com/glossary/pnf-physical-network-function) is a physical network node which has not undergone virtualization. Both PNFs and VNFs (Virtualized Network Functions) can be used to form an overall Network Service.
[Network functions virtualization infrastructure(NFVI)](https://docs.vmware.com/en/VMware-vCloud-NFV/2.0/vmware-vcloud-nfv-reference-architecture-20/GUID-FBEA6C6B-54D8-4A37-87B1-D825F9E0DBC7.html) is the foundation of the overall NFV architecture. It provides the physical compute, storage, and networking hardware that hosts the VNFs. Each NFVI block can be thought of as an NFVI node and many nodes can be deployed and controlled geographically.
# Open Source Security
[Back to the Top](https://github.com/mikeroyal/Self-Hosting-Guide#table-of-contents)
[Open Source Security Foundation (OpenSSF)](https://openssf.org/) is a cross-industry collaboration that brings together leaders to improve the security of open source software by building a broader community, targeted initiatives, and best practices. The OpenSSF brings together open source security initiatives under one foundation to accelerate work through cross-industry support. Along with the Core Infrastructure Initiative and the Open Source Security Coalition, and will include new working groups that address vulnerability disclosures, security tooling and more.
## Security Standards, Frameworks and Benchmarks
[STIGs Benchmarks - Security Technical Implementation Guides](https://public.cyber.mil/stigs/)
[CIS Benchmarks - CIS Center for Internet Security](https://www.cisecurity.org/cis-benchmarks/)
[NIST - Current FIPS](https://www.nist.gov/itl/current-fips)
[ISO Standards Catalogue](https://www.iso.org/standards.html)
[Common Criteria for Information Technology Security Evaluation (CC)](https://www.commoncriteriaportal.org/cc/) is an international standard (ISO / IEC 15408) for computer security. It allows an objective evaluation to validate that a particular product satisfies a defined set of security requirements.
[ISO 22301](https://www.iso.org/en/contents/data/standard/07/51/75106.html) is the international standard that provides a best-practice framework for implementing an optimised BCMS (business continuity management system).
[ISO27001](https://www.iso.org/isoiec-27001-information-security.html) is the international standard that describes the requirements for an ISMS (information security management system). The framework is designed to help organizations manage their security practices in one place, consistently and cost-effectively.
[ISO 27701](https://www.iso.org/en/contents/data/standard/07/16/71670.html) specifies the requirements for a PIMS (privacy information management system) based on the requirements of ISO 27001.
It is extended by a set of privacy-specific requirements, control objectives and controls. Companies that have implemented ISO 27001 will be able to use ISO 27701 to extend their security efforts to cover privacy management.
[EU GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation)](https://gdpr.eu/) is a privacy and data protection law that supersedes existing national data protection laws across the EU, bringing uniformity by introducing just one main data protection law for companies/organizations to comply with.
[CCPA (California Consumer Privacy Act)](https://www.oag.ca.gov/privacy/ccpa) is a data privacy law that took effect on January 1, 2020 in the State of California. It applies to businesses that collect California residents’ personal information, and its privacy requirements are similar to those of the EU’s GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation).
[Payment Card Industry (PCI) Data Security Standards (DSS)](https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/microsoft-365/compliance/offering-pci-dss) is a global information security standard designed to prevent fraud through increased control of credit card data.
[SOC 2](https://www.aicpa.org/interestareas/frc/assuranceadvisoryservices/aicpasoc2report.html) is an auditing procedure that ensures your service providers securely manage your data to protect the interests of your comapny/organization and the privacy of their clients.
[NIST CSF](https://www.nist.gov/national-security-standards) is a voluntary framework primarily intended for critical infrastructure organizations to manage and mitigate cybersecurity risk based on existing best practice.
## Security Tools
[SELinux](https://github.com/SELinuxProject/selinux) is a security enhancement to Linux which allows users and administrators more control over access control. Access can be constrained on such variables as which users and applications can access which resources. These resources may take the form of files. Standard Linux access controls, such as file modes (-rwxr-xr-x) are modifiable by the user and the applications which the user runs. Conversely, SELinux access controls are determined by a policy loaded on the system which may not be changed by careless users or misbehaving applications.
[AppArmor](https://www.apparmor.net/) is an effective and easy-to-use Linux application security system. AppArmor proactively protects the operating system and applications from external or internal threats, even zero-day attacks, by enforcing good behavior and preventing both known and unknown application flaws from being exploited. AppArmor supplements the traditional Unix discretionary access control (DAC) model by providing mandatory access control (MAC). It has been included in the mainline Linux kernel since version 2.6.36 and its development has been supported by Canonical since 2009.
[Control Groups(Cgroups)](https://www.redhat.com/sysadmin/cgroups-part-one) is a Linux kernel feature that allows you to allocate resources such as CPU time, system memory, network bandwidth, or any combination of these resources for user-defined groups of tasks (processes) running on a system.
[EarlyOOM](https://github.com/rfjakob/earlyoom) is a daemon for Linux that enables users to more quickly recover and regain control over their system in low-memory situations with heavy swap usage.
[Libgcrypt](https://www.gnupg.org/related_software/libgcrypt/) is a general purpose cryptographic library originally based on code from GnuPG.
[Kali Linux](https://www.kali.org/) is an open source project that is maintained and funded by Offensive Security, a provider of world-class information security training and penetration testing services.
[Pi-hole](https://pi-hole.net/) is a [DNS sinkhole](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/DNS_Sinkhole) that protects your devices from unwanted content, without installing any client-side software, intended for use on a private network. It is designed for use on embedded devices with network capability, such as the Raspberry Pi, but it can be used on other machines running Linux and cloud implementations.
[Aircrack-ng](https://www.aircrack-ng.org/) is a network software suite consisting of a detector, packet sniffer, WEP and WPA/WPA2-PSK cracker and analysis tool for 802.11 wireless LANs. It works with any wireless network interface controller whose driver supports raw monitoring mode and can sniff 802.11a, 802.11b and 802.11g traffic.
[Burp Suite](https://portswigger.net/burp) is a leading range of cybersecurity tools.
[KernelCI](https://foundation.kernelci.org/) is a community-based open source distributed test automation system focused on upstream kernel development. The primary goal of KernelCI is to use an open testing philosophy to ensure the quality, stability and long-term maintenance of the Linux kernel.
[Continuous Kernel Integration project](https://github.com/cki-project) helps find bugs in kernel patches before they are commited to an upstram kernel tree. We are team of kernel developers, kernel testers, and automation engineers.
[eBPF](https://ebpf.io) is a revolutionary technology that can run sandboxed programs in the Linux kernel without changing kernel source code or loading kernel modules. By making the Linux kernel programmable, infrastructure software can leverage existing layers, making them more intelligent and feature-rich without continuing to add additional layers of complexity to the system.
[Cilium](https://cilium.io/) uses eBPF to accelerate getting data in and out of L7 proxies such as Envoy, enabling efficient visibility into API protocols like HTTP, gRPC, and Kafka.
[Hubble](https://github.com/cilium/hubble) is a Network, Service & Security Observability for Kubernetes using eBPF.
[Istio](https://istio.io/) is an open platform to connect, manage, and secure microservices. Istio's control plane provides an abstraction layer over the underlying cluster management platform, such as Kubernetes and Mesos.
[Certgen](https://github.com/cilium/certgen) is a convenience tool to generate and store certificates for Hubble Relay mTLS.
[Scapy](https://scapy.net/) is a python-based interactive packet manipulation program & library.
[syzkaller](https://github.com/google/syzkaller) is an unsupervised, coverage-guided kernel fuzzer.
[SchedViz](https://github.com/google/schedviz) is a tool for gathering and visualizing kernel scheduling traces on Linux machines.
[oss-fuzz](https://google.github.io/oss-fuzz/) aims to make common open source software more secure and stable by combining modern fuzzing techniques with scalable, distributed execution.
[OSSEC](https://www.ossec.net/) is a free, open-source host-based intrusion detection system. It performs log analysis, integrity checking, Windows registry monitoring, rootkit detection, time-based alerting, and active response.
[Metasploit Project](https://www.metasploit.com/) is a computer security project that provides information about security vulnerabilities and aids in penetration testing and IDS signature development.
[Wfuzz](https://github.com/xmendez/wfuzz) was created to facilitate the task in web applications assessments and it is based on a simple concept: it replaces any reference to the FUZZ keyword by the value of a given payload.
[Nmap](https://nmap.org/) is a security scanner used to discover hosts and services on a computer network, thus building a "map" of the network.
[Patchwork](https://github.com/getpatchwork/patchwork) is a web-based patch tracking system designed to facilitate the contribution and management of contributions to an open-source project.
[pfSense](https://www.pfsense.org/) is a free and open source firewall and router that also features unified threat management, load balancing, multi WAN, and more.
[Snowpatch](https://github.com/ruscur/snowpatch) is a continuous integration tool for projects using a patch-based, mailing-list-centric git workflow. This workflow is used by a number of well-known open source projects such as the Linux kernel.
[Snort](https://www.snort.org/) is an open-source, free and lightweight network intrusion detection system (NIDS) software for Linux and Windows to detect emerging threats.
[Wireshark](https://www.wireshark.org/) is a free and open-source packet analyzer. It is used for network troubleshooting, analysis, software and communications protocol development, and education.
[OpenSCAP](https://www.open-scap.org/) is U.S. standard maintained by [National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST)](https://www.nist.gov/). It provides multiple tools to assist administrators and auditors with assessment, measurement, and enforcement of security baselines. OpenSCAP maintains great flexibility and interoperability by reducing the costs of performing security audits. Whether you want to evaluate DISA STIGs, NIST‘s USGCB, or Red Hat’s Security Response Team’s content, all are supported by OpenSCAP.
[Tink](https://github.com/google/tink) is a multi-language, cross-platform, open source library that provides cryptographic APIs that are secure, easy to use correctly, and harder to misuse.
[OWASP](https://www.owasp.org/index.php/Main_Page) is an online community, produces freely-available articles, methodologies, documentation, tools, and technologies in the field of web application security.
[Open Vulnerability and Assessment Language](https://oval.mitre.org/) is a community effort to standardize how to assess and report upon the machine state of computer systems. OVAL includes a language to encode system details, and community repositories of content. Tools and services that use OVAL provide enterprises with accurate, consistent, and actionable information to improve their security.
[ClamAV](https://www.clamav.net/) is an open source antivirus engine for detecting trojans, viruses, malware & other malicious threats.
## Open Source Security Learning Resources
[Microsoft Open Source Software Security](https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/securityengineering/opensource)
[Cloudflare Open Source Security](https://cloudflare.github.io)
[The Seven Properties of Highly Secure Devices](https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/research/publication/seven-properties-highly-secure-devices/)
[How Layer 7 of the Internet Works](https://www.cloudflare.com/learning/ddos/what-is-layer-7/)
[The 7 Kinds of Security](https://www.veracode.com/sites/default/files/Resources/eBooks/7-kinds-of-security.pdf)
[The Libgcrypt Reference Manual](https://www.gnupg.org/documentation/manuals/gcrypt/)
[The Open Web Application Security Project(OWASP) Foundation Top 10](https://owasp.org/www-project-top-ten/)
[Best Practices for Using Open Source Code from The Linux Foundation](https://www.linuxfoundation.org/blog/2017/11/best-practices-using-open-source-code/)
[AWS Certified Security - Specialty Certification](https://aws.amazon.com/certification/certified-security-specialty/)
[Microsoft Certified: Azure Security Engineer Associate](https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/learn/certifications/azure-security-engineer)
[Google Cloud Certified Professional Cloud Security Engineer](https://cloud.google.com/certification/cloud-security-engineer)
[Cisco Security Certifications](https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/training-events/training-certifications/certifications/security.html)
[The Red Hat Certified Specialist in Security: Linux](https://www.redhat.com/en/services/training/ex415-red-hat-certified-specialist-security-linux-exam)
[Linux Professional Institute LPIC-3 Enterprise Security Certification](https://www.lpi.org/our-certifications/lpic-3-303-overview)
[Cybersecurity Training and Courses from IBM Skills](https://www.ibm.com/skills/topics/cybersecurity/)
[Cybersecurity Courses and Certifications by Offensive Security](https://www.offensive-security.com/courses-and-certifications/)
[RSA Certification Program](https://community.rsa.com/community/training/certification)
[Check Point Certified Security Expert(CCSE) Certification](https://training-certifications.checkpoint.com/#/courses/Check%20Point%20Certified%20Expert%20(CCSE)%20R80.x)
[Check Point Certified Security Administrator(CCSA) Certification](https://training-certifications.checkpoint.com/#/courses/Check%20Point%20Certified%20Admin%20(CCSA)%20R80.x)
[Check Point Certified Security Master (CCSM) Certification](https://training-certifications.checkpoint.com/#/courses/Check%20Point%20Certified%20Master%20(CCSM)%20R80.x)
[Certified Cloud Security Professional(CCSP) Certification](https://www.isc2.org/Certifications/CCSP)
[Certified Information Systems Security Professional (CISSP) Certification](https://www.isc2.org/Certifications/CISSP)
[CCNP Routing and Switching](https://learningnetwork.cisco.com/s/ccnp-enterprise)
[Certified Information Security Manager(CISM)](https://www.isaca.org/credentialing/cism)
[Wireshark Certified Network Analyst (WCNA)](https://www.wiresharktraining.com/certification.html)
[Juniper Networks Certification Program Enterprise (JNCP)](https://www.juniper.net/us/en/training/certification/)
[Security Training Certifications and Courses from Udemy](https://www.udemy.com/courses/search/?src=ukw&q=secuirty)
[Security Training Certifications and Courses from Coursera](https://www.coursera.org/search?query=security&)
[Security Certifications Training from Pluarlsight](https://www.pluralsight.com/browse/information-cyber-security/security-certifications)
# Differential Privacy
[Back to the Top](https://github.com/mikeroyal/Self-Hosting-Guide#table-of-contents)
**VMware Telco Cloud Automation Components. Source: [VMware](https://www.vmware.com/products/telco-cloud-automation.html).**
## Telco Learning Resources
[HPE(Hewlett Packard Enterprise) Telco Blueprints overview](https://techhub.hpe.com/eginfolib/servers/docs/Telco/Blueprints/infocenter/index.html#GUID-9906A227-C1FB-4FD5-A3C3-F3B72EC81CAB.html)
[Network Functions Virtualization Infrastructure (NFVI) by Cisco](https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/solutions/service-provider/network-functions-virtualization-nfv-infrastructure/index.html)
[Introduction to vCloud NFV Telco Edge from VMware](https://docs.vmware.com/en/VMware-vCloud-NFV-OpenStack-Edition/3.1/vloud-nfv-edge-reference-arch-31/GUID-744C45F1-A8D5-4523-9E5E-EAF6336EE3A0.html)
[VMware Telco Cloud Automation(TCA) Architecture Overview](https://docs.vmware.com/en/VMware-Telco-Cloud-Platform-5G-Edition/1.0/telco-cloud-platform-5G-edition-reference-architecture/GUID-C19566B3-F42D-4351-BA55-DE70D55FB0DD.html)
[5G Telco Cloud from VMware](https://telco.vmware.com/)
[Maturing OpenStack Together To Solve Telco Needs from Red Hat](https://www.redhat.com/cms/managed-files/4.Nokia%20CloudBand%20&%20Red%20Hat%20-%20Maturing%20Openstack%20together%20to%20solve%20Telco%20needs%20Ehud%20Malik,%20Senior%20PLM,%20Nokia%20CloudBand.pdf)
[Red Hat telco ecosystem program](https://connect.redhat.com/en/programs/telco-ecosystem)
[OpenStack for Telcos by Canonical](https://ubuntu.com/blog/openstack-for-telcos-by-canonical)
[Open source NFV platform for 5G from Ubuntu](https://ubuntu.com/telco)
[Understanding 5G Technology from Verizon](https://www.verizon.com/5g/)
[Verizon and Unity partner to enable 5G & MEC gaming and enterprise applications](https://www.verizon.com/about/news/verizon-unity-partner-5g-mec-gaming-enterprise)
[Understanding 5G Technology from Intel](https://www.intel.com/content/www/us/en/wireless-network/what-is-5g.html)
[Understanding 5G Technology from Qualcomm](https://www.qualcomm.com/invention/5g/what-is-5g)
[Telco Acceleration with Xilinx](https://www.xilinx.com/applications/wired-wireless/telco.html)
[VIMs on OSM Public Wiki](https://osm.etsi.org/wikipub/index.php/VIMs)
[Amazon EC2 Overview and Networking Introduction for Telecom Companies](https://docs.aws.amazon.com/whitepapers/latest/ec2-networking-for-telecom/ec2-networking-for-telecom.pdf)
[Citrix Certified Associate – Networking(CCA-N)](http://training.citrix.com/cms/index.php/certification/networking/)
[Citrix Certified Professional – Virtualization(CCP-V)](https://www.globalknowledge.com/us-en/training/certification-prep/brands/citrix/section/virtualization/citrix-certified-professional-virtualization-ccp-v/)
[CCNP Routing and Switching](https://learningnetwork.cisco.com/s/ccnp-enterprise)
[Certified Information Security Manager(CISM)](https://www.isaca.org/credentialing/cism)
[Wireshark Certified Network Analyst (WCNA)](https://www.wiresharktraining.com/certification.html)
[Juniper Networks Certification Program Enterprise (JNCP)](https://www.juniper.net/us/en/training/certification/)
[Cloud Native Computing Foundation Training and Certification Program](https://www.cncf.io/certification/training/)
## Tools
[Open Stack](https://www.openstack.org/) is an open source cloud platform, deployed as infrastructure-as-a-service (IaaS) to orchestrate data center operations on bare metal, private cloud hardware, public cloud resources, or both (hybrid/multi-cloud architecture). OpenStack includes advance use of virtualization & SDN for network traffic optimization to handle the core cloud-computing services of compute, networking, storage, identity, and image services.
[StarlingX](https://www.starlingx.io/) is a complete cloud infrastructure software stack for the edge used by the most demanding applications in industrial IOT, telecom, video delivery and other ultra-low latency use cases.
[Airship](https://www.airshipit.org/) is a collection of open source tools for automating cloud provisioning and management. Airship provides a declarative framework for defining and managing the life cycle of open infrastructure tools and the underlying hardware.
[Network functions virtualization (NFV)](https://www.vmware.com/topics/glossary/content/network-functions-virtualization-nfv) is the replacement of network appliance hardware with virtual machines. The virtual machines use a hypervisor to run networking software and processes such as routing and load balancing. NFV allows for the separation of communication services from dedicated hardware, such as routers and firewalls. This separation means network operations can provide new services dynamically and without installing new hardware. Deploying network components with network functions virtualization only takes hours compared to months like with traditional networking solutions.
[Software Defined Networking (SDN)](https://www.vmware.com/topics/glossary/content/software-defined-networking) is an approach to networking that uses software-based controllers or application programming interfaces (APIs) to communicate with underlying hardware infrastructure and direct traffic on a network. This model differs from that of traditional networks, which use dedicated hardware devices (routers and switches) to control network traffic.
[Virtualized Infrastructure Manager (VIM)](https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/net_mgmt/network_function_virtualization_Infrastructure/3_2_2/install_guide/Cisco_VIM_Install_Guide_3_2_2/Cisco_VIM_Install_Guide_3_2_2_chapter_00.html) is a service delivery and reduce costs with high performance lifecycle management Manage the full lifecycle of the software and hardware comprising your NFV infrastructure (NFVI), and maintaining a live inventory and allocation plan of both physical and virtual resources.
[Management and Orchestration(MANO)](https://www.etsi.org/technologies/open-source-mano) is an ETSI-hosted initiative to develop an Open Source NFV Management and Orchestration (MANO) software stack aligned with ETSI NFV. Two of the key components of the ETSI NFV architectural framework are the NFV Orchestrator and VNF Manager, known as NFV MANO.
[Magma](https://www.magmacore.org/) is an open source software platform that gives network operators an open, flexible and extendable mobile core network solution. Their mission is to connect the world to a faster network by enabling service providers to build cost-effective and extensible carrier-grade networks. Magma is 3GPP generation (2G, 3G, 4G or upcoming 5G networks) and access network agnostic (cellular or WiFi). It can flexibly support a radio access network with minimal development and deployment effort.
[OpenRAN](https://open-ran.org/) is an intelligent Radio Access Network(RAN) integrated on general purpose platforms with open interface between software defined functions. Open RANecosystem enables enormous flexibility and interoperability with a complete openess to multi-vendor deployments.
[Open vSwitch(OVS)](https://www.openvswitch.org/)is an open source production quality, multilayer virtual switch licensed under the open source Apache 2.0 license. It is designed to enable massive network automation through programmatic extension, while still supporting standard management interfaces and protocols (NetFlow, sFlow, IPFIX, RSPAN, CLI, LACP, 802.1ag).
[Edge](https://www.ibm.com/cloud/what-is-edge-computing) is a distributed computing framework that brings enterprise applications closer to data sources such as IoT devices or local edge servers. This proximity to data at its source can deliver strong business benefits, including faster insights, improved response times and better bandwidth availability.
[Multi-access edge computing (MEC)](https://www.etsi.org/technologies/multi-access-edge-computing) is an Industry Specification Group (ISG) within ETSI to create a standardized, open environment which will allow the efficient and seamless integration of applications from vendors, service providers, and third-parties across multi-vendor Multi-access Edge Computing platforms.
[Virtualized network functions(VNFs)](https://www.juniper.net/documentation/en_US/cso4.1/topics/concept/nsd-vnf-overview.html) is a software application used in a Network Functions Virtualization (NFV) implementation that has well defined interfaces, and provides one or more component networking functions in a defined way. For example, a security VNF provides Network Address Translation (NAT) and firewall component functions.
[Cloud-Native Network Functions(CNF)](https://www.cncf.io/announcements/2020/11/18/cloud-native-network-functions-conformance-launched-by-cncf/) is a network function designed and implemented to run inside containers. CNFs inherit all the cloud native architectural and operational principles including Kubernetes(K8s) lifecycle management, agility, resilience, and observability.
[Physical Network Function(PNF)](https://www.mpirical.com/glossary/pnf-physical-network-function) is a physical network node which has not undergone virtualization. Both PNFs and VNFs (Virtualized Network Functions) can be used to form an overall Network Service.
[Network functions virtualization infrastructure(NFVI)](https://docs.vmware.com/en/VMware-vCloud-NFV/2.0/vmware-vcloud-nfv-reference-architecture-20/GUID-FBEA6C6B-54D8-4A37-87B1-D825F9E0DBC7.html) is the foundation of the overall NFV architecture. It provides the physical compute, storage, and networking hardware that hosts the VNFs. Each NFVI block can be thought of as an NFVI node and many nodes can be deployed and controlled geographically.
# Open Source Security
[Back to the Top](https://github.com/mikeroyal/Self-Hosting-Guide#table-of-contents)
[Open Source Security Foundation (OpenSSF)](https://openssf.org/) is a cross-industry collaboration that brings together leaders to improve the security of open source software by building a broader community, targeted initiatives, and best practices. The OpenSSF brings together open source security initiatives under one foundation to accelerate work through cross-industry support. Along with the Core Infrastructure Initiative and the Open Source Security Coalition, and will include new working groups that address vulnerability disclosures, security tooling and more.
## Security Standards, Frameworks and Benchmarks
[STIGs Benchmarks - Security Technical Implementation Guides](https://public.cyber.mil/stigs/)
[CIS Benchmarks - CIS Center for Internet Security](https://www.cisecurity.org/cis-benchmarks/)
[NIST - Current FIPS](https://www.nist.gov/itl/current-fips)
[ISO Standards Catalogue](https://www.iso.org/standards.html)
[Common Criteria for Information Technology Security Evaluation (CC)](https://www.commoncriteriaportal.org/cc/) is an international standard (ISO / IEC 15408) for computer security. It allows an objective evaluation to validate that a particular product satisfies a defined set of security requirements.
[ISO 22301](https://www.iso.org/en/contents/data/standard/07/51/75106.html) is the international standard that provides a best-practice framework for implementing an optimised BCMS (business continuity management system).
[ISO27001](https://www.iso.org/isoiec-27001-information-security.html) is the international standard that describes the requirements for an ISMS (information security management system). The framework is designed to help organizations manage their security practices in one place, consistently and cost-effectively.
[ISO 27701](https://www.iso.org/en/contents/data/standard/07/16/71670.html) specifies the requirements for a PIMS (privacy information management system) based on the requirements of ISO 27001.
It is extended by a set of privacy-specific requirements, control objectives and controls. Companies that have implemented ISO 27001 will be able to use ISO 27701 to extend their security efforts to cover privacy management.
[EU GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation)](https://gdpr.eu/) is a privacy and data protection law that supersedes existing national data protection laws across the EU, bringing uniformity by introducing just one main data protection law for companies/organizations to comply with.
[CCPA (California Consumer Privacy Act)](https://www.oag.ca.gov/privacy/ccpa) is a data privacy law that took effect on January 1, 2020 in the State of California. It applies to businesses that collect California residents’ personal information, and its privacy requirements are similar to those of the EU’s GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation).
[Payment Card Industry (PCI) Data Security Standards (DSS)](https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/microsoft-365/compliance/offering-pci-dss) is a global information security standard designed to prevent fraud through increased control of credit card data.
[SOC 2](https://www.aicpa.org/interestareas/frc/assuranceadvisoryservices/aicpasoc2report.html) is an auditing procedure that ensures your service providers securely manage your data to protect the interests of your comapny/organization and the privacy of their clients.
[NIST CSF](https://www.nist.gov/national-security-standards) is a voluntary framework primarily intended for critical infrastructure organizations to manage and mitigate cybersecurity risk based on existing best practice.
## Security Tools
[SELinux](https://github.com/SELinuxProject/selinux) is a security enhancement to Linux which allows users and administrators more control over access control. Access can be constrained on such variables as which users and applications can access which resources. These resources may take the form of files. Standard Linux access controls, such as file modes (-rwxr-xr-x) are modifiable by the user and the applications which the user runs. Conversely, SELinux access controls are determined by a policy loaded on the system which may not be changed by careless users or misbehaving applications.
[AppArmor](https://www.apparmor.net/) is an effective and easy-to-use Linux application security system. AppArmor proactively protects the operating system and applications from external or internal threats, even zero-day attacks, by enforcing good behavior and preventing both known and unknown application flaws from being exploited. AppArmor supplements the traditional Unix discretionary access control (DAC) model by providing mandatory access control (MAC). It has been included in the mainline Linux kernel since version 2.6.36 and its development has been supported by Canonical since 2009.
[Control Groups(Cgroups)](https://www.redhat.com/sysadmin/cgroups-part-one) is a Linux kernel feature that allows you to allocate resources such as CPU time, system memory, network bandwidth, or any combination of these resources for user-defined groups of tasks (processes) running on a system.
[EarlyOOM](https://github.com/rfjakob/earlyoom) is a daemon for Linux that enables users to more quickly recover and regain control over their system in low-memory situations with heavy swap usage.
[Libgcrypt](https://www.gnupg.org/related_software/libgcrypt/) is a general purpose cryptographic library originally based on code from GnuPG.
[Kali Linux](https://www.kali.org/) is an open source project that is maintained and funded by Offensive Security, a provider of world-class information security training and penetration testing services.
[Pi-hole](https://pi-hole.net/) is a [DNS sinkhole](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/DNS_Sinkhole) that protects your devices from unwanted content, without installing any client-side software, intended for use on a private network. It is designed for use on embedded devices with network capability, such as the Raspberry Pi, but it can be used on other machines running Linux and cloud implementations.
[Aircrack-ng](https://www.aircrack-ng.org/) is a network software suite consisting of a detector, packet sniffer, WEP and WPA/WPA2-PSK cracker and analysis tool for 802.11 wireless LANs. It works with any wireless network interface controller whose driver supports raw monitoring mode and can sniff 802.11a, 802.11b and 802.11g traffic.
[Burp Suite](https://portswigger.net/burp) is a leading range of cybersecurity tools.
[KernelCI](https://foundation.kernelci.org/) is a community-based open source distributed test automation system focused on upstream kernel development. The primary goal of KernelCI is to use an open testing philosophy to ensure the quality, stability and long-term maintenance of the Linux kernel.
[Continuous Kernel Integration project](https://github.com/cki-project) helps find bugs in kernel patches before they are commited to an upstram kernel tree. We are team of kernel developers, kernel testers, and automation engineers.
[eBPF](https://ebpf.io) is a revolutionary technology that can run sandboxed programs in the Linux kernel without changing kernel source code or loading kernel modules. By making the Linux kernel programmable, infrastructure software can leverage existing layers, making them more intelligent and feature-rich without continuing to add additional layers of complexity to the system.
[Cilium](https://cilium.io/) uses eBPF to accelerate getting data in and out of L7 proxies such as Envoy, enabling efficient visibility into API protocols like HTTP, gRPC, and Kafka.
[Hubble](https://github.com/cilium/hubble) is a Network, Service & Security Observability for Kubernetes using eBPF.
[Istio](https://istio.io/) is an open platform to connect, manage, and secure microservices. Istio's control plane provides an abstraction layer over the underlying cluster management platform, such as Kubernetes and Mesos.
[Certgen](https://github.com/cilium/certgen) is a convenience tool to generate and store certificates for Hubble Relay mTLS.
[Scapy](https://scapy.net/) is a python-based interactive packet manipulation program & library.
[syzkaller](https://github.com/google/syzkaller) is an unsupervised, coverage-guided kernel fuzzer.
[SchedViz](https://github.com/google/schedviz) is a tool for gathering and visualizing kernel scheduling traces on Linux machines.
[oss-fuzz](https://google.github.io/oss-fuzz/) aims to make common open source software more secure and stable by combining modern fuzzing techniques with scalable, distributed execution.
[OSSEC](https://www.ossec.net/) is a free, open-source host-based intrusion detection system. It performs log analysis, integrity checking, Windows registry monitoring, rootkit detection, time-based alerting, and active response.
[Metasploit Project](https://www.metasploit.com/) is a computer security project that provides information about security vulnerabilities and aids in penetration testing and IDS signature development.
[Wfuzz](https://github.com/xmendez/wfuzz) was created to facilitate the task in web applications assessments and it is based on a simple concept: it replaces any reference to the FUZZ keyword by the value of a given payload.
[Nmap](https://nmap.org/) is a security scanner used to discover hosts and services on a computer network, thus building a "map" of the network.
[Patchwork](https://github.com/getpatchwork/patchwork) is a web-based patch tracking system designed to facilitate the contribution and management of contributions to an open-source project.
[pfSense](https://www.pfsense.org/) is a free and open source firewall and router that also features unified threat management, load balancing, multi WAN, and more.
[Snowpatch](https://github.com/ruscur/snowpatch) is a continuous integration tool for projects using a patch-based, mailing-list-centric git workflow. This workflow is used by a number of well-known open source projects such as the Linux kernel.
[Snort](https://www.snort.org/) is an open-source, free and lightweight network intrusion detection system (NIDS) software for Linux and Windows to detect emerging threats.
[Wireshark](https://www.wireshark.org/) is a free and open-source packet analyzer. It is used for network troubleshooting, analysis, software and communications protocol development, and education.
[OpenSCAP](https://www.open-scap.org/) is U.S. standard maintained by [National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST)](https://www.nist.gov/). It provides multiple tools to assist administrators and auditors with assessment, measurement, and enforcement of security baselines. OpenSCAP maintains great flexibility and interoperability by reducing the costs of performing security audits. Whether you want to evaluate DISA STIGs, NIST‘s USGCB, or Red Hat’s Security Response Team’s content, all are supported by OpenSCAP.
[Tink](https://github.com/google/tink) is a multi-language, cross-platform, open source library that provides cryptographic APIs that are secure, easy to use correctly, and harder to misuse.
[OWASP](https://www.owasp.org/index.php/Main_Page) is an online community, produces freely-available articles, methodologies, documentation, tools, and technologies in the field of web application security.
[Open Vulnerability and Assessment Language](https://oval.mitre.org/) is a community effort to standardize how to assess and report upon the machine state of computer systems. OVAL includes a language to encode system details, and community repositories of content. Tools and services that use OVAL provide enterprises with accurate, consistent, and actionable information to improve their security.
[ClamAV](https://www.clamav.net/) is an open source antivirus engine for detecting trojans, viruses, malware & other malicious threats.
## Open Source Security Learning Resources
[Microsoft Open Source Software Security](https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/securityengineering/opensource)
[Cloudflare Open Source Security](https://cloudflare.github.io)
[The Seven Properties of Highly Secure Devices](https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/research/publication/seven-properties-highly-secure-devices/)
[How Layer 7 of the Internet Works](https://www.cloudflare.com/learning/ddos/what-is-layer-7/)
[The 7 Kinds of Security](https://www.veracode.com/sites/default/files/Resources/eBooks/7-kinds-of-security.pdf)
[The Libgcrypt Reference Manual](https://www.gnupg.org/documentation/manuals/gcrypt/)
[The Open Web Application Security Project(OWASP) Foundation Top 10](https://owasp.org/www-project-top-ten/)
[Best Practices for Using Open Source Code from The Linux Foundation](https://www.linuxfoundation.org/blog/2017/11/best-practices-using-open-source-code/)
[AWS Certified Security - Specialty Certification](https://aws.amazon.com/certification/certified-security-specialty/)
[Microsoft Certified: Azure Security Engineer Associate](https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/learn/certifications/azure-security-engineer)
[Google Cloud Certified Professional Cloud Security Engineer](https://cloud.google.com/certification/cloud-security-engineer)
[Cisco Security Certifications](https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/training-events/training-certifications/certifications/security.html)
[The Red Hat Certified Specialist in Security: Linux](https://www.redhat.com/en/services/training/ex415-red-hat-certified-specialist-security-linux-exam)
[Linux Professional Institute LPIC-3 Enterprise Security Certification](https://www.lpi.org/our-certifications/lpic-3-303-overview)
[Cybersecurity Training and Courses from IBM Skills](https://www.ibm.com/skills/topics/cybersecurity/)
[Cybersecurity Courses and Certifications by Offensive Security](https://www.offensive-security.com/courses-and-certifications/)
[RSA Certification Program](https://community.rsa.com/community/training/certification)
[Check Point Certified Security Expert(CCSE) Certification](https://training-certifications.checkpoint.com/#/courses/Check%20Point%20Certified%20Expert%20(CCSE)%20R80.x)
[Check Point Certified Security Administrator(CCSA) Certification](https://training-certifications.checkpoint.com/#/courses/Check%20Point%20Certified%20Admin%20(CCSA)%20R80.x)
[Check Point Certified Security Master (CCSM) Certification](https://training-certifications.checkpoint.com/#/courses/Check%20Point%20Certified%20Master%20(CCSM)%20R80.x)
[Certified Cloud Security Professional(CCSP) Certification](https://www.isc2.org/Certifications/CCSP)
[Certified Information Systems Security Professional (CISSP) Certification](https://www.isc2.org/Certifications/CISSP)
[CCNP Routing and Switching](https://learningnetwork.cisco.com/s/ccnp-enterprise)
[Certified Information Security Manager(CISM)](https://www.isaca.org/credentialing/cism)
[Wireshark Certified Network Analyst (WCNA)](https://www.wiresharktraining.com/certification.html)
[Juniper Networks Certification Program Enterprise (JNCP)](https://www.juniper.net/us/en/training/certification/)
[Security Training Certifications and Courses from Udemy](https://www.udemy.com/courses/search/?src=ukw&q=secuirty)
[Security Training Certifications and Courses from Coursera](https://www.coursera.org/search?query=security&)
[Security Certifications Training from Pluarlsight](https://www.pluralsight.com/browse/information-cyber-security/security-certifications)
# Differential Privacy
[Back to the Top](https://github.com/mikeroyal/Self-Hosting-Guide#table-of-contents)

Above is a simple diagram of how Differential Privacy-Preserving Data Sharing and Data Mining protects a User's Data
## Differential Privacy Learning Resources
[Differential Privacy](https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/ai/ai-lab-differential-privacy) is a system that simultaneously enables researchers and analysts to extract useful insights from datasets containing personal information and offers stronger privacy protections. This is achieved by introducing "statistical noise".
[Statistical Noise](https://news.microsoft.com/on-the-issues/2020/08/27/statistical-noise-data-differential-privacy/) is a process that small aletrations to masked datasets. The statistical noise hides identifiable characteristics of individuals, ensuring that the privacy of personal information is protected, but it's small enough to not materially impact the accuracy of the answers extracted by analysts and researchers.
[Laplacian Noise](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Laplace_distribution) is a mechanism that adds Laplacian-distributed noise to a function.
[Differential Privacy Blog Series by the National Institute of Standards and Technology(NIST)](https://www.nist.gov/itl/applied-cybersecurity/privacy-engineering/collaboration-space/focus-areas/de-id/dp-blog)
[Apple's Differential Privacy Overview](https://www.apple.com/privacy/docs/Differential_Privacy_Overview.pdf)
[Learning with Privacy at Scale with Apple Machine Learning](https://machinelearning.apple.com/research/learning-with-privacy-at-scale)
[Microsoft Research Differential Privacy Overview](https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/research/publication/differential-privacy/)
[Responsible Machine Learning with Microsoft Azure](https://azure.microsoft.com/en-us/services/machine-learning/responsibleml/)
[Responsible AI Resources with Microsoft AI](https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/ai/responsible-ai-resources)
[Preserve data privacy by using differential privacy and the SmartNoise package](https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/machine-learning/concept-differential-privacy)
[Open Differential Privacy(OpenDP) Initiative by Microsoft and Harvard](https://projects.iq.harvard.edu/opendp)
[Google's Differential Privacy Library](https://github.com/google/differential-privacy)
[Computing Private Statistics with Privacy on Beam from Google Codelabs](https://codelabs.developers.google.com/codelabs/privacy-on-beam/#0)
[Introducing TensorFlow Privacy: Learning with Differential Privacy for Training Data](https://blog.tensorflow.org/2020/06/introducing-new-privacy-testing-library.html)
[TensorFlow Federated: Machine Learning on Decentralized Data](https://www.tensorflow.org/federated/)
[Federated Analytics: Collaborative Data Science without Data Collection](https://ai.googleblog.com/2020/05/federated-analytics-collaborative-data.html)
[Differentially-Private Stochastic Gradient Descent(DP-SGD)](https://github.com/tensorflow/privacy/blob/master/tutorials/walkthrough/README.md)
[Learning Differential Privacy from Harvard University Privacy Tools Project](https://privacytools.seas.harvard.edu/differential-privacy)
[Harvard University Privacy Tools Project Courses & Educational Materials](https://privacytools.seas.harvard.edu/courses-educational-materials)
[The Weaknesses of Differential Privacy course on Coursera](https://www.coursera.org/lecture/data-results/weaknesses-of-differential-privacy-50Y9k)
[The Differential Privacy of Bayesian Inference](https://privacytools.seas.harvard.edu/publications/differential-privacy-bayesian-inference)
[Simultaneous private learning of multiple concepts](https://privacytools.seas.harvard.edu/publications/simultaneous-private-learning-multiple-concepts)
[The Complexity of Computing the Optimal Composition of Differential Privacy](https://privacytools.seas.harvard.edu/publications/complexity-computing-optimal-composition-differential-privacy)
[Order revealing encryption and the hardness of private learning](https://privacytools.seas.harvard.edu/publications/order-revealing-encryption-and-hardness-private-learning)
[SAP HANA data anonymization using SAP Software Solutions](https://www.sap.com/cmp/dg/crm-xt17-ddm-data-anony/index.html)
[SAP HANA Security using their In-Memory Database](https://www.sap.com/products/hana/features/security.html)
[DEFCON Differential Privacy Training Launch](https://opensource.googleblog.com/2020/08/defcon-differential-privacy-training.html)
[Secure and Private AI course on Udacity](https://www.udacity.com/course/secure-and-private-ai--ud185)
[Differential Privacy - Security and Privacy for Big Data - Part 1 course on Coursera](https://www.coursera.org/learn/security-privacy-big-data)
[Differential Privacy - Security and Privacy for Big Data - Part 2 course on Coursera](https://www.coursera.org/learn/security-privacy-big-data-protection)
[Certified Ethical Emerging Technologist Professional Certificate course on Coursera](https://www.coursera.org/professional-certificates/certified-ethical-emerging-technologist)
## Differential Privacy Tools
[PySyft](https://github.com/OpenMined/PySyft) is a Python library for secure and private Deep Learning. PySyft decouples private data from model training, using [Federated Learning](https://ai.googleblog.com/2017/04/federated-learning-collaborative.html), [Differential Privacy](https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/ai/ai-lab-differential-privacy), and Encrypted Computation (like [Multi-Party Computation (MPC)](https://multiparty.org) and [Homomorphic Encryption (HE)](https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/research/project/homomorphic-encryption/) within the main Deep Learning frameworks like [PyTorch](https://pytorch.org/) and [TensorFlow](https://www.tensorflow.org/).
[TensorFlow Privacy](https://github.com/tensorflow/privacy) is a Python library that includes implementations of TensorFlow optimizers for training machine learning models with differential privacy. The library comes with tutorials and analysis tools for computing the privacy guarantees provided.
[TensorFlow Federated (TFF)](https://github.com/tensorflow/federated) is an open-source framework for machine learning and other computations on decentralized data. TFF has been developed to facilitate open research and experimentation with [Federated Learning (FL)](https://ai.googleblog.com/2017/04/federated-learning-collaborative.html), an approach to machine learning where a shared global model is trained across many participating clients that keep their training data locally.
[Privacy on Beam](https://github.com/google/differential-privacy/tree/main/privacy-on-beam) is an end-to-end differential privacy solution built on [Apache Beam](https://beam.apache.org/documentation/). It is intended to be usable by all developers, regardless of their differential privacy expertise.
[PyDP](https://github.com/OpenMined/PyDP) is a Python wrapper for Google's Differential Privacy project.
[PennyLane](https://pennylane.ai) is a cross-platform Python library for [differentiable programming](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Differentiable_programming) of quantum computers. By training a quantum computer the same way as a neural network.
[BoTorch](https://botorch.org) is a library for Bayesian Optimization built on PyTorch.
[PyTorch Geometric (PyG)](https://github.com/rusty1s/pytorch_geometric) is a geometric deep learning extension library for [PyTorch](https://pytorch.org/).
[Skorch](https://github.com/skorch-dev/skorch) is a scikit-learn compatible neural network library that wraps PyTorch.
[Diffprivlib](https://github.com/IBM/differential-privacy-library) is the IBM Differential Privacy Library for experimenting with, investigating and developing applications in, differential privacy.
[Opacus](https://opacus.ai/) is a library that enables training PyTorch models with differential privacy. It supports training with minimal code changes required on the client, has little impact on training performance and allows the client to online track the privacy budget expended at any given moment.
[Smart Noise](https://github.com/opendifferentialprivacy/smartnoise-sdk) is a toolkit that uses state-of-the-art differential privacy (DP) techniques to inject noise into data, to prevent disclosure of sensitive information and manage exposure risk.
# Machine Learning
[Back to the Top](https://github.com/mikeroyal/Self-Hosting-Guide#table-of-contents)
 ## ML frameworks & applications
[TensorFlow](https://www.tensorflow.org) is an end-to-end open source platform for machine learning. It has a comprehensive, flexible ecosystem of tools, libraries and community resources that lets researchers push the state-of-the-art in ML and developers easily build and deploy ML powered applications.
[Tensorman](https://github.com/pop-os/tensorman) is a utility for easy management of Tensorflow containers by developed by [System76]( https://system76.com).Tensorman allows Tensorflow to operate in an isolated environment that is contained from the rest of the system. This virtual environment can operate independent of the base system, allowing you to use any version of Tensorflow on any version of a Linux distribution that supports the Docker runtime.
[Keras](https://keras.io) is a high-level neural networks API, written in Python and capable of running on top of TensorFlow, CNTK, or Theano.It was developed with a focus on enabling fast experimentation. It is capable of running on top of TensorFlow, Microsoft Cognitive Toolkit, R, Theano, or PlaidML.
[PyTorch](https://pytorch.org) is a library for deep learning on irregular input data such as graphs, point clouds, and manifolds. Primarily developed by Facebook's AI Research lab.
[Amazon SageMaker](https://aws.amazon.com/sagemaker/) is a fully managed service that provides every developer and data scientist with the ability to build, train, and deploy machine learning (ML) models quickly. SageMaker removes the heavy lifting from each step of the machine learning process to make it easier to develop high quality models.
[Azure Databricks](https://azure.microsoft.com/en-us/services/databricks/) is a fast and collaborative Apache Spark-based big data analytics service designed for data science and data engineering. Azure Databricks, sets up your Apache Spark environment in minutes, autoscale, and collaborate on shared projects in an interactive workspace. Azure Databricks supports Python, Scala, R, Java, and SQL, as well as data science frameworks and libraries including TensorFlow, PyTorch, and scikit-learn.
[Microsoft Cognitive Toolkit (CNTK)](https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/cognitive-toolkit/) is an open-source toolkit for commercial-grade distributed deep learning. It describes neural networks as a series of computational steps via a directed graph. CNTK allows the user to easily realize and combine popular model types such as feed-forward DNNs, convolutional neural networks (CNNs) and recurrent neural networks (RNNs/LSTMs). CNTK implements stochastic gradient descent (SGD, error backpropagation) learning with automatic differentiation and parallelization across multiple GPUs and servers.
[Apache Airflow](https://airflow.apache.org) is an open-source workflow management platform created by the community to programmatically author, schedule and monitor workflows. Install. Principles. Scalable. Airflow has a modular architecture and uses a message queue to orchestrate an arbitrary number of workers. Airflow is ready to scale to infinity.
[Open Neural Network Exchange(ONNX)](https://github.com/onnx) is an open ecosystem that empowers AI developers to choose the right tools as their project evolves. ONNX provides an open source format for AI models, both deep learning and traditional ML. It defines an extensible computation graph model, as well as definitions of built-in operators and standard data types.
[Apache MXNet](https://mxnet.apache.org/) is a deep learning framework designed for both efficiency and flexibility. It allows you to mix symbolic and imperative programming to maximize efficiency and productivity. At its core, MXNet contains a dynamic dependency scheduler that automatically parallelizes both symbolic and imperative operations on the fly. A graph optimization layer on top of that makes symbolic execution fast and memory efficient. MXNet is portable and lightweight, scaling effectively to multiple GPUs and multiple machines. Support for Python, R, Julia, Scala, Go, Javascript and more.
[AutoGluon](https://autogluon.mxnet.io/index.html) is toolkit for Deep learning that automates machine learning tasks enabling you to easily achieve strong predictive performance in your applications. With just a few lines of code, you can train and deploy high-accuracy deep learning models on tabular, image, and text data.
[Anaconda](https://www.anaconda.com/) is a very popular Data Science platform for machine learning and deep learning that enables users to develop models, train them, and deploy them.
[PlaidML](https://github.com/plaidml/plaidml) is an advanced and portable tensor compiler for enabling deep learning on laptops, embedded devices, or other devices where the available computing hardware is not well supported or the available software stack contains unpalatable license restrictions.
[OpenCV](https://opencv.org) is a highly optimized library with focus on real-time computer vision applications. The C++, Python, and Java interfaces support Linux, MacOS, Windows, iOS, and Android.
[Scikit-Learn](https://scikit-learn.org/stable/index.html) is a Python module for machine learning built on top of SciPy, NumPy, and matplotlib, making it easier to apply robust and simple implementations of many popular machine learning algorithms.
[Weka](https://www.cs.waikato.ac.nz/ml/weka/) is an open source machine learning software that can be accessed through a graphical user interface, standard terminal applications, or a Java API. It is widely used for teaching, research, and industrial applications, contains a plethora of built-in tools for standard machine learning tasks, and additionally gives transparent access to well-known toolboxes such as scikit-learn, R, and Deeplearning4j.
[Caffe](https://github.com/BVLC/caffe) is a deep learning framework made with expression, speed, and modularity in mind. It is developed by Berkeley AI Research (BAIR)/The Berkeley Vision and Learning Center (BVLC) and community contributors.
[Theano](https://github.com/Theano/Theano) is a Python library that allows you to define, optimize, and evaluate mathematical expressions involving multi-dimensional arrays efficiently including tight integration with NumPy.
[nGraph](https://github.com/NervanaSystems/ngraph) is an open source C++ library, compiler and runtime for Deep Learning. The nGraph Compiler aims to accelerate developing AI workloads using any deep learning framework and deploying to a variety of hardware targets.It provides the freedom, performance, and ease-of-use to AI developers.
[NVIDIA cuDNN](https://developer.nvidia.com/cudnn) is a GPU-accelerated library of primitives for [deep neural networks](https://developer.nvidia.com/deep-learning). cuDNN provides highly tuned implementations for standard routines such as forward and backward convolution, pooling, normalization, and activation layers. cuDNN accelerates widely used deep learning frameworks, including [Caffe2](https://caffe2.ai/), [Chainer](https://chainer.org/), [Keras](https://keras.io/), [MATLAB](https://www.mathworks.com/solutions/deep-learning.html), [MxNet](https://mxnet.incubator.apache.org/), [PyTorch](https://pytorch.org/), and [TensorFlow](https://www.tensorflow.org/).
[Jupyter Notebook](https://jupyter.org/) is an open-source web application that allows you to create and share documents that contain live code, equations, visualizations and narrative text. Jupyter is used widely in industries that do data cleaning and transformation, numerical simulation, statistical modeling, data visualization, data science, and machine learning.
[Apache Spark](https://spark.apache.org/) is a unified analytics engine for large-scale data processing. It provides high-level APIs in Scala, Java, Python, and R, and an optimized engine that supports general computation graphs for data analysis. It also supports a rich set of higher-level tools including Spark SQL for SQL and DataFrames, MLlib for machine learning, GraphX for graph processing, and Structured Streaming for stream processing.
[Apache Spark Connector for SQL Server and Azure SQL](https://github.com/microsoft/sql-spark-connector) is a high-performance connector that enables you to use transactional data in big data analytics and persists results for ad-hoc queries or reporting. The connector allows you to use any SQL database, on-premises or in the cloud, as an input data source or output data sink for Spark jobs.
[Apache PredictionIO](https://predictionio.apache.org/) is an open source machine learning framework for developers, data scientists, and end users. It supports event collection, deployment of algorithms, evaluation, querying predictive results via REST APIs. It is based on scalable open source services like Hadoop, HBase (and other DBs), Elasticsearch, Spark and implements what is called a Lambda Architecture.
[Cluster Manager for Apache Kafka(CMAK)](https://github.com/yahoo/CMAK) is a tool for managing [Apache Kafka](https://kafka.apache.org/) clusters.
[BigDL](https://bigdl-project.github.io/) is a distributed deep learning library for Apache Spark. With BigDL, users can write their deep learning applications as standard Spark programs, which can directly run on top of existing Spark or Hadoop clusters.
[Koalas](https://pypi.org/project/koalas/) is project makes data scientists more productive when interacting with big data, by implementing the pandas DataFrame API on top of Apache Spark.
[Apache Spark™ MLflow](https://mlflow.org/) is an open source platform to manage the ML lifecycle, including experimentation, reproducibility, deployment, and a central model registry. MLflow currently offers four components:
**[MLflow Tracking](https://mlflow.org/docs/latest/tracking.html)**: Record and query experiments: code, data, config, and results.
**[MLflow Projects](https://mlflow.org/docs/latest/projects.html)**: Package data science code in a format to reproduce runs on any platform.
**[MLflow Models](https://mlflow.org/docs/latest/models.html)**: Deploy machine learning models in diverse serving environments.
**[Model Registry](https://mlflow.org/docs/latest/model-registry.html)**: Store, annotate, discover, and manage models in a central repository.
[Eclipse Deeplearning4J (DL4J)](https://deeplearning4j.konduit.ai/) is a set of projects intended to support all the needs of a JVM-based(Scala, Kotlin, Clojure, and Groovy) deep learning application. This means starting with the raw data, loading and preprocessing it from wherever and whatever format it is in to building and tuning a wide variety of simple and complex deep learning networks.
[Numba](https://github.com/numba/numba) is an open source, NumPy-aware optimizing compiler for Python sponsored by Anaconda, Inc. It uses the LLVM compiler project to generate machine code from Python syntax. Numba can compile a large subset of numerically-focused Python, including many NumPy functions. Additionally, Numba has support for automatic parallelization of loops, generation of GPU-accelerated code, and creation of ufuncs and C callbacks.
[Chainer](https://chainer.org/) is a Python-based deep learning framework aiming at flexibility. It provides automatic differentiation APIs based on the define-by-run approach (dynamic computational graphs) as well as object-oriented high-level APIs to build and train neural networks. It also supports CUDA/cuDNN using [CuPy](https://github.com/cupy/cupy) for high performance training and inference.
[cuML](https://github.com/rapidsai/cuml) is a suite of libraries that implement machine learning algorithms and mathematical primitives functions that share compatible APIs with other RAPIDS projects. cuML enables data scientists, researchers, and software engineers to run traditional tabular ML tasks on GPUs without going into the details of CUDA programming. In most cases, cuML's Python API matches the API from scikit-learn.
## Online ML Learning Resources
[Machine Learning by Stanford University from Coursera](https://www.coursera.org/learn/machine-learning)
[Machine Learning Courses Online from Coursera](https://www.coursera.org/courses?query=machine%20learning&)
[Machine Learning Courses Online from Udemy](https://www.udemy.com/topic/machine-learning/)
[Learn Machine Learning with Online Courses and Classes from edX](https://www.edx.org/learn/machine-learning)
# IoT Protocols
[Back to the Top](https://github.com/mikeroyal/Self-Hosting-Guide#table-of-contents)
[DBus](https://www.freedesktop.org/wiki/Software/dbus/) is an open source software bus developed Red Hat for inter-process communication, and remote procedure call mechanism that allows communication between multiple processes running concurrently on the same machine.
[SOAP](https://www.soapui.org) is a messaging protocol specification for exchanging structured information in the implementation of web services in computer networks. SOAP can extend HTTP for XML messaging. SOAP provides data transport for Web services. SOAP can exchange complete documents or call a remote procedure. SOAP can be used for broadcasting a message.
[gRPC](https://grpc.io) is a modern, open source remote procedure call (RPC) framework developed by Google that can run anywhere. It enables client and server applications to communicate transparently, and makes it easier to build connected systems.It uses HTTP/2 for transport, Protocol Buffers as the interface description language, and provides features such as authentication, bidirectional streaming and flow control, blocking or nonblocking bindings, and cancellation and timeouts.
[LWM2M](https://www.omaspecworks.org/what-is-oma-specworks/iot/lightweight-m2m-lwm2m/) is a protocol from the Open Mobile Alliance for M2M or IoT device management. Lightweight M2M enabler defines the application layer communication protocol between a LWM2M Server and a LWM2M Client, which is located in a LWM2M Device.
[Advanced Message Queuing Protocol (AMQP)](https://www.amqp.org) is an open standard for passing business messages between applications or organizations. It connects systems, feeds business processes with the information they need and reliably transmits onward the instructions that achieve their goals. The defining features of AMQP are message orientation, queuing, routing, reliability and security.
[Constrained Application Protocol (CoAP)](https://coap.technology) is a specialized web transfer protocol for use with constrained nodes and constrained networks in the Internet of Things. The protocol is designed for machine-to-machine (M2M) applications such as smart energy and building automation."
[Extensible Messaging and Presence Protocol (XMPP)](https://xmpp.org) is a communication protocol for message-oriented middleware based on XML (Extensible Markup Language). It enables the near real-time exchange of structured yet extensible data between any two or more network entities.
[OASIS Message Queuing Telemetry Transport (MQTT)](https://www.oasis-open.org) is an open OASIS and ISO standard (ISO/IEC 20922) lightweight, publish-subscribe network protocol that transports messages between devices. The protocol usually runs over TCP/IP; however, any network protocol that provides ordered, lossless, bi-directional connections can support MQTT.
[Very Simple Control Protocol (VSCP)](https://vscp.org) is a free automation protocol suitable for all sorts of automation task where building- or home-automation is in the main focus. Its main advantage is that each VSCP-node can work completely autonomous, being part of distributed network of other nodes.
# Operating systems
[Back to the Top](https://github.com/mikeroyal/Self-Hosting-Guide#table-of-contents)
[Raspberry Pi OS](https://www.raspberrypi.org/software/operating-systems/)
[Hass.io(Home Assistant OS)](https://www.home-assistant.io/hassio/installation/)
[Manjaro Linux ARM](https://manjaro.org/download/#ARM)
[Arch Linux ARM](https://archlinuxarm.org/platforms/armv8/broadcom/raspberry-pi-4)
[Ubuntu MATE for Raspberry Pi](https://ubuntu-mate.org/ports/raspberry-pi/)
[Ubuntu Desktop for Raspberry Pi](https://ubuntu.com/raspberry-pi)
[Ubuntu Core on a Raspberry Pi](https://ubuntu.com/download/raspberry-pi-core)
[Ubuntu Server for ARM](https://ubuntu.com/download/server/arm)
[Debian](https://wiki.debian.org)
[Fedora ARM](https://arm.fedoraproject.org)
[openSUSE](https://en.opensuse.org/openSUSE)
[SUSE](https://documentation.suse.com/)
[Kali Linux for the Raspberry Pi](https://www.kali.org/docs/arm/kali-linux-raspberry-pi/)
[RetroArch](https://www.retroarch.com/?page=platforms)
[RetroPie](https://retropie.org.uk/)
[LibreELEC](https://libreelec.tv/)
[OSMC](https://osmc.tv)
[RISC OS](https://www.riscosopen.org/content/)
[Windows 10 IoT Core](https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/iot-core/windows-iot-core)
[HeliOS](https://www.arduino.cc/reference/en/libraries/helios/) is an embedded operating system that is free for anyone to use. While called an operating system for simplicity, HeliOS is better described as a multitasking kernel for embedded systems.
[Simba](https://simba-os.readthedocs.io/en/latest/getting-started.html) is a small OS for an Embedded Programming Platform like Arduino. It aims to make embedded programming easy and portable.
[Trampoline](https://github.com/TrampolineRTOS/) is a static RTOS for small embedded systems.
[DuinOS](https://github.com/DuinOS/DuinOS) is Framework (a wrapper) for use the FreeRTOSwith Arduino.
[VxWorks](https://www.windriver.com/products/vxworks) is an industry-leading real-time operating systems (RTOS) for building embedded devices and systems for more than 30 years.
[LynxOS](https://www.lynx.com/products/lynxos-posix-real-time-operating-system-rtos) is a native POSIX, hard real-time partitioning operating system developed by Lynx Software Technologies.
[Zephyr OS](https://www.zephyrproject.org/zephyr-rtos-featured-in-risc-v-getting-started-guide/) is a popular security-oriented RTOS with a small-footprint kernel designed for use on resource-constrained and embedded systems. Zephyr has a small-foorprint Kernel focusing on embedded devices compatible with x86, ARM, RISC-V, Xtensa and [others](https://docs.zephyrproject.org/latest/boards/index.html).
[FreeRTOS](https://freertos.org/) is an open source, real-time operating system for microcontrollers that makes small, low-power edge devices easy to program, deploy, secure, connect, and manage.
[Arm Mbed TLS](https://os.mbed.com) provides a comprehensive SSL/TLS solution and makes it easy for developers to include cryptographic and SSL/TLS capabilities in their software and embedded products. As an SSL library, it provides an intuitive API, readable source code and a minimal and highly configurable code footprint.
[Contiki-os](https://github.com/contiki-os) is an operating system for networked, memory-constrained systems with a focus on low-power wireless Internet of Things devices.
# Middleware
[Back to the Top](https://github.com/mikeroyal/Self-Hosting-Guide#table-of-contents)
[IoTSyS](https://iotsyst.com) is an integration middleware for the Internet of Things. It provides a communication stack for embedded devices based on IPv6, Web services, and OBIX to establish interoperable interfaces for smart objects.
[OpenIoT](https://github.com/OpenIotOrg/openiot) is an open source middleware infrastructure will support flexible configuration and deployment of algorithms for collection, and filtering information streams stemming from the internet-connected objects, while at the same time generating and processing important business/applications events.
[OpenRemote](https://github.com/openremote/openremote) is an open source middleware project, which integrates many different protocols and solutions available for smart building, and smart city automation, and offers visualization tools.
[Kaa](https://www.kaaproject.org/platform/) is a Enterprise IoT Platform has been designed with heavy-duty, enterprise-grade IoT solutions in mind. It banishes a monolithic approach to architecture in favour of highly portable microservices, which allow for flexible rearrangement and customization even in the middle of the solution's lifecycle.
# Node flow editors
[Back to the Top](https://github.com/mikeroyal/Self-Hosting-Guide#table-of-contents)
[Node-RED](https://nodered.org) is a programming tool for wiring together hardware devices, APIs and online services in new and interesting ways. It provides a browser-based editor that makes it easy to wire together flows using the wide range of nodes in the palette that can be deployed to its runtime in a single-click.
### Toolkits
[Back to the Top](https://github.com/mikeroyal/Self-Hosting-Guide#table-of-contents)
[KinomaJS](https://github.com/Kinoma/kinomajs) is a visual code editor designed to help developers build starter projects for Kinoma Create and Kinoma Element. The project is built on Angular 2(RC7) and runs in a web browser. The live version is hosted using Google App Engine, but you can modify and build it yourself by following the instructions in this document.
[IoT Toolkit](https://www.segger.com/products/security-iot/iot-toolkit/) is a collection of libraries that enables communication with modern IoT based environments and devices. It is a high-performance collection of libraries optimized for minimum memory consumption in RAM, ROM, high speed, and versatility working on any device.
# Data Visualization
[Back to the Top](https://github.com/mikeroyal/Self-Hosting-Guide#table-of-contents)
[Freeboard](https://github.com/Freeboard/freeboard) is an open source real-time dashboard builder for IOT and other web mashups. A free open-source alternative to Geckoboard.
[ThingSpeak](https://thingspeak.com) is an IoT analytics platform service that allows you to aggregate, visualize, and analyze live data streams in the cloud. You can send data to ThingSpeak from your devices, create instant visualization of live data, and send alerts.
# Search
[Back to the Top](https://github.com/mikeroyal/Self-Hosting-Guide#table-of-contents)
[Thingful](https://www.thingful.net) is a Search Engine for the Internet of Things Find & use open IoT data from around the world.
# Hardware
[Back to the Top](https://github.com/mikeroyal/Self-Hosting-Guide#table-of-contents)
[Arduino Ethernet Shield 2](https://www.arduino.cc/en/Guide/ArduinoEthernetShield) allows an Arduino board to connect to the internet using the Ethernet library and to read and write an SD card using the SD library.This shield is fully compatible with the former version, but relies on the newer W5500 chip.
[Raspberry Pi](https://www.raspberrypi.org) is a series of small single-board computers developed in the United Kingdom by the Raspberry Pi Foundation to promote teaching of basic computer science in schools and in developing countries. Price range from $10-45 depending on model.
[BeagleBone](https://beagleboard.org/bone) is a low-power open-source single-board computer produced by Texas Instruments. It runs Android, Ubuntu and other Linux flavors.
[openPicus FlyportPro](https://www.open-electronics.org/flyport-professional-iot-modules-by-openpicus/) is a system on a module dedicated to IoT and M2M application, especially for professional use. Following some details on the solution: Why FlyportPRO SoM? A system-on-module is the best solution for those customers looking for flexibility and for development time and risk reduction.
[Pinoccio](https://www.open-electronics.org/pinoccio-wifi-mesh-networking-for-arduino-and-iot-available-now/) is a solution to add mesh networking capability and WiFi-Internet access to all yout IoT devices, and it is Arduino compatible. Each board can assume the role of Scout in a Troop and one of the Scouts is the Lead to connect internet: Field Scouts talk to each other using a mesh network (called a Troop), using an extremely low-power radio.
### In-memory data grids
[Back to the Top](https://github.com/mikeroyal/Self-Hosting-Guide#table-of-contents)
[Ehcache](https://www.ehcache.org) is an open source, standards-based cache that boosts performance, offloads your database, and simplifies scalability. It's the most widely-used Java-based cache because it's robust, proven, full-featured, and integrates with other popular libraries and frameworks.
[Hazelcast](https://hazelcast.com) is an open source in-memory data grid based on Java.
# Home automation
[Back to the Top](https://github.com/mikeroyal/Self-Hosting-Guide#table-of-contents)
[Home Assistant](https://github.com/home-assistant/core) is open source home automation that puts local control and privacy first. Powered by a worldwide community of tinkerers and DIY enthusiasts. Perfect to run on a Raspberry Pi or a local server.
[openHAB](https://github.com/openhab) is a cross-platform software with the aim to integrate all kinds of Smart Home technologies, devices, etc.
[Eclipse SmartHome](https://www.eclipse.org/smarthome/) is a framework, not a ready-to-use solution. It offers a large set of features to choose from and leaves enough possibilities to design a Smart Home solution specific to your expectations. Its modular design brings millions of combinations and proves to be easily extensible by custom parts.
[The Thing System](https://github.com/TheThingSystem) is a set of software components and network protocols that aims to fix the Internet of Things. Our steward software is written in node.js making it both portable and easily extensible. It can run on your laptop, or fit onto a small single board computer like the Raspberry Pi.
# Robotics
[Back to the Top](https://github.com/mikeroyal/Self-Hosting-Guide#table-of-contents)
## ML frameworks & applications
[TensorFlow](https://www.tensorflow.org) is an end-to-end open source platform for machine learning. It has a comprehensive, flexible ecosystem of tools, libraries and community resources that lets researchers push the state-of-the-art in ML and developers easily build and deploy ML powered applications.
[Tensorman](https://github.com/pop-os/tensorman) is a utility for easy management of Tensorflow containers by developed by [System76]( https://system76.com).Tensorman allows Tensorflow to operate in an isolated environment that is contained from the rest of the system. This virtual environment can operate independent of the base system, allowing you to use any version of Tensorflow on any version of a Linux distribution that supports the Docker runtime.
[Keras](https://keras.io) is a high-level neural networks API, written in Python and capable of running on top of TensorFlow, CNTK, or Theano.It was developed with a focus on enabling fast experimentation. It is capable of running on top of TensorFlow, Microsoft Cognitive Toolkit, R, Theano, or PlaidML.
[PyTorch](https://pytorch.org) is a library for deep learning on irregular input data such as graphs, point clouds, and manifolds. Primarily developed by Facebook's AI Research lab.
[Amazon SageMaker](https://aws.amazon.com/sagemaker/) is a fully managed service that provides every developer and data scientist with the ability to build, train, and deploy machine learning (ML) models quickly. SageMaker removes the heavy lifting from each step of the machine learning process to make it easier to develop high quality models.
[Azure Databricks](https://azure.microsoft.com/en-us/services/databricks/) is a fast and collaborative Apache Spark-based big data analytics service designed for data science and data engineering. Azure Databricks, sets up your Apache Spark environment in minutes, autoscale, and collaborate on shared projects in an interactive workspace. Azure Databricks supports Python, Scala, R, Java, and SQL, as well as data science frameworks and libraries including TensorFlow, PyTorch, and scikit-learn.
[Microsoft Cognitive Toolkit (CNTK)](https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/cognitive-toolkit/) is an open-source toolkit for commercial-grade distributed deep learning. It describes neural networks as a series of computational steps via a directed graph. CNTK allows the user to easily realize and combine popular model types such as feed-forward DNNs, convolutional neural networks (CNNs) and recurrent neural networks (RNNs/LSTMs). CNTK implements stochastic gradient descent (SGD, error backpropagation) learning with automatic differentiation and parallelization across multiple GPUs and servers.
[Apache Airflow](https://airflow.apache.org) is an open-source workflow management platform created by the community to programmatically author, schedule and monitor workflows. Install. Principles. Scalable. Airflow has a modular architecture and uses a message queue to orchestrate an arbitrary number of workers. Airflow is ready to scale to infinity.
[Open Neural Network Exchange(ONNX)](https://github.com/onnx) is an open ecosystem that empowers AI developers to choose the right tools as their project evolves. ONNX provides an open source format for AI models, both deep learning and traditional ML. It defines an extensible computation graph model, as well as definitions of built-in operators and standard data types.
[Apache MXNet](https://mxnet.apache.org/) is a deep learning framework designed for both efficiency and flexibility. It allows you to mix symbolic and imperative programming to maximize efficiency and productivity. At its core, MXNet contains a dynamic dependency scheduler that automatically parallelizes both symbolic and imperative operations on the fly. A graph optimization layer on top of that makes symbolic execution fast and memory efficient. MXNet is portable and lightweight, scaling effectively to multiple GPUs and multiple machines. Support for Python, R, Julia, Scala, Go, Javascript and more.
[AutoGluon](https://autogluon.mxnet.io/index.html) is toolkit for Deep learning that automates machine learning tasks enabling you to easily achieve strong predictive performance in your applications. With just a few lines of code, you can train and deploy high-accuracy deep learning models on tabular, image, and text data.
[Anaconda](https://www.anaconda.com/) is a very popular Data Science platform for machine learning and deep learning that enables users to develop models, train them, and deploy them.
[PlaidML](https://github.com/plaidml/plaidml) is an advanced and portable tensor compiler for enabling deep learning on laptops, embedded devices, or other devices where the available computing hardware is not well supported or the available software stack contains unpalatable license restrictions.
[OpenCV](https://opencv.org) is a highly optimized library with focus on real-time computer vision applications. The C++, Python, and Java interfaces support Linux, MacOS, Windows, iOS, and Android.
[Scikit-Learn](https://scikit-learn.org/stable/index.html) is a Python module for machine learning built on top of SciPy, NumPy, and matplotlib, making it easier to apply robust and simple implementations of many popular machine learning algorithms.
[Weka](https://www.cs.waikato.ac.nz/ml/weka/) is an open source machine learning software that can be accessed through a graphical user interface, standard terminal applications, or a Java API. It is widely used for teaching, research, and industrial applications, contains a plethora of built-in tools for standard machine learning tasks, and additionally gives transparent access to well-known toolboxes such as scikit-learn, R, and Deeplearning4j.
[Caffe](https://github.com/BVLC/caffe) is a deep learning framework made with expression, speed, and modularity in mind. It is developed by Berkeley AI Research (BAIR)/The Berkeley Vision and Learning Center (BVLC) and community contributors.
[Theano](https://github.com/Theano/Theano) is a Python library that allows you to define, optimize, and evaluate mathematical expressions involving multi-dimensional arrays efficiently including tight integration with NumPy.
[nGraph](https://github.com/NervanaSystems/ngraph) is an open source C++ library, compiler and runtime for Deep Learning. The nGraph Compiler aims to accelerate developing AI workloads using any deep learning framework and deploying to a variety of hardware targets.It provides the freedom, performance, and ease-of-use to AI developers.
[NVIDIA cuDNN](https://developer.nvidia.com/cudnn) is a GPU-accelerated library of primitives for [deep neural networks](https://developer.nvidia.com/deep-learning). cuDNN provides highly tuned implementations for standard routines such as forward and backward convolution, pooling, normalization, and activation layers. cuDNN accelerates widely used deep learning frameworks, including [Caffe2](https://caffe2.ai/), [Chainer](https://chainer.org/), [Keras](https://keras.io/), [MATLAB](https://www.mathworks.com/solutions/deep-learning.html), [MxNet](https://mxnet.incubator.apache.org/), [PyTorch](https://pytorch.org/), and [TensorFlow](https://www.tensorflow.org/).
[Jupyter Notebook](https://jupyter.org/) is an open-source web application that allows you to create and share documents that contain live code, equations, visualizations and narrative text. Jupyter is used widely in industries that do data cleaning and transformation, numerical simulation, statistical modeling, data visualization, data science, and machine learning.
[Apache Spark](https://spark.apache.org/) is a unified analytics engine for large-scale data processing. It provides high-level APIs in Scala, Java, Python, and R, and an optimized engine that supports general computation graphs for data analysis. It also supports a rich set of higher-level tools including Spark SQL for SQL and DataFrames, MLlib for machine learning, GraphX for graph processing, and Structured Streaming for stream processing.
[Apache Spark Connector for SQL Server and Azure SQL](https://github.com/microsoft/sql-spark-connector) is a high-performance connector that enables you to use transactional data in big data analytics and persists results for ad-hoc queries or reporting. The connector allows you to use any SQL database, on-premises or in the cloud, as an input data source or output data sink for Spark jobs.
[Apache PredictionIO](https://predictionio.apache.org/) is an open source machine learning framework for developers, data scientists, and end users. It supports event collection, deployment of algorithms, evaluation, querying predictive results via REST APIs. It is based on scalable open source services like Hadoop, HBase (and other DBs), Elasticsearch, Spark and implements what is called a Lambda Architecture.
[Cluster Manager for Apache Kafka(CMAK)](https://github.com/yahoo/CMAK) is a tool for managing [Apache Kafka](https://kafka.apache.org/) clusters.
[BigDL](https://bigdl-project.github.io/) is a distributed deep learning library for Apache Spark. With BigDL, users can write their deep learning applications as standard Spark programs, which can directly run on top of existing Spark or Hadoop clusters.
[Koalas](https://pypi.org/project/koalas/) is project makes data scientists more productive when interacting with big data, by implementing the pandas DataFrame API on top of Apache Spark.
[Apache Spark™ MLflow](https://mlflow.org/) is an open source platform to manage the ML lifecycle, including experimentation, reproducibility, deployment, and a central model registry. MLflow currently offers four components:
**[MLflow Tracking](https://mlflow.org/docs/latest/tracking.html)**: Record and query experiments: code, data, config, and results.
**[MLflow Projects](https://mlflow.org/docs/latest/projects.html)**: Package data science code in a format to reproduce runs on any platform.
**[MLflow Models](https://mlflow.org/docs/latest/models.html)**: Deploy machine learning models in diverse serving environments.
**[Model Registry](https://mlflow.org/docs/latest/model-registry.html)**: Store, annotate, discover, and manage models in a central repository.
[Eclipse Deeplearning4J (DL4J)](https://deeplearning4j.konduit.ai/) is a set of projects intended to support all the needs of a JVM-based(Scala, Kotlin, Clojure, and Groovy) deep learning application. This means starting with the raw data, loading and preprocessing it from wherever and whatever format it is in to building and tuning a wide variety of simple and complex deep learning networks.
[Numba](https://github.com/numba/numba) is an open source, NumPy-aware optimizing compiler for Python sponsored by Anaconda, Inc. It uses the LLVM compiler project to generate machine code from Python syntax. Numba can compile a large subset of numerically-focused Python, including many NumPy functions. Additionally, Numba has support for automatic parallelization of loops, generation of GPU-accelerated code, and creation of ufuncs and C callbacks.
[Chainer](https://chainer.org/) is a Python-based deep learning framework aiming at flexibility. It provides automatic differentiation APIs based on the define-by-run approach (dynamic computational graphs) as well as object-oriented high-level APIs to build and train neural networks. It also supports CUDA/cuDNN using [CuPy](https://github.com/cupy/cupy) for high performance training and inference.
[cuML](https://github.com/rapidsai/cuml) is a suite of libraries that implement machine learning algorithms and mathematical primitives functions that share compatible APIs with other RAPIDS projects. cuML enables data scientists, researchers, and software engineers to run traditional tabular ML tasks on GPUs without going into the details of CUDA programming. In most cases, cuML's Python API matches the API from scikit-learn.
## Online ML Learning Resources
[Machine Learning by Stanford University from Coursera](https://www.coursera.org/learn/machine-learning)
[Machine Learning Courses Online from Coursera](https://www.coursera.org/courses?query=machine%20learning&)
[Machine Learning Courses Online from Udemy](https://www.udemy.com/topic/machine-learning/)
[Learn Machine Learning with Online Courses and Classes from edX](https://www.edx.org/learn/machine-learning)
# IoT Protocols
[Back to the Top](https://github.com/mikeroyal/Self-Hosting-Guide#table-of-contents)
[DBus](https://www.freedesktop.org/wiki/Software/dbus/) is an open source software bus developed Red Hat for inter-process communication, and remote procedure call mechanism that allows communication between multiple processes running concurrently on the same machine.
[SOAP](https://www.soapui.org) is a messaging protocol specification for exchanging structured information in the implementation of web services in computer networks. SOAP can extend HTTP for XML messaging. SOAP provides data transport for Web services. SOAP can exchange complete documents or call a remote procedure. SOAP can be used for broadcasting a message.
[gRPC](https://grpc.io) is a modern, open source remote procedure call (RPC) framework developed by Google that can run anywhere. It enables client and server applications to communicate transparently, and makes it easier to build connected systems.It uses HTTP/2 for transport, Protocol Buffers as the interface description language, and provides features such as authentication, bidirectional streaming and flow control, blocking or nonblocking bindings, and cancellation and timeouts.
[LWM2M](https://www.omaspecworks.org/what-is-oma-specworks/iot/lightweight-m2m-lwm2m/) is a protocol from the Open Mobile Alliance for M2M or IoT device management. Lightweight M2M enabler defines the application layer communication protocol between a LWM2M Server and a LWM2M Client, which is located in a LWM2M Device.
[Advanced Message Queuing Protocol (AMQP)](https://www.amqp.org) is an open standard for passing business messages between applications or organizations. It connects systems, feeds business processes with the information they need and reliably transmits onward the instructions that achieve their goals. The defining features of AMQP are message orientation, queuing, routing, reliability and security.
[Constrained Application Protocol (CoAP)](https://coap.technology) is a specialized web transfer protocol for use with constrained nodes and constrained networks in the Internet of Things. The protocol is designed for machine-to-machine (M2M) applications such as smart energy and building automation."
[Extensible Messaging and Presence Protocol (XMPP)](https://xmpp.org) is a communication protocol for message-oriented middleware based on XML (Extensible Markup Language). It enables the near real-time exchange of structured yet extensible data between any two or more network entities.
[OASIS Message Queuing Telemetry Transport (MQTT)](https://www.oasis-open.org) is an open OASIS and ISO standard (ISO/IEC 20922) lightweight, publish-subscribe network protocol that transports messages between devices. The protocol usually runs over TCP/IP; however, any network protocol that provides ordered, lossless, bi-directional connections can support MQTT.
[Very Simple Control Protocol (VSCP)](https://vscp.org) is a free automation protocol suitable for all sorts of automation task where building- or home-automation is in the main focus. Its main advantage is that each VSCP-node can work completely autonomous, being part of distributed network of other nodes.
# Operating systems
[Back to the Top](https://github.com/mikeroyal/Self-Hosting-Guide#table-of-contents)
[Raspberry Pi OS](https://www.raspberrypi.org/software/operating-systems/)
[Hass.io(Home Assistant OS)](https://www.home-assistant.io/hassio/installation/)
[Manjaro Linux ARM](https://manjaro.org/download/#ARM)
[Arch Linux ARM](https://archlinuxarm.org/platforms/armv8/broadcom/raspberry-pi-4)
[Ubuntu MATE for Raspberry Pi](https://ubuntu-mate.org/ports/raspberry-pi/)
[Ubuntu Desktop for Raspberry Pi](https://ubuntu.com/raspberry-pi)
[Ubuntu Core on a Raspberry Pi](https://ubuntu.com/download/raspberry-pi-core)
[Ubuntu Server for ARM](https://ubuntu.com/download/server/arm)
[Debian](https://wiki.debian.org)
[Fedora ARM](https://arm.fedoraproject.org)
[openSUSE](https://en.opensuse.org/openSUSE)
[SUSE](https://documentation.suse.com/)
[Kali Linux for the Raspberry Pi](https://www.kali.org/docs/arm/kali-linux-raspberry-pi/)
[RetroArch](https://www.retroarch.com/?page=platforms)
[RetroPie](https://retropie.org.uk/)
[LibreELEC](https://libreelec.tv/)
[OSMC](https://osmc.tv)
[RISC OS](https://www.riscosopen.org/content/)
[Windows 10 IoT Core](https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/iot-core/windows-iot-core)
[HeliOS](https://www.arduino.cc/reference/en/libraries/helios/) is an embedded operating system that is free for anyone to use. While called an operating system for simplicity, HeliOS is better described as a multitasking kernel for embedded systems.
[Simba](https://simba-os.readthedocs.io/en/latest/getting-started.html) is a small OS for an Embedded Programming Platform like Arduino. It aims to make embedded programming easy and portable.
[Trampoline](https://github.com/TrampolineRTOS/) is a static RTOS for small embedded systems.
[DuinOS](https://github.com/DuinOS/DuinOS) is Framework (a wrapper) for use the FreeRTOSwith Arduino.
[VxWorks](https://www.windriver.com/products/vxworks) is an industry-leading real-time operating systems (RTOS) for building embedded devices and systems for more than 30 years.
[LynxOS](https://www.lynx.com/products/lynxos-posix-real-time-operating-system-rtos) is a native POSIX, hard real-time partitioning operating system developed by Lynx Software Technologies.
[Zephyr OS](https://www.zephyrproject.org/zephyr-rtos-featured-in-risc-v-getting-started-guide/) is a popular security-oriented RTOS with a small-footprint kernel designed for use on resource-constrained and embedded systems. Zephyr has a small-foorprint Kernel focusing on embedded devices compatible with x86, ARM, RISC-V, Xtensa and [others](https://docs.zephyrproject.org/latest/boards/index.html).
[FreeRTOS](https://freertos.org/) is an open source, real-time operating system for microcontrollers that makes small, low-power edge devices easy to program, deploy, secure, connect, and manage.
[Arm Mbed TLS](https://os.mbed.com) provides a comprehensive SSL/TLS solution and makes it easy for developers to include cryptographic and SSL/TLS capabilities in their software and embedded products. As an SSL library, it provides an intuitive API, readable source code and a minimal and highly configurable code footprint.
[Contiki-os](https://github.com/contiki-os) is an operating system for networked, memory-constrained systems with a focus on low-power wireless Internet of Things devices.
# Middleware
[Back to the Top](https://github.com/mikeroyal/Self-Hosting-Guide#table-of-contents)
[IoTSyS](https://iotsyst.com) is an integration middleware for the Internet of Things. It provides a communication stack for embedded devices based on IPv6, Web services, and OBIX to establish interoperable interfaces for smart objects.
[OpenIoT](https://github.com/OpenIotOrg/openiot) is an open source middleware infrastructure will support flexible configuration and deployment of algorithms for collection, and filtering information streams stemming from the internet-connected objects, while at the same time generating and processing important business/applications events.
[OpenRemote](https://github.com/openremote/openremote) is an open source middleware project, which integrates many different protocols and solutions available for smart building, and smart city automation, and offers visualization tools.
[Kaa](https://www.kaaproject.org/platform/) is a Enterprise IoT Platform has been designed with heavy-duty, enterprise-grade IoT solutions in mind. It banishes a monolithic approach to architecture in favour of highly portable microservices, which allow for flexible rearrangement and customization even in the middle of the solution's lifecycle.
# Node flow editors
[Back to the Top](https://github.com/mikeroyal/Self-Hosting-Guide#table-of-contents)
[Node-RED](https://nodered.org) is a programming tool for wiring together hardware devices, APIs and online services in new and interesting ways. It provides a browser-based editor that makes it easy to wire together flows using the wide range of nodes in the palette that can be deployed to its runtime in a single-click.
### Toolkits
[Back to the Top](https://github.com/mikeroyal/Self-Hosting-Guide#table-of-contents)
[KinomaJS](https://github.com/Kinoma/kinomajs) is a visual code editor designed to help developers build starter projects for Kinoma Create and Kinoma Element. The project is built on Angular 2(RC7) and runs in a web browser. The live version is hosted using Google App Engine, but you can modify and build it yourself by following the instructions in this document.
[IoT Toolkit](https://www.segger.com/products/security-iot/iot-toolkit/) is a collection of libraries that enables communication with modern IoT based environments and devices. It is a high-performance collection of libraries optimized for minimum memory consumption in RAM, ROM, high speed, and versatility working on any device.
# Data Visualization
[Back to the Top](https://github.com/mikeroyal/Self-Hosting-Guide#table-of-contents)
[Freeboard](https://github.com/Freeboard/freeboard) is an open source real-time dashboard builder for IOT and other web mashups. A free open-source alternative to Geckoboard.
[ThingSpeak](https://thingspeak.com) is an IoT analytics platform service that allows you to aggregate, visualize, and analyze live data streams in the cloud. You can send data to ThingSpeak from your devices, create instant visualization of live data, and send alerts.
# Search
[Back to the Top](https://github.com/mikeroyal/Self-Hosting-Guide#table-of-contents)
[Thingful](https://www.thingful.net) is a Search Engine for the Internet of Things Find & use open IoT data from around the world.
# Hardware
[Back to the Top](https://github.com/mikeroyal/Self-Hosting-Guide#table-of-contents)
[Arduino Ethernet Shield 2](https://www.arduino.cc/en/Guide/ArduinoEthernetShield) allows an Arduino board to connect to the internet using the Ethernet library and to read and write an SD card using the SD library.This shield is fully compatible with the former version, but relies on the newer W5500 chip.
[Raspberry Pi](https://www.raspberrypi.org) is a series of small single-board computers developed in the United Kingdom by the Raspberry Pi Foundation to promote teaching of basic computer science in schools and in developing countries. Price range from $10-45 depending on model.
[BeagleBone](https://beagleboard.org/bone) is a low-power open-source single-board computer produced by Texas Instruments. It runs Android, Ubuntu and other Linux flavors.
[openPicus FlyportPro](https://www.open-electronics.org/flyport-professional-iot-modules-by-openpicus/) is a system on a module dedicated to IoT and M2M application, especially for professional use. Following some details on the solution: Why FlyportPRO SoM? A system-on-module is the best solution for those customers looking for flexibility and for development time and risk reduction.
[Pinoccio](https://www.open-electronics.org/pinoccio-wifi-mesh-networking-for-arduino-and-iot-available-now/) is a solution to add mesh networking capability and WiFi-Internet access to all yout IoT devices, and it is Arduino compatible. Each board can assume the role of Scout in a Troop and one of the Scouts is the Lead to connect internet: Field Scouts talk to each other using a mesh network (called a Troop), using an extremely low-power radio.
### In-memory data grids
[Back to the Top](https://github.com/mikeroyal/Self-Hosting-Guide#table-of-contents)
[Ehcache](https://www.ehcache.org) is an open source, standards-based cache that boosts performance, offloads your database, and simplifies scalability. It's the most widely-used Java-based cache because it's robust, proven, full-featured, and integrates with other popular libraries and frameworks.
[Hazelcast](https://hazelcast.com) is an open source in-memory data grid based on Java.
# Home automation
[Back to the Top](https://github.com/mikeroyal/Self-Hosting-Guide#table-of-contents)
[Home Assistant](https://github.com/home-assistant/core) is open source home automation that puts local control and privacy first. Powered by a worldwide community of tinkerers and DIY enthusiasts. Perfect to run on a Raspberry Pi or a local server.
[openHAB](https://github.com/openhab) is a cross-platform software with the aim to integrate all kinds of Smart Home technologies, devices, etc.
[Eclipse SmartHome](https://www.eclipse.org/smarthome/) is a framework, not a ready-to-use solution. It offers a large set of features to choose from and leaves enough possibilities to design a Smart Home solution specific to your expectations. Its modular design brings millions of combinations and proves to be easily extensible by custom parts.
[The Thing System](https://github.com/TheThingSystem) is a set of software components and network protocols that aims to fix the Internet of Things. Our steward software is written in node.js making it both portable and easily extensible. It can run on your laptop, or fit onto a small single board computer like the Raspberry Pi.
# Robotics
[Back to the Top](https://github.com/mikeroyal/Self-Hosting-Guide#table-of-contents)

## Tools for Robotics
[Open Source Robotics Foundation](https://www.openrobotics.org/) works with industry, academia, and government to create and support open software and hardware for use in robotics, from research and education to product development.
[ROS](https://www.ros.org/) is robotics middleware. Although ROS is not an operating system, it provides services designed for a heterogeneous computer cluster such as hardware abstraction, low-level device control, implementation of commonly used functionality, message-passing between processes, and package management.
[ROS2](https://index.ros.org/doc/ros2/) is a set of [software libraries and tools](https://github.com/ros2) that help you build robot applications. From drivers to state-of-the-art algorithms, and with powerful developer tools, ROS has what you need for your next robotics project. And it’s all open source.
[Robot Framework](https://robotframework.org/) is a generic open source automation framework. It can be used for test automation and robotic process automation. It has easy syntax, utilizing human-readable keywords. Its capabilities can be extended by libraries implemented with Python or Java.
[The Robotics Library (RL)](https://github.com/roboticslibrary/rl) is a self-contained C++ library for robot kinematics, motion planning and control. It covers mathematics, kinematics and dynamics, hardware abstraction, motion planning, collision detection, and visualization.RL runs on many different systems, including Linux, macOS, and Windows. It uses CMake as a build system and can be compiled with Clang, GCC, and Visual Studio.
[MoveIt](https://moveit.ros.org/) is the most widely used software for manipulation and has been used on over 100 robots. It provides an easy-to-use robotics platform for developing advanced applications, evaluating new designs and building integrated products for industrial, commercial, R&D, and other domains.
[AutoGluon](https://autogluon.mxnet.io/index.html) is toolkit for [Deep learning](https://gitlab.com/maos20008/intro-to-machine-learning) that automates machine learning tasks enabling you to easily achieve strong predictive performance in your applications. With just a few lines of code, you can train and deploy high-accuracy deep learning models on tabular, image, and text data.
[Gazebo](http://gazebosim.org/) accurately and efficiently simulates indoor and outdoor robots. You get a robust physics engine, high-quality graphics, and programmatic and graphical interfaces.
[Robotics System Toolbox](https://www.mathworks.com/products/robotics.html) provides tools and algorithms for designing, simulating, and testing manipulators, mobile robots, and humanoid robots. For manipulators and humanoid robots, the toolbox includes algorithms for collision checking, trajectory generation, forward and inverse kinematics, and dynamics using a rigid body tree representation.
For mobile robots, it includes algorithms for mapping, localization, path planning, path following, and motion control. The toolbox provides reference examples of common industrial robot applications. It also includes a library of
commercially available industrial robot models that you can import, visualize, and simulate.
[Intel Robot DevKit](https://github.com/intel/robot_devkit) is the tool to generate Robotics Software Development Kit (RDK) designed for autonomous devices, including the ROS2 core and capacibilities packages like perception, planning, control driver etc. It provides flexible build/runtime configurations to meet different autonomous requirement on top of diversity hardware choices, for example use different hareware engine CPU/GPU/VPU to accelerate AI related features.
[Arduino](https://www.arduino.cc/) is an open-source platform used for building electronics projects. Arduino consists of both a physical programmable circuit board (often referred to as a microcontroller) and a piece of software, or IDE (Integrated Development Environment) that runs on your computer, used to write and upload computer code to the physical board.
[ArduPilot](https://ardupilot.org/ardupilot/index.html) enables the creation and use of trusted, autonomous, unmanned vehicle systems for the peaceful benefit of all. ArduPilot provides a comprehensive suite of tools suitable for almost any vehicle and application.
[AirSim](https://github.com/Microsoft/AirSim) is a simulator for drones, cars and more, built on Unreal Engine (we now also have an experimental Unity release). It is open-source, cross platform, and supports hardware-in-loop with popular flight controllers such as PX4 for physically and visually realistic simulations.
[F´ (F Prime)](https://github.com/nasa/fprime) is a component-driven framework that enables rapid development and deployment of spaceflight and other embedded software applications. Originally developed at the Jet Propulsion Laboratory, F´ has been successfully deployed on several space applications.
[The JPL Open Source Rover](https://github.com/nasa-jpl/open-source-rover) is an open source, build it yourself, scaled down version of the 6 wheel rover design that JPL uses to explore the surface of Mars. The Open Source Rover is designed almost entirely out of consumer off the shelf (COTS) parts. This project is intended to be a teaching and learning experience for those who want to get involved in mechanical engineering, software, electronics, or robotics.
[Light Detection and Ranging(LiDAR)](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lidar) is a remote sensing method that uses light in the form of a pulsed laser at an object, and uses the time and wavelength of the reflected beam of light to estimate the distance and in some applications ([Laser Imaging](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Laser_scanning)), to create a 3D representation of the object and its surface characteristics. This technology is commonly used in aircraft and self-driving vehicles.
[Neurorobotics Platform (NRP)](https://neurorobotics.net/) is an Internet-accessible simulation system that allows the simulation of robots controlled by spiking neural networks.
[ViSP](http://visp.inria.fr/) is an open-source visual servoing platform library, is able to compute control laws that can be applied to robotic systems.
[ROS Behavior Trees](https://github.com/miccol/ROS-Behavior-Tree) is an open-source library to create robot's behaviors in form of Behavior Trees running in ROS (Robot Operating System).
[g2core](https://github.com/synthetos/g2) is an open-source motion control software for CNC and Robotics, designed to run on Arduino Due class microcontrollers.
[ur5controller](https://github.com/roboticsleeds/ur5controller) is an open-source OpenRAVE controller for UR5 robot integrated with ROS.
[RBDL](https://github.com/rbdl/rbdl) is an open-source (zlib) C++ libray for both forward and inverse dynamics and kinematics. Also supports contacts and loops.
[Unity Robotics Hub](https://github.com/Unity-Technologies/Unity-Robotics-Hub) is a Central repository for open-source Unity packages, tutorials, and other resources demonstrating how to use Unity for robotics simulations. Includes new support for ROS integration.
[AliceVision](https://github.com/alicevision/AliceVision) is a Photogrammetric Computer Vision Framework which provides a 3D Reconstruction and Camera Tracking algorithms. AliceVision aims to provide strong software basis with state-of-the-art computer vision algorithms that can be tested, analyzed and reused. The project is a result of collaboration between academia and industry to provide cutting-edge algorithms with the robustness and the quality required for production usage.
[CARLA](https://github.com/carla-simulator/carla) is an open-source simulator for autonomous driving research. CARLA has been developed from the ground up to support development, training, and validation of autonomous driving systems. In addition to open-source code and protocols, CARLA provides open digital assets (urban layouts, buildings, vehicles) that were created for this purpose and can be used freely. The simulation platform supports flexible specification of sensor suites and environmental conditions.
[ROS bridge](https://github.com/carla-simulator/ros-bridge) is a package to bridge ROS for CARLA Simulator.
[ROS-Industrial](https://rosindustrial.org/) is an open source project that extends the advanced capabilities of ROS software to manufacturing.
[AWS RoboMaker](https://aws.amazon.com/robomaker/) is the most complete cloud solution for robotic developers to simulate, test and securely deploy robotic applications at scale. RoboMaker provides a fully-managed, scalable infrastructure for simulation that customers use for multi-robot simulation and CI/CD integration with regression testing in simulation.
[Microsoft Robotics Developer Studio](https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/download/details.aspx?id=29081) is a free .NET-based programming environment for building robotics applications.
[Visual Studio Code Extension for ROS](https://github.com/ms-iot/vscode-ros) is an extension provides support for Robot Operating System (ROS) development.
[Azure Kinect ROS Driver](https://github.com/microsoft/azure_kinect_ros_driver) is a node which publishes sensor data from the [Azure Kinect Developer Kit](https://azure.microsoft.com/en-us/services/kinect-dk/) to the [Robot Operating System (ROS)](http://www.ros.org/). Developers working with ROS can use this node to connect an Azure Kinect Developer Kit to an existing ROS installation.
[Azure IoT Hub for ROS](https://github.com/microsoft/ros_azure_iothub) is a ROS package works with the Microsoft Azure IoT Hub service to relay telemetry messages from the Robot to Azure IoT Hub or reflect properties from the Digital Twin to the robot using dynamic reconfigure.
[ROS 2 with ONNX Runtime](https://github.com/ms-iot/ros_msft_onnx) is a program that uses ROS 2 to run on different hardware platforms using their respective AI acceleration libraries for optimized execution of the ONNX model.
[Azure Cognitive Services LUIS ROS Node](https://github.com/ms-iot/ros_msft_luis) is a ROS node that bridges between ROS and the Azure Language Understanding Service. it can be configured to process audio directly from a microphone, or can subscribe to a ROS audio topic, then processes speech and generates "intent" ROS messages which can be processed by another ROS node to generate ROS commands.
## Robotics Learning Resources
[Robotics courses from Coursera](https://www.edx.org/learn/robotics)
[Learn Robotics with Online Courses and Classes from edX](https://www.edx.org/learn/robotics)
[Top Robotics Courses Online from Udemy](https://www.udemy.com/topic/robotics/)
[Free Online AI & Robotics Courses](https://www.futurelearn.com/subjects/it-and-computer-science-courses/ai-and-robotics)
[REC Foundation Robotics Industry Certification](https://www.roboticseducation.org/industry-certifications/)
[Carnegie Mellon Robotics Academy](https://www.cmu.edu/roboticsacademy/Training/Certifications.html)
[RIA Robotic Integrator Certification Program](https://www.robotics.org/robotics/integrator-certification)
[AWS RoboMaker – Develop, Test, Deploy, and Manage Intelligent Robotics Apps](https://aws.amazon.com/blogs/aws/aws-robomaker-develop-test-deploy-and-manage-intelligent-robotics-apps/)
[Microsoft AI School](https://aischool.microsoft.com/en-us/home)
[Language Understanding (LUIS) for Azure Cognitive Services](https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/cognitive-services/luis/what-is-luis)
[Azure VM templates to bootstrap ROS and ROS 2 environments](https://ms-iot.github.io/ROSOnWindows/ROSAtMS/AzureVM.html)
[Google Robotics Research](https://research.google/teams/brain/robotics/)
# Mesh networks
[Back to the Top](https://github.com/mikeroyal/Self-Hosting-Guide#table-of-contents)
[Zigbee](https://csa-iot.org/all-solutions/zigbee/) is the full-stack, secure, reliable, and market-proven solution used by a majority of large smart home ecosystem providers, such as Amazon's Echo Plus, Samsung SmartThings, Signify (Philips Hue), and more.
[Open Garden](https://opengarden.com) develops the FireChat mobile application, which enables peer-to-peer mobile Internet connection sharing with faster and more efficient data transmissions by automatically and actively choosing and switching to the best available network without requiring users to manually sift through available networks to find the best one available.
[OpenWSN](https://github.com/openwsn-berkeley/) is a project created at the University of California Berkeley and extended at the INRIA and at the Open University of Catalonia which aims to build an open standard-based and open source implementation of a complete constrained network protocol stack for wireless sensor networks and Internet of Things.
# Blockchain Development
[Back to the Top](https://github.com/mikeroyal/Self-Hosting-Guide#table-of-contents)

## Blockchain Learning Resources
[Blockchain](https://www.blockchain.com/) is a distributed database meaning that the storage devices used for the database are not all connected to a common processor. It maintains a growing decentralized digital list of ordered records, called blocks. Each block has a timestamp and a link to a previous block. By the system being decentralization it allows for complete transparency in all shared information.
[IBM Blockchain Essentials](https://www.ibm.com/skills/topics/blockchain/)
[Getting started with Blockchain Development](https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/learn/paths/ethereum-blockchain-development/)
[Blockchain Developer Nanodegree program | Udacity](https://www.udacity.com/course/blockchain-developer-nanodegree--nd1309)
[Blockchain Programming: Build a blockchain and cryptocurrency from scratch using Python | Udemy](https://www.udemy.com/course/build-your-own-cryptocurrency-in-48-hours/)
[Blockchain Courses by Coursera](https://www.coursera.org/courses?query=blockchain)
[Blockchain Courses by edX](https://www.edx.org/learn/blockchain)
[Blockchain Certifications](https://www.blockchain-council.org/)
## Blockchain Tools, Libraries and Frameworks
[Lightning Network (LN)](https://lightning.network/) is a decentralized network using smart contract functionality in the blockchain to enable instant payments across a network of participants. It was created in response to scalability issues with Bitcoin, namely the speed and cost of Bitcoin transactions. Bitcoin's current theoretical maximum transactions per second (TPS) is 10, though in reality it is between 3 and 7.

[Hyperledger](https://www.hyperledger.org) is an open source community focused on developing a suite of stable frameworks, tools and libraries for enterprise-grade blockchain deployments. It serves as a neutral home for various distributed ledger frameworks including Hyperledger Fabric, Sawtooth, Indy, as well as tools like Hyperledger Caliper and libraries like Hyperledger Ursa.
[Hyperledger Caliper](https://www.hyperledger.org/use/caliper) is a blockchain benchmark tool, it allows users to measure the performance of a blockchain implementation with a set of predefined use cases. Hyperledger Caliper will produce reports containing a number of performance indicators to serve as a reference when using the following blockchain solutions: Hyperledger Besu, Hyperledger Burrow, Ethereum, Hyperledger Fabric, FISCO BCOS, Hyperledger Iroha and Hyperledger Sawtooth.
[Hyperledger Ursa](https://www.hyperledger.org/use/ursa) is a shared cryptographic library, it enables implementations to avoid duplicating other cryptographic work and hopefully increase security in the process. The library is an opt-in repository (for Hyperledger and non Hyperledger projects) to place and use crypto. Hyperledger Ursa consists of sub-projects, which are cohesive implementations of cryptographic code or interfaces to cryptographic code.
[Hyperledger Fabric](https://wiki.hyperledger.org/display/fabric) is an enterprise-grade permissioned distributed ledger framework for developing solutions and applications. Its modular and versatile design satisfies a broad range of industry use cases. It offers a unique approach to consensus that enables performance at scale while preserving privacy.
[Geth](https://geth.ethereum.org/) is an implementation of an [Ethereum](https://ethereum.org/en/) node in the Go programming language.
[Solidity](https://solidity.readthedocs.io/) is a purposefully slimmed down, loosely-typed language with a syntax very similar to ECMAScript (Javascript) that is used for the creation of smart contracts on the Ethereum blockchain.
[GanacheCLI (NodeJS package)](https://www.trufflesuite.com/ganache) is a fast and customizable blockchain emulator. It simulates the Ethereum network on a single computer and allows you to make calls to the blockchain without any of the hassles of running a real Ethereum node.
[Truffle](https://trufflesuite.com/) is a development environment, testing framework and asset pipeline for Ethereum, aiming to make life as an Ethereum developer easier.
[Ethers.js](https://github.com/ethers-io/ethers.js/) is a library which was made for and is used by ethers.io. It is designed to make it easier to write client-side JavaScript based wallets, keeping the private key on the owner’s machine at all times.
[OpenEthereum](https://github.com/openethereum/openethereum) is a fast and feature-rich multi-network Ethereum client.
[Quorum](https://www.goquorum.com/) is an Ethereum-based distributed ledger protocol with transaction/contract privacy and new consensus mechanisms.
[Diesel](https://diesel.rs/) is a safe, extensible ORM and Query Builder for [Rust](https://www.rust-lang.org/).
[BlockShell](https://github.com/daxeel/blockshell) is a minimal command line utility for learning Blockchain technical concepts like chaining & mining.
[Tendermint Core](https://tendermint.com/) is [Byzantine Fault Tolerant (BFT)](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Byzantine_fault_tolerance) middleware that takes a state transition machine written in any programming language and securely replicates it on many machines.
[inDEX](https://distribuyed.github.io/index/) is a comprehensive list of decentralized exchanges (DEX) of cryptocurrencies, tokens, derivatives and futures, and their protocols.
[Squeezer](https://squeezer.io/) is a platform that empowers new-entry blockchain developers to build serverless dApps easily.
# Node.js Development
[Back to the Top](https://github.com/mikeroyal/Self-Hosting-Guide#table-of-contents)

## Node.js Learning Resources
[Node.js](https://nodejs.org/) is a JavaScript runtime built on Chrome's V8 JavaScript engine that lets developers write command line tools and server-side scripts outside of a browser.
[Node.js Build Working Group](https://github.com/nodejs/build) maintains and controls infrastructure used for continuous integration (CI), releases, benchmarks, web hosting (of nodejs.org and other Node.js web properties) and more.
[The OpenJS Foundation](https://openjsf.org/) is made up of 32 open source JavaScript projects including Appium, Dojo, Electron, jQuery, Node.js, and webpack. The foundation's mission is to support the healthy growth of JavaScript and web technologies by providing a neutral organization to host and sustain projects, as well as collaboratively fund activities that benefit the ecosystem as a whole.
[Set up NodeJS on WSL 2](https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/nodejs/setup-on-wsl2)
[Getting started with Node.js in Google Cloud](https://cloud.google.com/nodejs/getting-started)
[Getting Started with Node.js in AWS](https://docs.aws.amazon.com/sdk-for-javascript/v2/developer-guide/getting-started-nodejs.html)
[Node.js App Hosting & Deployment in Microsoft Azure](https://azure.microsoft.com/en-us/develop/nodejs/)
[The Node.js best practices list ](https://github.com/goldbergyoni/nodebestpractices)
[Introduction to Node.js by W3Schools](https://www.w3schools.com/nodejs/nodejs_intro.asp)
[The Node.js Community Committee](https://github.com/nodejs/community-committee)
[Node.js Mentorship Program Initiative](https://github.com/nodejs/mentorship)
[Node.js tutorial in Visual Studio Code](https://code.visualstudio.com/docs/nodejs/nodejs-tutorial)
[Server-side Development with NodeJS, Express and MongoDB on Coursera](https://www.coursera.org/learn/server-side-nodejs)
## Node.js Tools
[NPM](https://www.npmjs.com/) is the company behind Node package manager, the npm Registry, and npm CLI.
[node-gyp](https://github.com/nodejs/node-gyp) is a cross-platform command-line tool written in Node.js for compiling native addon modules for Node.js. It contains a vendored copy of the gyp-next project that was previously used by the Chromium team, extended to support the development of Node.js native addons.
[nvm ](https://github.com/nvm-sh/nvm) is a version manager for node.js, designed to be installed per-user, and invoked per-shell. nvm works on any POSIX-compliant shell (sh, dash, ksh, zsh, bash), in particular on these platforms: unix, macOS, and windows WSL.
[node-docker](https://hub.docker.com/_/node/) is the official Node.js docker image, made with love by the node community.
[Mocha](https://github.com/mochajs/mocha) is a simple, flexible, fun JavaScript test framework for Node.js & The Browser.
[AVA](https://github.com/avajs/ava) is a test runner for Node.js with a concise API, detailed error output, embrace of new language features and process isolation that lets you develop with confidence.
[egg](https://eggjs.org/) is a born to build better enterprise frameworks and apps with Node.js & Koa.
[mysqljs](https://github.com/mysqljs/mysql) is a pure node.js JavaScript Client implementing the MySQL protocol.
[axios](https://github.com/axios/axios) is a promise based HTTP client for the browser and node.js.
[Fastify](https://www.fastify.io/) is a fast and low overhead web framework, for Node.js.
[Express](https://expressjs.com/) is a fast, unopinionated, minimalist web framework for node.
[Meteor](https://www.meteor.com/) is an ultra-simple environment for building modern web applications with JavavScript.
[NW.js](https://nwjs.io/) is an app runtime based on Chromium and node.js. You can write native apps in HTML and JavaScript with NW.js. It also lets you call Node.js modules directly from the DOM and enables a new way of writing native applications with all Web technologies.
[PM2](https://pm2.io/) is a production process manager for Node.js applications with a built-in load balancer. It allows you to keep applications alive forever, to reload them without downtime and to facilitate common system admin tasks.
[NestJS](https://nestjs.com/) is a framework for building efficient, scalable Node.js web applications. It uses modern JavaScript, is built with TypeScript and combines elements of OOP (Object Oriented Progamming), FP (Functional Programming), and FRP (Functional Reactive Programming).
[jenkins-nodejs](https://plugins.jenkins.io/nodejs/) is a Jenkins plugin for Node.js that provides the NodeJS auto-installer, allowing to create as many NodeJS installations "profiles" as you want.
[Strapi](https://strapi.io/) is an open source Node.js Headless CMS to easily build customisable APIs.
[Standard](https://standardjs.com/) is a JavaScript Style Guide, with linter & automatic code fixer.
[React Starter Kit](https://www.reactstarterkit.com/) is an isomorphic web app boilerplate for web development built on top of [Node.js](https://nodejs.org/), [Express](http://expressjs.com/), [GraphQL](http://graphql.org/) and [React](https://facebook.github.io/react/), containing modern web development tools such as [Webpack](https://webpack.github.io/), [Babel](https://babeljs.io/) and [Browsersync](https://www.browsersync.io/). Helping you to stay productive following the best practices.
[Hexo](https://hexo.io/) is a A fast, simple & powerful blog framework, powered by Node.js.
# C/C++ Development
[Back to the Top](https://github.com/mikeroyal/Self-Hosting-Guide#table-of-contents)

## C/C++ Learning Resources
[C++](https://www.cplusplus.com/doc/tutorial/) is a cross-platform language that can be used to build high-performance applications developed by Bjarne Stroustrup, as an extension to the C language.
[C](https://www.iso.org/standard/74528.html) is a general-purpose, high-level language that was originally developed by Dennis M. Ritchie to develop the UNIX operating system at Bell Labs. It supports structured programming, lexical variable scope, and recursion, with a static type system. C also provides constructs that map efficiently to typical machine instructions, which makes it one was of the most widely used programming languages today.
[Embedded C](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Embedded_C) is a set of language extensions for the C programming language by the [C Standards Committee](https://isocpp.org/std/the-committee) to address issues that exist between C extensions for different [embedded systems](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Embedded_system). The extensions hep enhance microprocessor features such as fixed-point arithmetic, multiple distinct memory banks, and basic I/O operations. This makes Embedded C the most popular embedded software language in the world.
[C & C++ Developer Tools from JetBrains](https://www.jetbrains.com/cpp/)
[Open source C++ libraries on cppreference.com](https://en.cppreference.com/w/cpp/links/libs)
[C++ Graphics libraries](https://cpp.libhunt.com/libs/graphics)
[C++ Libraries in MATLAB](https://www.mathworks.com/help/matlab/call-cpp-library-functions.html)
[C++ Tools and Libraries Articles](https://www.cplusplus.com/articles/tools/)
[Google C++ Style Guide](https://google.github.io/styleguide/cppguide.html)
[Introduction C++ Education course on Google Developers](https://developers.google.com/edu/c++/)
[C++ style guide for Fuchsia](https://fuchsia.dev/fuchsia-src/development/languages/c-cpp/cpp-style)
[C and C++ Coding Style Guide by OpenTitan](https://docs.opentitan.org/doc/rm/c_cpp_coding_style/)
[Chromium C++ Style Guide](https://chromium.googlesource.com/chromium/src/+/master/styleguide/c++/c++.md)
[C++ Core Guidelines](https://github.com/isocpp/CppCoreGuidelines/blob/master/CppCoreGuidelines.md)
[C++ Style Guide for ROS](http://wiki.ros.org/CppStyleGuide)
[Learn C++](https://www.learncpp.com/)
[Learn C : An Interactive C Tutorial](https://www.learn-c.org/)
[C++ Institute](https://cppinstitute.org/free-c-and-c-courses)
[C++ Online Training Courses on LinkedIn Learning](https://www.linkedin.com/learning/topics/c-plus-plus)
[C++ Tutorials on W3Schools](https://www.w3schools.com/cpp/default.asp)
[Learn C Programming Online Courses on edX](https://www.edx.org/learn/c-programming)
[Learn C++ with Online Courses on edX](https://www.edx.org/learn/c-plus-plus)
[Learn C++ on Codecademy](https://www.codecademy.com/learn/learn-c-plus-plus)
[Coding for Everyone: C and C++ course on Coursera](https://www.coursera.org/specializations/coding-for-everyone)
[C++ For C Programmers on Coursera](https://www.coursera.org/learn/c-plus-plus-a)
[Top C Courses on Coursera](https://www.coursera.org/courses?query=c%20programming)
[C++ Online Courses on Udemy](https://www.udemy.com/topic/c-plus-plus/)
[Top C Courses on Udemy](https://www.udemy.com/topic/c-programming/)
[C++ For Programmers Course on Udacity](https://www.udacity.com/course/c-for-programmers--ud210)
[C++ Fundamentals Course on Pluralsight](https://www.pluralsight.com/courses/learn-program-cplusplus)
[Introduction to C++ on MIT Free Online Course Materials](https://ocw.mit.edu/courses/electrical-engineering-and-computer-science/6-096-introduction-to-c-january-iap-2011/)
[Introduction to C++ for Programmers | Harvard ](https://online-learning.harvard.edu/course/introduction-c-programmers)
[Online C Courses | Harvard University](https://online-learning.harvard.edu/subject/c)
## C/C++ Tools
[Visual Studio](https://visualstudio.microsoft.com/) is an integrated development environment (IDE) from Microsoft; which is a feature-rich application that can be used for many aspects of software development. Visual Studio makes it easy to edit, debug, build, and publish your app. By using Microsoft software development platforms such as Windows API, Windows Forms, Windows Presentation Foundation, and Windows Store.
[Visual Studio Code](https://code.visualstudio.com/) is a code editor redefined and optimized for building and debugging modern web and cloud applications.
[Vcpkg](https://github.com/microsoft/vcpkg) is a C++ Library Manager for Windows, Linux, and MacOS.
[ReSharper C++](https://www.jetbrains.com/resharper-cpp/features/) is a Visual Studio Extension for C++ developers developed by JetBrains.
[AppCode](https://www.jetbrains.com/objc/) is constantly monitoring the quality of your code. It warns you of errors and smells and suggests quick-fixes to resolve them automatically. AppCode provides lots of code inspections for Objective-C, Swift, C/C++, and a number of code inspections for other supported languages. All code inspections are run on the fly.
[CLion](https://www.jetbrains.com/clion/features/) is a cross-platform IDE for C and C++ developers developed by JetBrains.
[Code::Blocks](https://www.codeblocks.org/) is a free C/C++ and Fortran IDE built to meet the most demanding needs of its users. It is designed to be very extensible and fully configurable. Built around a plugin framework, Code::Blocks can be extended with plugins.
[CppSharp](https://github.com/mono/CppSharp) is a tool and set of libraries which facilitates the usage of native C/C++ code with the .NET ecosystem. It consumes C/C++ header and library files and generates the necessary glue code to surface the native API as a managed API. Such an API can be used to consume an existing native library in your managed code or add managed scripting support to a native codebase.
[Conan](https://conan.io/) is an Open Source Package Manager for C++ development and dependency management into the 21st century and on par with the other development ecosystems.
[High Performance Computing (HPC) SDK](https://developer.nvidia.com/hpc) is a comprehensive toolbox for GPU accelerating HPC modeling and simulation applications. It includes the C, C++, and Fortran compilers, libraries, and analysis tools necessary for developing HPC applications on the NVIDIA platform.
[Thrust](https://github.com/NVIDIA/thrust) is a C++ parallel programming library which resembles the C++ Standard Library. Thrust's high-level interface greatly enhances programmer productivity while enabling performance portability between GPUs and multicore CPUs. Interoperability with established technologies such as CUDA, TBB, and OpenMP integrates with existing software.
[Boost](https://www.boost.org/) is an educational opportunity focused on cutting-edge C++. Boost has been a participant in the annual Google Summer of Code since 2007, in which students develop their skills by working on Boost Library development.
[Automake](https://www.gnu.org/software/automake/) is a tool for automatically generating Makefile.in files compliant with the GNU Coding Standards. Automake requires the use of GNU Autoconf.
[Cmake](https://cmake.org/) is an open-source, cross-platform family of tools designed to build, test and package software. CMake is used to control the software compilation process using simple platform and compiler independent configuration files, and generate native makefiles and workspaces that can be used in the compiler environment of your choice.
[GDB](http://www.gnu.org/software/gdb/) is a debugger, that allows you to see what is going on `inside' another program while it executes or what another program was doing at the moment it crashed.
[GCC](https://gcc.gnu.org/) is a compiler Collection that includes front ends for C, C++, Objective-C, Fortran, Ada, Go, and D, as well as libraries for these languages.
[GSL](https://www.gnu.org/software/gsl/) is a numerical library for C and C++ programmers. It is free software under the GNU General Public License. The library provides a wide range of mathematical routines such as random number generators, special functions and least-squares fitting. There are over 1000 functions in total with an extensive test suite.
[OpenGL Extension Wrangler Library (GLEW)](https://www.opengl.org/sdk/libs/GLEW/) is a cross-platform open-source C/C++ extension loading library. GLEW provides efficient run-time mechanisms for determining which OpenGL extensions are supported on the target platform.
[Libtool](https://www.gnu.org/software/libtool/) is a generic library support script that hides the complexity of using shared libraries behind a consistent, portable interface. To use Libtool, add the new generic library building commands to your Makefile, Makefile.in, or Makefile.am.
[Maven](https://maven.apache.org/) is a software project management and comprehension tool. Based on the concept of a project object model (POM), Maven can manage a project's build, reporting and documentation from a central piece of information.
[TAU (Tuning And Analysis Utilities)](http://www.cs.uoregon.edu/research/tau/home.php) is capable of gathering performance information through instrumentation of functions, methods, basic blocks, and statements as well as event-based sampling. All C++ language features are supported including templates and namespaces.
[Clang](https://clang.llvm.org/) is a production quality C, Objective-C, C++ and Objective-C++ compiler when targeting X86-32, X86-64, and ARM (other targets may have caveats, but are usually easy to fix). Clang is used in production to build performance-critical software like Google Chrome or Firefox.
[OpenCV](https://opencv.org/) is a highly optimized library with focus on real-time applications. Cross-Platform C++, Python and Java interfaces support Linux, MacOS, Windows, iOS, and Android.
[Libcu++](https://nvidia.github.io/libcudacxx) is the NVIDIA C++ Standard Library for your entire system. It provides a heterogeneous implementation of the C++ Standard Library that can be used in and between CPU and GPU code.
[ANTLR (ANother Tool for Language Recognition)](https://www.antlr.org/) is a powerful parser generator for reading, processing, executing, or translating structured text or binary files. It's widely used to build languages, tools, and frameworks. From a grammar, ANTLR generates a parser that can build parse trees and also generates a listener interface that makes it easy to respond to the recognition of phrases of interest.
[Oat++](https://oatpp.io/) is a light and powerful C++ web framework for highly scalable and resource-efficient web application. It's zero-dependency and easy-portable.
[JavaCPP](https://github.com/bytedeco/javacpp) is a program that provides efficient access to native C++ inside Java, not unlike the way some C/C++ compilers interact with assembly language.
[Cython](https://cython.org/) is a language that makes writing C extensions for Python as easy as Python itself. Cython is based on Pyrex, but supports more cutting edge functionality and optimizations such as calling C functions and declaring C types on variables and class attributes.
[Spdlog](https://github.com/gabime/spdlog) is a very fast, header-only/compiled, C++ logging library.
[Infer](https://fbinfer.com/) is a static analysis tool for Java, C++, Objective-C, and C. Infer is written in [OCaml](https://ocaml.org/).
# Java Development
[Back to the Top](https://github.com/mikeroyal/Self-Hosting-Guide#table-of-contents)

## Java Learning Resources
[Java](https://www.oracle.com/java/) is a popular programming language and development platform(JDK). It reduces costs, shortens development timeframes, drives innovation, and improves application services. With millions of developers running more than 51 billion Java Virtual Machines worldwide.
[The Eclipse Foundation](https://www.eclipse.org/downloads/) is home to a worldwide community of developers, the Eclipse IDE, Jakarta EE and over 375 open source projects, including runtimes, tools and frameworks for Java and other languages.
[Getting Started with Java](https://docs.oracle.com/javase/tutorial/)
[Oracle Java certifications from Oracle University](https://education.oracle.com/java-certification-benefits)
[Google Developers Training](https://developers.google.com/training/)
[Google Developers Certification](https://developers.google.com/certification/)
[Java Tutorial by W3Schools](https://www.w3schools.com/java/)
[Building Your First Android App in Java](codelabs.developers.google.com/codelabs/build-your-first-android-app/)
[Getting Started with Java in Visual Studio Code](https://code.visualstudio.com/docs/java/java-tutorial)
[Google Java Style Guide](https://google.github.io/styleguide/javaguide.html)
[AOSP Java Code Style for Contributors](https://source.android.com/setup/contribute/code-style)
[Chromium Java style guide](https://chromium.googlesource.com/chromium/src/+/master/styleguide/java/java.md)
[Get Started with OR-Tools for Java](https://developers.google.com/optimization/introduction/java)
[Getting started with Java Tool Installer task for Azure Pipelines](https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/devops/pipelines/tasks/tool/java-tool-installer)
[Gradle User Manual](https://docs.gradle.org/current/userguide/userguide.html)
## Java Tools & Frameworks
[Java SE](https://www.oracle.com/java/technologies/javase/tools-jsp.html) contains several tools to assist in program development and debugging, and in the monitoring and troubleshooting of production applications.
[JDK Development Tools](https://docs.oracle.com/javase/7/docs/technotes/tools/) includes the Java Web Start Tools (javaws) Java Troubleshooting, Profiling, Monitoring and Management Tools (jcmd, jconsole, jmc, jvisualvm); and Java Web Services Tools (schemagen, wsgen, wsimport, xjc).
[Android Studio](https://developer.android.com/studio/) is the official integrated development environment for Google's Android operating system, built on JetBrains' IntelliJ IDEA software and designed specifically for Android development. Availble on Windows, macOS, Linux, Chrome OS.
[IntelliJ IDEA](https://www.jetbrains.com/idea/) is an IDE for Java, but it also understands and provides intelligent coding assistance for a large variety of other languages such as Kotlin, SQL, JPQL, HTML, JavaScript, etc., even if the language expression is injected into a String literal in your Java code.
[NetBeans](https://netbeans.org/features/java/index.html) is an IDE provides Java developers with all the tools needed to create professional desktop, mobile and enterprise applications. Creating, Editing, and Refactoring. The IDE provides wizards and templates to let you create Java EE, Java SE, and Java ME applications.
[Java Design Patterns ](https://github.com/iluwatar/java-design-patterns) is a collection of the best formalized practices a programmer can use to solve common problems when designing an application or system.
[Elasticsearch](https://www.elastic.co/products/elasticsearch) is a distributed RESTful search engine built for the cloud written in Java.
[RxJava](https://github.com/ReactiveX/RxJava) is a Java VM implementation of [Reactive Extensions](http://reactivex.io/): a library for composing asynchronous and event-based programs by using observable sequences. It extends the [observer pattern](http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Observer_pattern) to support sequences of data/events and adds operators that allow you to compose sequences together declaratively while abstracting away concerns about things like low-level threading, synchronization, thread-safety and concurrent data structures.
[Guava](https://github.com/google/guava) is a set of core Java libraries from Google that includes new collection types (such as multimap and multiset), immutable collections, a graph library, and utilities for concurrency, I/O, hashing, caching, primitives, strings, and more! It is widely used on most Java projects within Google, and widely used by many other companies as well.
[okhttp](https://square.github.io/okhttp/) is a HTTP client for Java and Kotlin developed by Square.
[Retrofit](https://square.github.io/retrofit/) is a type-safe HTTP client for Android and Java develped by Square.
[LeakCanary](https://square.github.io/leakcanary/) is a memory leak detection library for Android develped by Square.
[Apache Spark](https://spark.apache.org/) is a unified analytics engine for large-scale data processing. It provides high-level APIs in Scala, Java, Python, and R, and an optimized engine that supports general computation graphs for data analysis. It also supports a rich set of higher-level tools including Spark SQL for SQL and DataFrames, MLlib for machine learning, GraphX for graph processing, and Structured Streaming for stream processing.
[Apache Flink](https://flink.apache.org/) is an open source stream processing framework with powerful stream- and batch-processing capabilities with elegant and fluent APIs in Java and Scala.
[Fastjson](https://github.com/alibaba/fastjson/wiki) is a Java library that can be used to convert Java Objects into their JSON representation. It can also be used to convert a JSON string to an equivalent Java object.
[libGDX](https://libgdx.com/) is a cross-platform Java game development framework based on OpenGL (ES) that works on Windows, Linux, Mac OS X, Android, your WebGL enabled browser and iOS.
[Jenkins](https://www.jenkins.io/) is the leading open-source automation server. Built with Java, it provides over 1700 [plugins](https://plugins.jenkins.io/) to support automating virtually anything, so that humans can actually spend their time doing things machines cannot.
[DBeaver](https://dbeaver.io/) is a free multi-platform database tool for developers, SQL programmers, database administrators and analysts. Supports any database which has JDBC driver (which basically means - ANY database). EE version also supports non-JDBC datasources (MongoDB, Cassandra, Redis, DynamoDB, etc).
[Redisson](https://redisson.pro/) is a Redis Java client with features of In-Memory Data Grid. Over 50 Redis based Java objects and services: Set, Multimap, SortedSet, Map, List, Queue, Deque, Semaphore, Lock, AtomicLong, Map Reduce, Publish / Subscribe, Bloom filter, Spring Cache, Tomcat, Scheduler, JCache API, Hibernate, MyBatis, RPC, and local cache.
[GraalVM](https://www.graalvm.org/) is a universal virtual machine for running applications written in JavaScript, Python, Ruby, R, JVM-based languages like Java, Scala, Clojure, Kotlin, and LLVM-based languages such as C and C++.
[Gradle](https://gradle.org/) is a build automation tool for multi-language software development. From mobile apps to microservices, from small startups to big enterprises, Gradle helps teams build, automate and deliver better software, faster. Write in Java, C++, Python or your language of choice.
[Apache Groovy](http://www.groovy-lang.org/) is a powerful, optionally typed and dynamic language, with static-typing and static compilation capabilities, for the Java platform aimed at improving developer productivity thanks to a concise, familiar and easy to learn syntax. It integrates smoothly with any Java program, and immediately delivers to your application powerful features, including scripting capabilities, Domain-Specific Language authoring, runtime and compile-time meta-programming and functional programming.
[JaCoCo](https://www.jacoco.org/jacoco/) is a free code coverage library for Java, which has been created by the EclEmma team based on the lessons learned from using and integration existing libraries for many years.
[Apache JMeter](http://jmeter.apache.org/) is used to test performance both on static and dynamic resources, Web dynamic applications. It also used to simulate a heavy load on a server, group of servers, network or object to test its strength or to analyze overall performance under different load types.
[Junit](https://junit.org/) is a simple framework to write repeatable tests. It is an instance of the xUnit architecture for unit testing frameworks.
[Mockito](https://site.mockito.org/) is the most popular Mocking framework for unit tests written in Java.
[SpotBugs](https://spotbugs.github.io/) is a program which uses static analysis to look for bugs in Java code.
[SpringBoot](https://spring.io/projects/spring-boot) is a great tool that helps you to create Spring-powered, production-grade applications and services with absolute minimum fuss. It takes an opinionated view of the Spring platform so that new and existing users can quickly get to the bits they need.
[YourKit](https://www.yourkit.com/) is a technology leader, creator of the most innovative and intelligent tools for profiling Java & .NET applications.
# Python Development
[Back to the Top](https://github.com/mikeroyal/Self-Hosting-Guide#table-of-contents)

## Python Learning Resources
[Python](https://www.python.org) is an interpreted, high-level programming language. Python is used heavily in the fields of Data Science and Machine Learning.
[Python Developer’s Guide](https://devguide.python.org) is a comprehensive resource for contributing to Python – for both new and experienced contributors. It is maintained by the same community that maintains Python.
[Azure Functions Python developer guide](https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/azure-functions/functions-reference-python) is an introduction to developing Azure Functions using Python. The content below assumes that you've already read the [Azure Functions developers guide](https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/azure-functions/functions-reference).
[CheckiO](https://checkio.org/) is a programming learning platform and a gamified website that teaches Python through solving code challenges and competing for the most elegant and creative solutions.
[Python Institute](https://pythoninstitute.org)
[PCEP – Certified Entry-Level Python Programmer certification](https://pythoninstitute.org/pcep-certification-entry-level/)
[PCAP – Certified Associate in Python Programming certification](https://pythoninstitute.org/pcap-certification-associate/)
[PCPP – Certified Professional in Python Programming 1 certification](https://pythoninstitute.org/pcpp-certification-professional/)
[PCPP – Certified Professional in Python Programming 2](https://pythoninstitute.org/pcpp-certification-professional/)
[MTA: Introduction to Programming Using Python Certification](https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/learn/certifications/mta-introduction-to-programming-using-python)
[Getting Started with Python in Visual Studio Code](https://code.visualstudio.com/docs/python/python-tutorial)
[Google's Python Style Guide](https://google.github.io/styleguide/pyguide.html)
[Google's Python Education Class](https://developers.google.com/edu/python/)
[Real Python](https://realpython.com)
[The Python Open Source Computer Science Degree by Forrest Knight](https://github.com/ForrestKnight/open-source-cs-python)
[Intro to Python for Data Science](https://www.datacamp.com/courses/intro-to-python-for-data-science)
[Intro to Python by W3schools](https://www.w3schools.com/python/python_intro.asp)
[Codecademy's Python 3 course](https://www.codecademy.com/learn/learn-python-3)
[Learn Python with Online Courses and Classes from edX](https://www.edx.org/learn/python)
[Python Courses Online from Coursera](https://www.coursera.org/courses?query=python)
## Python Frameworks and Tools
[Python Package Index (PyPI)](https://pypi.org/) is a repository of software for the Python programming language. PyPI helps you find and install software developed and shared by the Python community.
[PyCharm](https://www.jetbrains.com/pycharm/) is the best IDE I've ever used. With PyCharm, you can access the command line, connect to a database, create a virtual environment, and manage your version control system all in one place, saving time by avoiding constantly switching between windows.
[Python Tools for Visual Studio(PTVS)](https://microsoft.github.io/PTVS/) is a free, open source plugin that turns Visual Studio into a Python IDE. It supports editing, browsing, IntelliSense, mixed Python/C++ debugging, remote Linux/MacOS debugging, profiling, IPython, and web development with Django and other frameworks.
[Pylance](https://github.com/microsoft/pylance-release) is an extension that works alongside Python in Visual Studio Code to provide performant language support. Under the hood, Pylance is powered by Pyright, Microsoft's static type checking tool.
[Pyright](https://github.com/Microsoft/pyright) is a fast type checker meant for large Python source bases. It can run in a “watch” mode and performs fast incremental updates when files are modified.
[Django](https://www.djangoproject.com/) is a high-level Python Web framework that encourages rapid development and clean, pragmatic design.
[Flask](https://flask.palletsprojects.com/) is a micro web framework written in Python. It is classified as a microframework because it does not require particular tools or libraries.
[Web2py](http://web2py.com/) is an open-source web application framework written in Python allowing allows web developers to program dynamic web content. One web2py instance can run multiple web sites using different databases.
[AWS Chalice](https://github.com/aws/chalice) is a framework for writing serverless apps in python. It allows you to quickly create and deploy applications that use AWS Lambda.
[Tornado](https://www.tornadoweb.org/) is a Python web framework and asynchronous networking library. Tornado uses a non-blocking network I/O, which can scale to tens of thousands of open connections.
[HTTPie](https://github.com/httpie/httpie) is a command line HTTP client that makes CLI interaction with web services as easy as possible. HTTPie is designed for testing, debugging, and generally interacting with APIs & HTTP servers.
[Scrapy](https://scrapy.org/) is a fast high-level web crawling and web scraping framework, used to crawl websites and extract structured data from their pages. It can be used for a wide range of purposes, from data mining to monitoring and automated testing.
[Sentry](https://sentry.io/) is a service that helps you monitor and fix crashes in realtime. The server is in Python, but it contains a full API for sending events from any language, in any application.
[Pipenv](https://github.com/pypa/pipenv) is a tool that aims to bring the best of all packaging worlds (bundler, composer, npm, cargo, yarn, etc.) to the Python world.
[Python Fire](https://github.com/google/python-fire) is a library for automatically generating command line interfaces (CLIs) from absolutely any Python object.
[Bottle](https://github.com/bottlepy/bottle) is a fast, simple and lightweight [WSGI](https://www.wsgi.org/) micro web-framework for Python. It is distributed as a single file module and has no dependencies other than the [Python Standard Library](https://docs.python.org/library/).
[CherryPy](https://cherrypy.org) is a minimalist Python object-oriented HTTP web framework.
[Sanic](https://github.com/huge-success/sanic) is a Python 3.6+ web server and web framework that's written to go fast.
[Pyramid](https://trypyramid.com) is a small and fast open source Python web framework. It makes real-world web application development and deployment more fun and more productive.
[TurboGears](https://turbogears.org) is a hybrid web framework able to act both as a Full Stack framework or as a Microframework.
[Falcon](https://falconframework.org/) is a reliable, high-performance Python web framework for building large-scale app backends and microservices with support for MongoDB, Pluggable Applications and autogenerated Admin.
[Neural Network Intelligence(NNI)](https://github.com/microsoft/nni) is an open source AutoML toolkit for automate machine learning lifecycle, including [Feature Engineering](https://github.com/microsoft/nni/blob/master/docs/en_US/FeatureEngineering/Overview.md), [Neural Architecture Search](https://github.com/microsoft/nni/blob/master/docs/en_US/NAS/Overview.md), [Model Compression](https://github.com/microsoft/nni/blob/master/docs/en_US/Compressor/Overview.md) and [Hyperparameter Tuning](https://github.com/microsoft/nni/blob/master/docs/en_US/Tuner/BuiltinTuner.md).
[Dash](https://plotly.com/dash) is a popular Python framework for building ML & data science web apps for Python, R, Julia, and Jupyter.
[Luigi](https://github.com/spotify/luigi) is a Python module that helps you build complex pipelines of batch jobs. It handles dependency resolution, workflow management, visualization etc. It also comes with Hadoop support built-in.
[Locust](https://github.com/locustio/locust) is an easy to use, scriptable and scalable performance testing tool.
[spaCy](https://github.com/explosion/spaCy) is a library for advanced Natural Language Processing in Python and Cython.
[NumPy](https://www.numpy.org/) is the fundamental package needed for scientific computing with Python.
[Pillow](https://python-pillow.org/) is a friendly PIL(Python Imaging Library) fork.
[IPython](https://ipython.org/) is a command shell for interactive computing in multiple programming languages, originally developed for the Python programming language, that offers enhanced introspection, rich media, additional shell syntax, tab completion, and rich history.
[GraphLab Create](https://turi.com/) is a Python library, backed by a C++ engine, for quickly building large-scale, high-performance machine learning models.
[Pandas](https://pandas.pydata.org/) is a fast, powerful, and easy to use open source data structrures, data analysis and manipulation tool, built on top of the Python programming language.
[PuLP](https://coin-or.github.io/pulp/) is an Linear Programming modeler written in python. PuLP can generate LP files and call on use highly optimized solvers, GLPK, COIN CLP/CBC, CPLEX, and GUROBI, to solve these linear problems.
[Matplotlib](https://matplotlib.org/) is a 2D plotting library for creating static, animated, and interactive visualizations in Python. Matplotlib produces publication-quality figures in a variety of hardcopy formats and interactive environments across platforms.
[Scikit-Learn](https://scikit-learn.org/stable/index.html) is a simple and efficient tool for data mining and data analysis. It is built on NumPy,SciPy, and mathplotlib.
# Rust Development
[Back to the Top](https://github.com/mikeroyal/Self-Hosting-Guide#table-of-contents)

## Rust Learning Resources
[Rust](https://www.rust-lang.org) is a multi-paradigm programming language focused on performance and safety. Rust has a comparable amount of runtime to C and C++, and has set up its standard library to be amenable towards OS development. Specifically, the standard library is split into two parts: core and std. Core is the lowest-level aspects only, and doesn't include things like allocation, threading, and other higher-level features.
[The Rust Language Reference](https://doc.rust-lang.org/nightly/reference/)
[The Rust Programming Language Book](https://doc.rust-lang.org/book/)
[Learning Rust](https://www.rust-lang.org/learn)
[Why AWS loves Rust](https://aws.amazon.com/blogs/opensource/why-aws-loves-rust-and-how-wed-like-to-help/)
[Rust Programming courses on Udemy](https://www.udemy.com/courses/search/?src=ukw&q=Rust)
[Safety in Systems Programming with Rust at Standford by Ryan Eberhardt](https://reberhardt.com/blog/2020/10/05/designing-a-new-class-at-stanford-safety-in-systems-programming.html)
[WebAssembly meets Kubernetes with Krustlet using Rust](https://cloudblogs.microsoft.com/opensource/2020/04/07/announcing-krustlet-kubernetes-rust-kubelet-webassembly-wasm/)
[Microsoft's Project Verona](https://github.com/microsoft/verona/blob/master/docs/explore.md)
## Rust Tools
[Cargo](https://github.com/rust-lang/cargo) is a package manager that downloads your Rust project’s dependencies and compiles your project.
[Crater](https://crater.rust-lang.org/) is a tool to run experiments across parts of the Rust ecosystem. Its primary purpose is to detect regressions in the Rust compiler, and it does this by building a large number of crates, running their test suites and comparing the results between two versions of the Rust compiler. It can operate locally (with Docker as the only dependency) or distributed on the cloud.
[VSCode-Rust](https://github.com/rust-lang/vscode-rust) is plugin that adds language support for Rust to Visual Studio Code. Rust support is powered by a separate language server - either by the official Rust Language Server (RLS) or rust-analyzer, depending on the user's preference. If you don't have it installed, the extension will install it for you (with permission). This extension is built and maintained by the Rust IDEs and editors team with the focus on providing a stable, high quality extension that makes the best use of the respective language server.
[Apache Arrow](https://github.com/apache/arrow) is a development platform for in-memory analytics. It contains a set of technologies that enable big data systems to process and move data fast. Arrow's libraries are available for C, C++, C#, Go, Java, JavaScript, MATLAB, Python, R, Ruby, and Rust.
[Wasmer](https://wasmer.io/) enables super lightweight containers based on [WebAssembly](https://webassembly.org/) that can run anywhere such as the Desktop to the Cloud and IoT devices, and also embedded in [any programming language](https://github.com/wasmerio/wasmer#language-integrations).
[Firecracker](https://firecracker-microvm.github.io) is an open source virtualization technology that is purpose-built for creating and managing secure, multi-tenant container and function-based services that provide serverless operational models. Firecracker runs workloads in lightweight virtual machines, called microVMs, which combine the security and isolation properties provided by hardware virtualization technology with the speed and flexibility of containers. Firecracker has also been integrated in container runtimes, for example [Kata Containers](https://github.com/kata-containers/documentation/wiki/Initial-release-of-Kata-Containers-with-Firecracker-support) and [Weaveworks Ignite](https://github.com/weaveworks/ignite).
[Tokio](https://github.com/tokio-rs/tokio) is an event-driven, non-blocking I/O platform for writing asynchronous applications with the Rust programming language.
[TiKV](https://github.com/tikv/tikv) is an open-source distributed transactional key-value database that also provides classical key-vlue APIs, but also transactional APIs with ACID compliance.
[Sonic](https://crates.io/crates/sonic-server) is a fast, lightweight and schema-less search backend similar to Elasticsearch in some use-cases.
[Hyper](https://github.com/hyperium/hyper) is a fast and correct HTTP library for Rust.
[Rocket](https://github.com/SergioBenitez/Rocket) is an async web framework for Rust with a focus on usability, security, extensibility, and speed.
[Clippy](https://rust-lang.github.io/rust-clippy/) is a collection of lints to catch common mistakes and improve your Rust code.
[Servo](https://github.com/servo/servo) is a prototype web browser engine written in the Rust language.
[Vector](https://vector.dev/) is a high-performance, end-to-end (agent & aggregator) observability data platform that puts the user in control of their observability data.
[RustPython](https://github.com/RustPython/RustPython) is a Python Interpreter written in Rust.
[Miri](https://github.com/rust-lang/miri) is an interpreter for Rust's mid-level intermediate representation. It can run binaries and test suites of cargo projects and detect certain classes of undefined behavior. Miri will alsowill also tell you about memory leaks: when there is memory still allocated at the end of the execution, and that memory is not reachable from a global static, Miri will raise an error.
[Chalk](https://rust-lang.github.io/chalk/book/) is an implementation and definition of the Rust trait system using a PROLOG-like logic solver.
[stdarch](https://doc.rust-lang.org/stable/core/arch/) is Rust's standard library vendor-specific APIs and run-time feature detection.
[Simpleinfra](https://github.com/rust-lang/simpleinfra) is rep that contains the tools and automation written by the Rust infrastructure team to manage our services. Using some of the tools in this repo require privileges only infra team members have.
[Rustlings](https://github.com/rust-lang/rustlings) is a small set of exercises to get you used to reading and writing Rust code.
[Krustlet](https://krustlet.dev/) acts as a Kubernetes Kubelet(written in Rust) by listening on the event stream for new pods that the scheduler assigns to it based on specific Kubernetes [tolerations](https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/configuration/taint-and-toleration/). The project is currently experimental.
## Operating System
[Redox](https://www.redox-os.org) is a Unix-like Operating System written in Rust, aiming to bring the innovations of Rust to a modern microkernel and full set of applications. Acitvely being developed by [Jeremy Soeller](https://gitlab.redox-os.org/jackpot51).
[Bottlerocket OS](https://github.com/bottlerocket-os/bottlerocket) is an open-source Linux-based operating system meant for hosting containers. Bottlerocket focuses on security and maintainability, providing a reliable, consistent, and safe platform for container-based workloads.
[Tock](https://www.tockos.org) is an embedded operating system designed for running multiple concurrent, mutually distrustful applications on Cortex-M and RISC-V based embedded platforms. Tock's design centers around protection, both from potentially malicious applications and from device drivers. Tock uses two mechanisms to protect different components of the operating system. First, the kernel and device drivers are written in Rust, a systems programming language that provides compile-time memory safety, type safety and strict aliasing. Tock uses Rust to protect the kernel (the scheduler and hardware abstraction layer) from platform specific device drivers as well as isolate device drivers from each other. Second, Tock uses memory protection units to isolate applications from each other and the kernel.
[Rust on Chrome OS](https://chromium.googlesource.com/chromiumos/docs/+/master/rust_on_cros.md) is a document that provides information on creating Rust projects for installation within Chrome OS and Chrome OS SDK.
[Writing an OS in Rust ](https://os.phil-opp.com) is a blog series creates a small operating system in the Rust programming language by [Philipp Oppermann](https://github.com/phil-opp).
# Swift Development
[Back to the Top](https://github.com/mikeroyal/Self-Hosting-Guide#table-of-contents)

## Swift Learning Resources
[Swift](https://developer.apple.com/swift/) is Apple's main programming language for iOS, macOS, watchOS, and tvOS app development. Though, many parts of Swift will be familiar to developers from their experience of developing in C and Objective-C.
[Swift Evolution](https://github.com/apple/swift-evolution) maintains proposals for changes and user-visible enhancements to the Swift Programming Language.
[Xcode + Swift](https://developer.apple.com/swift/resources/) makes developing applications for MacOS and iOS fast and fun.
[Swift 5.3 Basics](https://docs.swift.org/swift-book/LanguageGuide/TheBasics.html)
[Start Developing iOS Apps with Swift](https://developer.apple.com/library/archive/referencelibrary/GettingStarted/DevelopiOSAppsSwift/)
[Apple Developer Documentation](https://developer.apple.com/documentation)
[Apple Foundation Framework](https://developer.apple.com/documentation/foundation)
[Apple Core Animation Framework](https://developer.apple.com/documentation/quartzcore)
[Apple Core Graphics Framework](https://developer.apple.com/documentation/coregraphics)
[Getting Started with LLDB](https://developer.apple.com/library/archive/documentation/IDEs/Conceptual/gdb_to_lldb_transition_guide/document/lldb-basics.html)
[Mac Catalyst - iOS - Human Interface Guidelines](https://developer.apple.com/design/human-interface-guidelines/ios/overview/mac-catalyst/)
[Amazon EC2 Mac Instances](https://aws.amazon.com/ec2/instance-types/mac/)
[Swift GitHub](https://github.com/apple/swift)
[Apple Developer Forums](https://developer.apple.com/forums/)
[Swift Forums](https://forums.swift.org/)
[Google's Swift Style Guide](https://google.github.io/swift/)
[Swift Courses Online from Coursera](https://www.coursera.org/courses?query=swift)
[Swift Courses Online from Udemy](https://www.udemy.com/topic/swift/)
[Learning Swift course from Codecademy](https://www.codecademy.com/learn/learn-swift)
## Swift Tools
[Xcode](https://developer.apple.com/xcode/) includes everything developers need to create great applications for Mac, iPhone, iPad, Apple TV, and Apple Watch. Xcode provides developers a unified workflow for user interface design, coding, testing, and debugging. Xcode 12 is built as an Universal app that runs 100% natively on Intel-based CPUs and Apple Silicon. It includes a unified macOS SDK that features all the frameworks, compilers, debuggers, and other tools you need to build apps that run natively on Apple Silicon and the Intel x86_64 CPU.
[SwiftUI](https://developer.apple.com/documentation/swiftui) is a user interface toolkit that provides views, controls, and layout structures for declaring your app's user interface. The SwiftUI framework provides event handlers for delivering taps, gestures, and other types of input to your application.
[UIKit](https://developer.apple.com/documentation/uikit) is a framework provides the required infrastructure for your iOS or tvOS apps. It provides the window and view architecture for implementing your interface, the event handling infrastructure for delivering Multi-Touch and other types of input to your app, and the main run loop needed to manage interactions among the user, the system, and your app.
[AppKit](https://developer.apple.com/documentation/appkit) is a graphical user interface toolkit that contains all the objects you need to implement the user interface for a macOS app such as windows, panels, buttons, menus, scrollers, and text fields, and it handles all the details for you as it efficiently draws on the screen, communicates with hardware devices and screen buffers, clears areas of the screen before drawing, and clips views.
[ARKit](https://developer.apple.com/augmented-reality/arkit/) is a set set of software development tools to enable developers to build augmented-reality apps for iOS developed by Apple. The latest version ARKit 3.5 takes advantage of the new LiDAR Scanner and depth sensing system on iPad Pro(2020) to support a new generation of AR apps that use Scene Geometry for enhanced scene understanding and object occlusion.
[RealityKit](https://developer.apple.com/documentation/realitykit) is a framework to implement high-performance 3D simulation and rendering with information provided by the ARKit framework to seamlessly integrate virtual objects into the real world.
[SceneKit](https://developer.apple.com/scenekit/) is a high-level 3D graphics framework that helps you create 3D animated scenes and effects in your iOS apps.
[Mac Catalyst](https://developer.apple.com/mac-catalyst/) is a set of Apple APIs that developers can use to rapidly port their iOS apps to [Apple Silicon M1 Chip](https://www.apple.com/mac/m1/) and take full advantage of the new capabilities on the new Apple hardware.
[Instruments](https://help.apple.com/instruments/mac/current/#/dev7b09c84f5) is a powerful and flexible performance-analysis and testing tool that’s part of the Xcode tool set. It’s designed to help you profile your iOS, watchOS, tvOS, and macOS apps, processes, and devices in order to better understand and optimize their behavior and performance.
[Cocoapods](https://cocoapods.org/) is a dependency manager for Swift and Objective-C used in Xcode projects by specifying the dependencies for your project in a simple text file. CocoaPods then recursively resolves dependencies between libraries, fetches source code for all dependencies, and creates and maintains an Xcode workspace to build your project.
[AppCode](https://www.jetbrains.com/objc/) is constantly monitoring the quality of your code. It warns you of errors and smells and suggests quick-fixes to resolve them automatically. AppCode provides lots of code inspections for Objective-C, Swift, C/C++, and a number of code inspections for other supported languages.
[Vapor](https://github.com/vapor/vapor) is a web framework for Swift. It provides a beautifully expressive and easy to use foundation for your next website, API, or cloud project.
[Hero](https://github.com/HeroTransitions/Hero) is a library for building iOS view controller transitions. It provides a declarative layer on top of the UIKit's cumbersome transition APIs—making custom transitions an easy task for developers.
[Kingfisher](https://github.com/onevcat/Kingfisher) is a powerful, pure-Swift library for downloading and caching images from the web. It provides you a chance to use a pure-Swift way to work with remote images in your next app.
[Realm](https://github.com/realm/realm-cocoa) is a mobile database that runs directly inside phones, tablets or wearables. This repository holds the source code for the iOS, macOS, tvOS & watchOS versions of Realm Swift & Realm Objective-C.
[Perfect](https://github.com/PerfectlySoft/Perfect) is a complete and powerful toolbox, framework, and application server for Linux, iOS, and macOS (OS X). It provides everything a Swift engineer needs for developing lightweight, maintainable, and scalable apps and other REST services entirely in the Swift programming language for both client-facing and server-side applications.
[Alamofire](https://github.com/Alamofire/Alamofire) is an HTTP networking library written in Swift.
[Eureka](https://github.com/xmartlabs/Eureka) is an elegant iOS form builder in Swift
[Carthage](https://github.com/Carthage/Carthage) is intended to be the simplest way to add frameworks to your Cocoa application. Carthage builds your dependencies and provides you with binary frameworks, but you retain full control over your project structure and setup. Carthage does not automatically modify your project files or your build settings.
[ReactiveCocoa](https://github.com/ReactiveCocoa/ReactiveCocoa) is reactive extensions to Cocoa frameworks, built on top of ReactiveSwift.
# XML Development
[Back to the Top](https://github.com/mikeroyal/Self-Hosting-Guide#table-of-contents)

## XML Learning Resources
[XML(Extensible Markup Language)](https://www.w3.org/XML/) is a markup language that is similar to HTML but without predefined tags. Instead, the user define their own tags designed specifically for their needs.
[XAML](https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/dotnet/desktop/wpf/fundamentals/xaml) is a declarative XML-based markup language that is applied to the .NET Core programming model, which XAML simplifies creating a UI for a [.NET Core app](https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/uwp/xaml-platform/xaml-overview).
[Using XML editor in Visual Studio](https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/visualstudio/xml-tools/xml-editor)
[XMLmind XML Editor Tutorial](https://www.xmlmind.com/xmleditor/tutorial.html)
[XMLReader for Android Developers](https://developer.android.com/reference/org/xml/sax/XMLReader)
[Adding app configuration policies for managed iOS/iPadOS devices](https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/mem/intune/apps/app-configuration-policies-use-ios)
[XML Processing Modules for Python 3](https://docs.python.org/3/library/xml.html)
[PHP: XML Parser Manual](https://www.php.net/manual/en/book.xml.php)
[Introduction to XML on W3Schools](https://www.w3schools.com/xml/)
[Introduction to XML by IBM](https://www.ibm.com/developerworks/xml/tutorials/xmlintro/xmlintro.html)
[XML Fundamentals Training Program from Oracle University](https://education.oracle.com/xml-fundamentals/courP_1492)
[XML Online Training Courses on Udemy](https://www.udemy.com/topic/xml/)
[XML Schema (XSD) Crash Course for Beginners on Udemy](https://www.udemy.com/course/xml-schema-xsd-crash-course-for-beginners/)
[XML Online Training Courses on Coursera](https://www.coursera.org/search?query=XML&)
[XML Online Training Courses on LinkedIn Learning](https://www.linkedin.com/learning/topics/xml)
[Introduction to Microsoft Office Open XML on Pluralsight](https://www.pluralsight.com/courses/introduction-microsoft-office-open-xml)
[XML Fundamentals in C# on Pluralsight](https://www.pluralsight.com/courses/csharp-xml-fundamentals)
[Working with XML in Java Using JAXB](https://www.pluralsight.com/courses/xml-java-using-jaxb)
[Querying JSON, XML, and Temporal Data with T-SQL](https://www.pluralsight.com/courses/querying-json-xml-temporal-data-tsql)
[XML Training Courses on NobleProg](https://www.nobleprog.com/xml-training)
## XML Tools and Frameworks
[Visual Studio](https://visualstudio.microsoft.com/) is an integrated development environment (IDE) from Microsoft; which is a feature-rich application that can be used for many aspects of software development. Visual Studio makes it easy to edit, debug, build, and publish your app. By using Microsoft software development platforms such as Windows API, Windows Forms, Windows Presentation Foundation, and Windows Store.
[MSBuild](https://github.com/dotnet/msbuild) is the build platform for .NET and Visual Studio. MSBuild, provides an XML schema for a project file that controls how the build platform processes and builds software. Visual Studio uses MSBuild to perform team builds through Azure DevOps Server, but MSBuild can run without Visual Studio.
[WebStorm](https://www.jetbrains.com/webstorm/) is a professional IDE for JavaScript(including support for both HTML and CSS) developed by JetBrains. WebStorm comes with intelligent code completion, on-the-fly error detection, powerful navigation and refactoring for JavaScript, TypeScript, stylesheet languages, and all the most popular frameworks([Angular](https://angular.io/), [React](https://reactjs.org/), [Vue.js](https://vuejs.org/), [Ionic](https://ionicframework.com/), [Apache Cordova](https://cordova.apache.org/), [React Native](https://reactnative.dev/), [Node.js](https://nodejs.org/), [Meteor](https://www.meteor.com/#!), and [Electron](https://www.electronjs.org/)).
[Uno Platform](https://platform.uno/) is a Universal Windows Platform Bridge that allows UWP-based code (C# and XAML) to run on iOS, Android, macOS, WebAssembly, Linux and Windows. It provides the full definitions of the UWP [Windows 10 2004 (19041)](https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/uwp/whats-new/windows-10-build-19041), and the implementation of a growing number of parts of the UWP API, such as Windows.UI.Xaml, to enable UWP and WinUI applications to run on these platforms.
[Android Studio](https://developer.android.com/studio/) is the official integrated development environment for Google's Android operating system, built on JetBrains' IntelliJ IDEA software and designed specifically for Android development. Availble on Windows, macOS, Linux, Chrome OS.
[Oxygen XML Editor](https://www.oxygenxml.com/) is a cross platform tool setting the standard in XML editing. The advanced XML editor provides the most intuitive tools for XML editing, authoring, and development. It is availble on Windows, macOS, and Linux.
[XMLmind XML Editor](https://www.xmlmind.com/xmleditor/) is a strictly validating XML editor. It has Extensive DITA 1.3 support, and includes lightweight DITA, XDITA, HDITA, MDITA.
[Refit](https://github.com/reactiveui/refit) is the automatic type-safe REST library for .NET Core,.NET and Xamarin.
[Pugixml](https://github.com/zeux/pugixml) is a C++ XML processing library, which consists of a DOM-like interface with rich traversal/modification capabilities, an extremely fast XML parser which constructs the DOM tree from an XML file/buffer, and an XPath 1.0 implementation for complex data-driven tree queries.
[Serializer](https://symfony.com/serializer) is a component that makes it easier to handle serializing data structures, including object graphs, into array structures or other formats like XML and JSON. It can also handle deserializing XML and JSON back to object graphs.
[Erlsom](https://github.com/willemdj/erlsom) is an XML parser for Erlang.
[REST-assured](https://github.com/rest-assured/rest-assured) is a Java DSL for easy testing of REST services.
## Contribute
- [x] If would you like to contribute to this guide simply make a [Pull Request](https://github.com/mikeroyal/Self-Hosting-Guide/pulls).
## License
[Back to the Top](https://github.com/mikeroyal/Self-Hosting-Guide#table-of-contents)
Distributed under the [Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0) Public License](https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).

































































 ## Raspberry Pi Learning Resources
[Back to the Top](https://github.com/mikeroyal/Self-Hosting-Guide#table-of-contents)
[Raspberry Pi](https://www.raspberrypi.org/) is an ARM powered single board computer(SBC) that is the size of a credit card and costs around $35.
[Raspberry Pi Foundation](https://www.raspberrypi.org/about/) is a UK-based charity that works to put the power of computing and digital making into the hands of people all over the world.
[Getting Started with Raspberry Pi Projects](https://projects.raspberrypi.org/)
[Online learning for the Raspberry Pi](https://www.raspberrypi.org/training/online/)
[Raspberry Pi Training Program](https://www.raspberrypi.org/training/)
[Raspberry Pi Online Courses on Udemy](https://www.udemy.com/topic/raspberry-pi/)
[Raspberry Pi Online Courses on Coursera](https://www.coursera.org/courses?languages=en&query=raspberry%20pi)
[The Raspberry Pi Platform and Python Programming course on Coursera](https://www.coursera.org/learn/raspberry-pi-platform)
[Learning Raspberry Pi with Online Courses on edX](https://www.edx.org/learn/raspberry-pi)
[Raspberry Pi Online Training Courses on LinkedIn Learning](https://www.linkedin.com/learning/topics/raspberry-pi)
[Getting Started with Raspberry Pi course on FutureLearn](https://www.futurelearn.com/courses/getting-started-with-your-raspberry-pi)
[Home Assistant on Raspberry Pi](https://www.home-assistant.io/getting-started/)
[PiSwitch: Build your own Nintendo Switch-style console](https://magpi.raspberrypi.org/articles/piswitch-nintendo-switch-console)
## Raspberry Pi Operating Systems
[Back to the Top](https://github.com/mikeroyal/Self-Hosting-Guide#table-of-contents)
[Raspberry Pi OS](https://www.raspberrypi.org/software/operating-systems/)
[Hass.io(Home Assistant OS)](https://www.home-assistant.io/hassio/installation/)
[OmniROM(Android 11) based on ASOP](https://forum.xda-developers.com/t/omnirom-android-r-11-for-pi-4.4183121/)
[Manjaro Linux ARM](https://manjaro.org/download/#ARM)
[Arch Linux ARM](https://archlinuxarm.org/platforms/armv8/broadcom/raspberry-pi-4)
[Ubuntu MATE for Raspberry Pi](https://ubuntu-mate.org/ports/raspberry-pi/)
[Ubuntu Desktop for Raspberry Pi](https://ubuntu.com/raspberry-pi)
[Ubuntu Core on a Raspberry Pi](https://ubuntu.com/download/raspberry-pi-core)
[Ubuntu Server for ARM](https://ubuntu.com/download/server/arm)
[Fedora ARM](https://arm.fedoraproject.org)
[Kali Linux for the Raspberry Pi](https://www.kali.org/docs/arm/kali-linux-raspberry-pi/)
[Twister OS](https://twisteros.com/)
[TitusPi](https://github.com/ChrisTitusTech/TitusPi)
[RetroArch](https://www.retroarch.com/?page=platforms)
[RetroPie](https://retropie.org.uk/)
[LibreELEC](https://libreelec.tv/)
[OSMC](https://osmc.tv)
[RISC OS](https://www.riscosopen.org/content/)
[DietPi](https://github.com/MichaIng/DietPi)
[Windows 10 IoT Core](https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/iot-core/windows-iot-core)
## Raspberry Pi Tools
[Back to the Top](#table-of-contents)
[Raspberry Pi Imager](https://www.raspberrypi.org/software/) is the quick and easy way to install Raspberry Pi OS and other operating systems to a microSD card, ready to use with your Raspberry Pi.
[Raspberry Pi Locator](https://rpilocator.com/) is a website to track Raspberry Pi 4 model B, Compute Module 4, Pi Zero 2 W, and Pico availability across multiple retailers in different countries.
[Raspberry Pi Network Install (Beta)](https://www.raspberrypi.com/documentation/computers/getting-started.html#installing-over-the-network-beta) is a feature can be used to start the Raspberry Pi Imager application directly on a Raspberry Pi 4, or a Raspberry Pi 400, by downloading it from the internet using an Ethernet cable. The Raspberry Pi Imager application, which will run in memory on your Raspberry Pi, can then be used to flash the operating system onto a blank SD Card or USB disk, just like normal.
[Raspberry Pi Bootloader](https://www.raspberrypi.com/documentation/computers/raspberry-pi.html#updating-the-bootloader) is a feature, which is now available in beta, that utilize an **EEPROM(Electrically Erasable Programmable Read-Only Memory)** to store the system’s bootloader. This EEPROM is persistent storage that is located on the Pi’s mainboard. The advantage of using the EEPROM instead is that the Raspberry Pi 4 can perform tasks without needing any storage to be attached.
[Etcher](https://www.balena.io/etcher/) is an open source, cross-platform software that makes it easy to flash operating system images to a microSD card or USB device.
[Home Assistant](https://www.home-assistant.io/) is an open source home automation that puts local control and privacy first. Home Assistant is powered by a worldwide community of tinkerers and DIY enthusiasts that runs great on Raspberry Pi.
[Gladys Assistant](https://github.com/gladysassistant/gladys) is a privacy-first, open-source home assistant and runs great on Raspberry Pi.
[Kodi for Raspberry Pi](https://kodi.tv/download/853) is a free and open source media player application developed by the XBMC/Kodi Foundation.
[Pi-hole](https://pi-hole.net/) is a [DNS sinkhole](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/DNS_Sinkhole) that protects your devices from unwanted content, without installing any client-side software, intended for use on a private network. It is designed for use on embedded devices with network capability, such as the Raspberry Pi, but it can be used on other machines running Linux and cloud implementations.
[PiKVM](https://github.com/pikvm/pikvm) is a very simple and fully functional Raspberry Pi-based KVM over IP.
[PiShrink](https://github.com/Drewsif/PiShrink) is a bash script that automatically shrink a pi image that will then resize to the max size of the SD card on boot.
[RPiPlay](https://github.com/FD-/RPiPlay) is an open-source implementation of an AirPlay mirroring server for the Raspberry Pi that supports iOS 9 and later.
[Gpiozero](https://github.com/gpiozero/gpiozero) is a simple interface to GPIO(General-Purpose Input/Output) devices with the Raspberry Pi.
[Balena Sound](https://sound.balenalabs.io/) is a single or multi-room streamer for an existing audio device using a Raspberry Pi! It supports Bluetooth, Airplay and Spotify Connect.
[OpenBalena](https://balena.io/open) is a platform to deploy and manage connected devices.
### Home Assistant
[Back to the Top](#table-of-contents)
## Raspberry Pi Learning Resources
[Back to the Top](https://github.com/mikeroyal/Self-Hosting-Guide#table-of-contents)
[Raspberry Pi](https://www.raspberrypi.org/) is an ARM powered single board computer(SBC) that is the size of a credit card and costs around $35.
[Raspberry Pi Foundation](https://www.raspberrypi.org/about/) is a UK-based charity that works to put the power of computing and digital making into the hands of people all over the world.
[Getting Started with Raspberry Pi Projects](https://projects.raspberrypi.org/)
[Online learning for the Raspberry Pi](https://www.raspberrypi.org/training/online/)
[Raspberry Pi Training Program](https://www.raspberrypi.org/training/)
[Raspberry Pi Online Courses on Udemy](https://www.udemy.com/topic/raspberry-pi/)
[Raspberry Pi Online Courses on Coursera](https://www.coursera.org/courses?languages=en&query=raspberry%20pi)
[The Raspberry Pi Platform and Python Programming course on Coursera](https://www.coursera.org/learn/raspberry-pi-platform)
[Learning Raspberry Pi with Online Courses on edX](https://www.edx.org/learn/raspberry-pi)
[Raspberry Pi Online Training Courses on LinkedIn Learning](https://www.linkedin.com/learning/topics/raspberry-pi)
[Getting Started with Raspberry Pi course on FutureLearn](https://www.futurelearn.com/courses/getting-started-with-your-raspberry-pi)
[Home Assistant on Raspberry Pi](https://www.home-assistant.io/getting-started/)
[PiSwitch: Build your own Nintendo Switch-style console](https://magpi.raspberrypi.org/articles/piswitch-nintendo-switch-console)
## Raspberry Pi Operating Systems
[Back to the Top](https://github.com/mikeroyal/Self-Hosting-Guide#table-of-contents)
[Raspberry Pi OS](https://www.raspberrypi.org/software/operating-systems/)
[Hass.io(Home Assistant OS)](https://www.home-assistant.io/hassio/installation/)
[OmniROM(Android 11) based on ASOP](https://forum.xda-developers.com/t/omnirom-android-r-11-for-pi-4.4183121/)
[Manjaro Linux ARM](https://manjaro.org/download/#ARM)
[Arch Linux ARM](https://archlinuxarm.org/platforms/armv8/broadcom/raspberry-pi-4)
[Ubuntu MATE for Raspberry Pi](https://ubuntu-mate.org/ports/raspberry-pi/)
[Ubuntu Desktop for Raspberry Pi](https://ubuntu.com/raspberry-pi)
[Ubuntu Core on a Raspberry Pi](https://ubuntu.com/download/raspberry-pi-core)
[Ubuntu Server for ARM](https://ubuntu.com/download/server/arm)
[Fedora ARM](https://arm.fedoraproject.org)
[Kali Linux for the Raspberry Pi](https://www.kali.org/docs/arm/kali-linux-raspberry-pi/)
[Twister OS](https://twisteros.com/)
[TitusPi](https://github.com/ChrisTitusTech/TitusPi)
[RetroArch](https://www.retroarch.com/?page=platforms)
[RetroPie](https://retropie.org.uk/)
[LibreELEC](https://libreelec.tv/)
[OSMC](https://osmc.tv)
[RISC OS](https://www.riscosopen.org/content/)
[DietPi](https://github.com/MichaIng/DietPi)
[Windows 10 IoT Core](https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/iot-core/windows-iot-core)
## Raspberry Pi Tools
[Back to the Top](#table-of-contents)
[Raspberry Pi Imager](https://www.raspberrypi.org/software/) is the quick and easy way to install Raspberry Pi OS and other operating systems to a microSD card, ready to use with your Raspberry Pi.
[Raspberry Pi Locator](https://rpilocator.com/) is a website to track Raspberry Pi 4 model B, Compute Module 4, Pi Zero 2 W, and Pico availability across multiple retailers in different countries.
[Raspberry Pi Network Install (Beta)](https://www.raspberrypi.com/documentation/computers/getting-started.html#installing-over-the-network-beta) is a feature can be used to start the Raspberry Pi Imager application directly on a Raspberry Pi 4, or a Raspberry Pi 400, by downloading it from the internet using an Ethernet cable. The Raspberry Pi Imager application, which will run in memory on your Raspberry Pi, can then be used to flash the operating system onto a blank SD Card or USB disk, just like normal.
[Raspberry Pi Bootloader](https://www.raspberrypi.com/documentation/computers/raspberry-pi.html#updating-the-bootloader) is a feature, which is now available in beta, that utilize an **EEPROM(Electrically Erasable Programmable Read-Only Memory)** to store the system’s bootloader. This EEPROM is persistent storage that is located on the Pi’s mainboard. The advantage of using the EEPROM instead is that the Raspberry Pi 4 can perform tasks without needing any storage to be attached.
[Etcher](https://www.balena.io/etcher/) is an open source, cross-platform software that makes it easy to flash operating system images to a microSD card or USB device.
[Home Assistant](https://www.home-assistant.io/) is an open source home automation that puts local control and privacy first. Home Assistant is powered by a worldwide community of tinkerers and DIY enthusiasts that runs great on Raspberry Pi.
[Gladys Assistant](https://github.com/gladysassistant/gladys) is a privacy-first, open-source home assistant and runs great on Raspberry Pi.
[Kodi for Raspberry Pi](https://kodi.tv/download/853) is a free and open source media player application developed by the XBMC/Kodi Foundation.
[Pi-hole](https://pi-hole.net/) is a [DNS sinkhole](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/DNS_Sinkhole) that protects your devices from unwanted content, without installing any client-side software, intended for use on a private network. It is designed for use on embedded devices with network capability, such as the Raspberry Pi, but it can be used on other machines running Linux and cloud implementations.
[PiKVM](https://github.com/pikvm/pikvm) is a very simple and fully functional Raspberry Pi-based KVM over IP.
[PiShrink](https://github.com/Drewsif/PiShrink) is a bash script that automatically shrink a pi image that will then resize to the max size of the SD card on boot.
[RPiPlay](https://github.com/FD-/RPiPlay) is an open-source implementation of an AirPlay mirroring server for the Raspberry Pi that supports iOS 9 and later.
[Gpiozero](https://github.com/gpiozero/gpiozero) is a simple interface to GPIO(General-Purpose Input/Output) devices with the Raspberry Pi.
[Balena Sound](https://sound.balenalabs.io/) is a single or multi-room streamer for an existing audio device using a Raspberry Pi! It supports Bluetooth, Airplay and Spotify Connect.
[OpenBalena](https://balena.io/open) is a platform to deploy and manage connected devices.
### Home Assistant
[Back to the Top](#table-of-contents)

































 **VMware Cloud First Approach. Source: [VMware](https://www.vmware.com/products/telco-cloud-automation.html).**
**VMware Cloud First Approach. Source: [VMware](https://www.vmware.com/products/telco-cloud-automation.html).**
 **VMware Telco Cloud Automation Components. Source: [VMware](https://www.vmware.com/products/telco-cloud-automation.html).**
## Telco Learning Resources
[HPE(Hewlett Packard Enterprise) Telco Blueprints overview](https://techhub.hpe.com/eginfolib/servers/docs/Telco/Blueprints/infocenter/index.html#GUID-9906A227-C1FB-4FD5-A3C3-F3B72EC81CAB.html)
[Network Functions Virtualization Infrastructure (NFVI) by Cisco](https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/solutions/service-provider/network-functions-virtualization-nfv-infrastructure/index.html)
[Introduction to vCloud NFV Telco Edge from VMware](https://docs.vmware.com/en/VMware-vCloud-NFV-OpenStack-Edition/3.1/vloud-nfv-edge-reference-arch-31/GUID-744C45F1-A8D5-4523-9E5E-EAF6336EE3A0.html)
[VMware Telco Cloud Automation(TCA) Architecture Overview](https://docs.vmware.com/en/VMware-Telco-Cloud-Platform-5G-Edition/1.0/telco-cloud-platform-5G-edition-reference-architecture/GUID-C19566B3-F42D-4351-BA55-DE70D55FB0DD.html)
[5G Telco Cloud from VMware](https://telco.vmware.com/)
[Maturing OpenStack Together To Solve Telco Needs from Red Hat](https://www.redhat.com/cms/managed-files/4.Nokia%20CloudBand%20&%20Red%20Hat%20-%20Maturing%20Openstack%20together%20to%20solve%20Telco%20needs%20Ehud%20Malik,%20Senior%20PLM,%20Nokia%20CloudBand.pdf)
[Red Hat telco ecosystem program](https://connect.redhat.com/en/programs/telco-ecosystem)
[OpenStack for Telcos by Canonical](https://ubuntu.com/blog/openstack-for-telcos-by-canonical)
[Open source NFV platform for 5G from Ubuntu](https://ubuntu.com/telco)
[Understanding 5G Technology from Verizon](https://www.verizon.com/5g/)
[Verizon and Unity partner to enable 5G & MEC gaming and enterprise applications](https://www.verizon.com/about/news/verizon-unity-partner-5g-mec-gaming-enterprise)
[Understanding 5G Technology from Intel](https://www.intel.com/content/www/us/en/wireless-network/what-is-5g.html)
[Understanding 5G Technology from Qualcomm](https://www.qualcomm.com/invention/5g/what-is-5g)
[Telco Acceleration with Xilinx](https://www.xilinx.com/applications/wired-wireless/telco.html)
[VIMs on OSM Public Wiki](https://osm.etsi.org/wikipub/index.php/VIMs)
[Amazon EC2 Overview and Networking Introduction for Telecom Companies](https://docs.aws.amazon.com/whitepapers/latest/ec2-networking-for-telecom/ec2-networking-for-telecom.pdf)
[Citrix Certified Associate – Networking(CCA-N)](http://training.citrix.com/cms/index.php/certification/networking/)
[Citrix Certified Professional – Virtualization(CCP-V)](https://www.globalknowledge.com/us-en/training/certification-prep/brands/citrix/section/virtualization/citrix-certified-professional-virtualization-ccp-v/)
[CCNP Routing and Switching](https://learningnetwork.cisco.com/s/ccnp-enterprise)
[Certified Information Security Manager(CISM)](https://www.isaca.org/credentialing/cism)
[Wireshark Certified Network Analyst (WCNA)](https://www.wiresharktraining.com/certification.html)
[Juniper Networks Certification Program Enterprise (JNCP)](https://www.juniper.net/us/en/training/certification/)
[Cloud Native Computing Foundation Training and Certification Program](https://www.cncf.io/certification/training/)
## Tools
[Open Stack](https://www.openstack.org/) is an open source cloud platform, deployed as infrastructure-as-a-service (IaaS) to orchestrate data center operations on bare metal, private cloud hardware, public cloud resources, or both (hybrid/multi-cloud architecture). OpenStack includes advance use of virtualization & SDN for network traffic optimization to handle the core cloud-computing services of compute, networking, storage, identity, and image services.
[StarlingX](https://www.starlingx.io/) is a complete cloud infrastructure software stack for the edge used by the most demanding applications in industrial IOT, telecom, video delivery and other ultra-low latency use cases.
[Airship](https://www.airshipit.org/) is a collection of open source tools for automating cloud provisioning and management. Airship provides a declarative framework for defining and managing the life cycle of open infrastructure tools and the underlying hardware.
[Network functions virtualization (NFV)](https://www.vmware.com/topics/glossary/content/network-functions-virtualization-nfv) is the replacement of network appliance hardware with virtual machines. The virtual machines use a hypervisor to run networking software and processes such as routing and load balancing. NFV allows for the separation of communication services from dedicated hardware, such as routers and firewalls. This separation means network operations can provide new services dynamically and without installing new hardware. Deploying network components with network functions virtualization only takes hours compared to months like with traditional networking solutions.
[Software Defined Networking (SDN)](https://www.vmware.com/topics/glossary/content/software-defined-networking) is an approach to networking that uses software-based controllers or application programming interfaces (APIs) to communicate with underlying hardware infrastructure and direct traffic on a network. This model differs from that of traditional networks, which use dedicated hardware devices (routers and switches) to control network traffic.
[Virtualized Infrastructure Manager (VIM)](https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/net_mgmt/network_function_virtualization_Infrastructure/3_2_2/install_guide/Cisco_VIM_Install_Guide_3_2_2/Cisco_VIM_Install_Guide_3_2_2_chapter_00.html) is a service delivery and reduce costs with high performance lifecycle management Manage the full lifecycle of the software and hardware comprising your NFV infrastructure (NFVI), and maintaining a live inventory and allocation plan of both physical and virtual resources.
[Management and Orchestration(MANO)](https://www.etsi.org/technologies/open-source-mano) is an ETSI-hosted initiative to develop an Open Source NFV Management and Orchestration (MANO) software stack aligned with ETSI NFV. Two of the key components of the ETSI NFV architectural framework are the NFV Orchestrator and VNF Manager, known as NFV MANO.
[Magma](https://www.magmacore.org/) is an open source software platform that gives network operators an open, flexible and extendable mobile core network solution. Their mission is to connect the world to a faster network by enabling service providers to build cost-effective and extensible carrier-grade networks. Magma is 3GPP generation (2G, 3G, 4G or upcoming 5G networks) and access network agnostic (cellular or WiFi). It can flexibly support a radio access network with minimal development and deployment effort.
[OpenRAN](https://open-ran.org/) is an intelligent Radio Access Network(RAN) integrated on general purpose platforms with open interface between software defined functions. Open RANecosystem enables enormous flexibility and interoperability with a complete openess to multi-vendor deployments.
[Open vSwitch(OVS)](https://www.openvswitch.org/)is an open source production quality, multilayer virtual switch licensed under the open source Apache 2.0 license. It is designed to enable massive network automation through programmatic extension, while still supporting standard management interfaces and protocols (NetFlow, sFlow, IPFIX, RSPAN, CLI, LACP, 802.1ag).
[Edge](https://www.ibm.com/cloud/what-is-edge-computing) is a distributed computing framework that brings enterprise applications closer to data sources such as IoT devices or local edge servers. This proximity to data at its source can deliver strong business benefits, including faster insights, improved response times and better bandwidth availability.
[Multi-access edge computing (MEC)](https://www.etsi.org/technologies/multi-access-edge-computing) is an Industry Specification Group (ISG) within ETSI to create a standardized, open environment which will allow the efficient and seamless integration of applications from vendors, service providers, and third-parties across multi-vendor Multi-access Edge Computing platforms.
[Virtualized network functions(VNFs)](https://www.juniper.net/documentation/en_US/cso4.1/topics/concept/nsd-vnf-overview.html) is a software application used in a Network Functions Virtualization (NFV) implementation that has well defined interfaces, and provides one or more component networking functions in a defined way. For example, a security VNF provides Network Address Translation (NAT) and firewall component functions.
[Cloud-Native Network Functions(CNF)](https://www.cncf.io/announcements/2020/11/18/cloud-native-network-functions-conformance-launched-by-cncf/) is a network function designed and implemented to run inside containers. CNFs inherit all the cloud native architectural and operational principles including Kubernetes(K8s) lifecycle management, agility, resilience, and observability.
[Physical Network Function(PNF)](https://www.mpirical.com/glossary/pnf-physical-network-function) is a physical network node which has not undergone virtualization. Both PNFs and VNFs (Virtualized Network Functions) can be used to form an overall Network Service.
[Network functions virtualization infrastructure(NFVI)](https://docs.vmware.com/en/VMware-vCloud-NFV/2.0/vmware-vcloud-nfv-reference-architecture-20/GUID-FBEA6C6B-54D8-4A37-87B1-D825F9E0DBC7.html) is the foundation of the overall NFV architecture. It provides the physical compute, storage, and networking hardware that hosts the VNFs. Each NFVI block can be thought of as an NFVI node and many nodes can be deployed and controlled geographically.
# Open Source Security
[Back to the Top](https://github.com/mikeroyal/Self-Hosting-Guide#table-of-contents)
[Open Source Security Foundation (OpenSSF)](https://openssf.org/) is a cross-industry collaboration that brings together leaders to improve the security of open source software by building a broader community, targeted initiatives, and best practices. The OpenSSF brings together open source security initiatives under one foundation to accelerate work through cross-industry support. Along with the Core Infrastructure Initiative and the Open Source Security Coalition, and will include new working groups that address vulnerability disclosures, security tooling and more.
## Security Standards, Frameworks and Benchmarks
[STIGs Benchmarks - Security Technical Implementation Guides](https://public.cyber.mil/stigs/)
[CIS Benchmarks - CIS Center for Internet Security](https://www.cisecurity.org/cis-benchmarks/)
[NIST - Current FIPS](https://www.nist.gov/itl/current-fips)
[ISO Standards Catalogue](https://www.iso.org/standards.html)
[Common Criteria for Information Technology Security Evaluation (CC)](https://www.commoncriteriaportal.org/cc/) is an international standard (ISO / IEC 15408) for computer security. It allows an objective evaluation to validate that a particular product satisfies a defined set of security requirements.
[ISO 22301](https://www.iso.org/en/contents/data/standard/07/51/75106.html) is the international standard that provides a best-practice framework for implementing an optimised BCMS (business continuity management system).
[ISO27001](https://www.iso.org/isoiec-27001-information-security.html) is the international standard that describes the requirements for an ISMS (information security management system). The framework is designed to help organizations manage their security practices in one place, consistently and cost-effectively.
[ISO 27701](https://www.iso.org/en/contents/data/standard/07/16/71670.html) specifies the requirements for a PIMS (privacy information management system) based on the requirements of ISO 27001.
It is extended by a set of privacy-specific requirements, control objectives and controls. Companies that have implemented ISO 27001 will be able to use ISO 27701 to extend their security efforts to cover privacy management.
[EU GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation)](https://gdpr.eu/) is a privacy and data protection law that supersedes existing national data protection laws across the EU, bringing uniformity by introducing just one main data protection law for companies/organizations to comply with.
[CCPA (California Consumer Privacy Act)](https://www.oag.ca.gov/privacy/ccpa) is a data privacy law that took effect on January 1, 2020 in the State of California. It applies to businesses that collect California residents’ personal information, and its privacy requirements are similar to those of the EU’s GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation).
[Payment Card Industry (PCI) Data Security Standards (DSS)](https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/microsoft-365/compliance/offering-pci-dss) is a global information security standard designed to prevent fraud through increased control of credit card data.
[SOC 2](https://www.aicpa.org/interestareas/frc/assuranceadvisoryservices/aicpasoc2report.html) is an auditing procedure that ensures your service providers securely manage your data to protect the interests of your comapny/organization and the privacy of their clients.
[NIST CSF](https://www.nist.gov/national-security-standards) is a voluntary framework primarily intended for critical infrastructure organizations to manage and mitigate cybersecurity risk based on existing best practice.
## Security Tools
[SELinux](https://github.com/SELinuxProject/selinux) is a security enhancement to Linux which allows users and administrators more control over access control. Access can be constrained on such variables as which users and applications can access which resources. These resources may take the form of files. Standard Linux access controls, such as file modes (-rwxr-xr-x) are modifiable by the user and the applications which the user runs. Conversely, SELinux access controls are determined by a policy loaded on the system which may not be changed by careless users or misbehaving applications.
[AppArmor](https://www.apparmor.net/) is an effective and easy-to-use Linux application security system. AppArmor proactively protects the operating system and applications from external or internal threats, even zero-day attacks, by enforcing good behavior and preventing both known and unknown application flaws from being exploited. AppArmor supplements the traditional Unix discretionary access control (DAC) model by providing mandatory access control (MAC). It has been included in the mainline Linux kernel since version 2.6.36 and its development has been supported by Canonical since 2009.
[Control Groups(Cgroups)](https://www.redhat.com/sysadmin/cgroups-part-one) is a Linux kernel feature that allows you to allocate resources such as CPU time, system memory, network bandwidth, or any combination of these resources for user-defined groups of tasks (processes) running on a system.
[EarlyOOM](https://github.com/rfjakob/earlyoom) is a daemon for Linux that enables users to more quickly recover and regain control over their system in low-memory situations with heavy swap usage.
[Libgcrypt](https://www.gnupg.org/related_software/libgcrypt/) is a general purpose cryptographic library originally based on code from GnuPG.
[Kali Linux](https://www.kali.org/) is an open source project that is maintained and funded by Offensive Security, a provider of world-class information security training and penetration testing services.
[Pi-hole](https://pi-hole.net/) is a [DNS sinkhole](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/DNS_Sinkhole) that protects your devices from unwanted content, without installing any client-side software, intended for use on a private network. It is designed for use on embedded devices with network capability, such as the Raspberry Pi, but it can be used on other machines running Linux and cloud implementations.
[Aircrack-ng](https://www.aircrack-ng.org/) is a network software suite consisting of a detector, packet sniffer, WEP and WPA/WPA2-PSK cracker and analysis tool for 802.11 wireless LANs. It works with any wireless network interface controller whose driver supports raw monitoring mode and can sniff 802.11a, 802.11b and 802.11g traffic.
[Burp Suite](https://portswigger.net/burp) is a leading range of cybersecurity tools.
[KernelCI](https://foundation.kernelci.org/) is a community-based open source distributed test automation system focused on upstream kernel development. The primary goal of KernelCI is to use an open testing philosophy to ensure the quality, stability and long-term maintenance of the Linux kernel.
[Continuous Kernel Integration project](https://github.com/cki-project) helps find bugs in kernel patches before they are commited to an upstram kernel tree. We are team of kernel developers, kernel testers, and automation engineers.
[eBPF](https://ebpf.io) is a revolutionary technology that can run sandboxed programs in the Linux kernel without changing kernel source code or loading kernel modules. By making the Linux kernel programmable, infrastructure software can leverage existing layers, making them more intelligent and feature-rich without continuing to add additional layers of complexity to the system.
[Cilium](https://cilium.io/) uses eBPF to accelerate getting data in and out of L7 proxies such as Envoy, enabling efficient visibility into API protocols like HTTP, gRPC, and Kafka.
[Hubble](https://github.com/cilium/hubble) is a Network, Service & Security Observability for Kubernetes using eBPF.
[Istio](https://istio.io/) is an open platform to connect, manage, and secure microservices. Istio's control plane provides an abstraction layer over the underlying cluster management platform, such as Kubernetes and Mesos.
[Certgen](https://github.com/cilium/certgen) is a convenience tool to generate and store certificates for Hubble Relay mTLS.
[Scapy](https://scapy.net/) is a python-based interactive packet manipulation program & library.
[syzkaller](https://github.com/google/syzkaller) is an unsupervised, coverage-guided kernel fuzzer.
[SchedViz](https://github.com/google/schedviz) is a tool for gathering and visualizing kernel scheduling traces on Linux machines.
[oss-fuzz](https://google.github.io/oss-fuzz/) aims to make common open source software more secure and stable by combining modern fuzzing techniques with scalable, distributed execution.
[OSSEC](https://www.ossec.net/) is a free, open-source host-based intrusion detection system. It performs log analysis, integrity checking, Windows registry monitoring, rootkit detection, time-based alerting, and active response.
[Metasploit Project](https://www.metasploit.com/) is a computer security project that provides information about security vulnerabilities and aids in penetration testing and IDS signature development.
[Wfuzz](https://github.com/xmendez/wfuzz) was created to facilitate the task in web applications assessments and it is based on a simple concept: it replaces any reference to the FUZZ keyword by the value of a given payload.
[Nmap](https://nmap.org/) is a security scanner used to discover hosts and services on a computer network, thus building a "map" of the network.
[Patchwork](https://github.com/getpatchwork/patchwork) is a web-based patch tracking system designed to facilitate the contribution and management of contributions to an open-source project.
[pfSense](https://www.pfsense.org/) is a free and open source firewall and router that also features unified threat management, load balancing, multi WAN, and more.
[Snowpatch](https://github.com/ruscur/snowpatch) is a continuous integration tool for projects using a patch-based, mailing-list-centric git workflow. This workflow is used by a number of well-known open source projects such as the Linux kernel.
[Snort](https://www.snort.org/) is an open-source, free and lightweight network intrusion detection system (NIDS) software for Linux and Windows to detect emerging threats.
[Wireshark](https://www.wireshark.org/) is a free and open-source packet analyzer. It is used for network troubleshooting, analysis, software and communications protocol development, and education.
[OpenSCAP](https://www.open-scap.org/) is U.S. standard maintained by [National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST)](https://www.nist.gov/). It provides multiple tools to assist administrators and auditors with assessment, measurement, and enforcement of security baselines. OpenSCAP maintains great flexibility and interoperability by reducing the costs of performing security audits. Whether you want to evaluate DISA STIGs, NIST‘s USGCB, or Red Hat’s Security Response Team’s content, all are supported by OpenSCAP.
[Tink](https://github.com/google/tink) is a multi-language, cross-platform, open source library that provides cryptographic APIs that are secure, easy to use correctly, and harder to misuse.
[OWASP](https://www.owasp.org/index.php/Main_Page) is an online community, produces freely-available articles, methodologies, documentation, tools, and technologies in the field of web application security.
[Open Vulnerability and Assessment Language](https://oval.mitre.org/) is a community effort to standardize how to assess and report upon the machine state of computer systems. OVAL includes a language to encode system details, and community repositories of content. Tools and services that use OVAL provide enterprises with accurate, consistent, and actionable information to improve their security.
[ClamAV](https://www.clamav.net/) is an open source antivirus engine for detecting trojans, viruses, malware & other malicious threats.
## Open Source Security Learning Resources
[Microsoft Open Source Software Security](https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/securityengineering/opensource)
[Cloudflare Open Source Security](https://cloudflare.github.io)
[The Seven Properties of Highly Secure Devices](https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/research/publication/seven-properties-highly-secure-devices/)
[How Layer 7 of the Internet Works](https://www.cloudflare.com/learning/ddos/what-is-layer-7/)
[The 7 Kinds of Security](https://www.veracode.com/sites/default/files/Resources/eBooks/7-kinds-of-security.pdf)
[The Libgcrypt Reference Manual](https://www.gnupg.org/documentation/manuals/gcrypt/)
[The Open Web Application Security Project(OWASP) Foundation Top 10](https://owasp.org/www-project-top-ten/)
[Best Practices for Using Open Source Code from The Linux Foundation](https://www.linuxfoundation.org/blog/2017/11/best-practices-using-open-source-code/)
[AWS Certified Security - Specialty Certification](https://aws.amazon.com/certification/certified-security-specialty/)
[Microsoft Certified: Azure Security Engineer Associate](https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/learn/certifications/azure-security-engineer)
[Google Cloud Certified Professional Cloud Security Engineer](https://cloud.google.com/certification/cloud-security-engineer)
[Cisco Security Certifications](https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/training-events/training-certifications/certifications/security.html)
[The Red Hat Certified Specialist in Security: Linux](https://www.redhat.com/en/services/training/ex415-red-hat-certified-specialist-security-linux-exam)
[Linux Professional Institute LPIC-3 Enterprise Security Certification](https://www.lpi.org/our-certifications/lpic-3-303-overview)
[Cybersecurity Training and Courses from IBM Skills](https://www.ibm.com/skills/topics/cybersecurity/)
[Cybersecurity Courses and Certifications by Offensive Security](https://www.offensive-security.com/courses-and-certifications/)
[RSA Certification Program](https://community.rsa.com/community/training/certification)
[Check Point Certified Security Expert(CCSE) Certification](https://training-certifications.checkpoint.com/#/courses/Check%20Point%20Certified%20Expert%20(CCSE)%20R80.x)
[Check Point Certified Security Administrator(CCSA) Certification](https://training-certifications.checkpoint.com/#/courses/Check%20Point%20Certified%20Admin%20(CCSA)%20R80.x)
[Check Point Certified Security Master (CCSM) Certification](https://training-certifications.checkpoint.com/#/courses/Check%20Point%20Certified%20Master%20(CCSM)%20R80.x)
[Certified Cloud Security Professional(CCSP) Certification](https://www.isc2.org/Certifications/CCSP)
[Certified Information Systems Security Professional (CISSP) Certification](https://www.isc2.org/Certifications/CISSP)
[CCNP Routing and Switching](https://learningnetwork.cisco.com/s/ccnp-enterprise)
[Certified Information Security Manager(CISM)](https://www.isaca.org/credentialing/cism)
[Wireshark Certified Network Analyst (WCNA)](https://www.wiresharktraining.com/certification.html)
[Juniper Networks Certification Program Enterprise (JNCP)](https://www.juniper.net/us/en/training/certification/)
[Security Training Certifications and Courses from Udemy](https://www.udemy.com/courses/search/?src=ukw&q=secuirty)
[Security Training Certifications and Courses from Coursera](https://www.coursera.org/search?query=security&)
[Security Certifications Training from Pluarlsight](https://www.pluralsight.com/browse/information-cyber-security/security-certifications)
# Differential Privacy
[Back to the Top](https://github.com/mikeroyal/Self-Hosting-Guide#table-of-contents)
**VMware Telco Cloud Automation Components. Source: [VMware](https://www.vmware.com/products/telco-cloud-automation.html).**
## Telco Learning Resources
[HPE(Hewlett Packard Enterprise) Telco Blueprints overview](https://techhub.hpe.com/eginfolib/servers/docs/Telco/Blueprints/infocenter/index.html#GUID-9906A227-C1FB-4FD5-A3C3-F3B72EC81CAB.html)
[Network Functions Virtualization Infrastructure (NFVI) by Cisco](https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/solutions/service-provider/network-functions-virtualization-nfv-infrastructure/index.html)
[Introduction to vCloud NFV Telco Edge from VMware](https://docs.vmware.com/en/VMware-vCloud-NFV-OpenStack-Edition/3.1/vloud-nfv-edge-reference-arch-31/GUID-744C45F1-A8D5-4523-9E5E-EAF6336EE3A0.html)
[VMware Telco Cloud Automation(TCA) Architecture Overview](https://docs.vmware.com/en/VMware-Telco-Cloud-Platform-5G-Edition/1.0/telco-cloud-platform-5G-edition-reference-architecture/GUID-C19566B3-F42D-4351-BA55-DE70D55FB0DD.html)
[5G Telco Cloud from VMware](https://telco.vmware.com/)
[Maturing OpenStack Together To Solve Telco Needs from Red Hat](https://www.redhat.com/cms/managed-files/4.Nokia%20CloudBand%20&%20Red%20Hat%20-%20Maturing%20Openstack%20together%20to%20solve%20Telco%20needs%20Ehud%20Malik,%20Senior%20PLM,%20Nokia%20CloudBand.pdf)
[Red Hat telco ecosystem program](https://connect.redhat.com/en/programs/telco-ecosystem)
[OpenStack for Telcos by Canonical](https://ubuntu.com/blog/openstack-for-telcos-by-canonical)
[Open source NFV platform for 5G from Ubuntu](https://ubuntu.com/telco)
[Understanding 5G Technology from Verizon](https://www.verizon.com/5g/)
[Verizon and Unity partner to enable 5G & MEC gaming and enterprise applications](https://www.verizon.com/about/news/verizon-unity-partner-5g-mec-gaming-enterprise)
[Understanding 5G Technology from Intel](https://www.intel.com/content/www/us/en/wireless-network/what-is-5g.html)
[Understanding 5G Technology from Qualcomm](https://www.qualcomm.com/invention/5g/what-is-5g)
[Telco Acceleration with Xilinx](https://www.xilinx.com/applications/wired-wireless/telco.html)
[VIMs on OSM Public Wiki](https://osm.etsi.org/wikipub/index.php/VIMs)
[Amazon EC2 Overview and Networking Introduction for Telecom Companies](https://docs.aws.amazon.com/whitepapers/latest/ec2-networking-for-telecom/ec2-networking-for-telecom.pdf)
[Citrix Certified Associate – Networking(CCA-N)](http://training.citrix.com/cms/index.php/certification/networking/)
[Citrix Certified Professional – Virtualization(CCP-V)](https://www.globalknowledge.com/us-en/training/certification-prep/brands/citrix/section/virtualization/citrix-certified-professional-virtualization-ccp-v/)
[CCNP Routing and Switching](https://learningnetwork.cisco.com/s/ccnp-enterprise)
[Certified Information Security Manager(CISM)](https://www.isaca.org/credentialing/cism)
[Wireshark Certified Network Analyst (WCNA)](https://www.wiresharktraining.com/certification.html)
[Juniper Networks Certification Program Enterprise (JNCP)](https://www.juniper.net/us/en/training/certification/)
[Cloud Native Computing Foundation Training and Certification Program](https://www.cncf.io/certification/training/)
## Tools
[Open Stack](https://www.openstack.org/) is an open source cloud platform, deployed as infrastructure-as-a-service (IaaS) to orchestrate data center operations on bare metal, private cloud hardware, public cloud resources, or both (hybrid/multi-cloud architecture). OpenStack includes advance use of virtualization & SDN for network traffic optimization to handle the core cloud-computing services of compute, networking, storage, identity, and image services.
[StarlingX](https://www.starlingx.io/) is a complete cloud infrastructure software stack for the edge used by the most demanding applications in industrial IOT, telecom, video delivery and other ultra-low latency use cases.
[Airship](https://www.airshipit.org/) is a collection of open source tools for automating cloud provisioning and management. Airship provides a declarative framework for defining and managing the life cycle of open infrastructure tools and the underlying hardware.
[Network functions virtualization (NFV)](https://www.vmware.com/topics/glossary/content/network-functions-virtualization-nfv) is the replacement of network appliance hardware with virtual machines. The virtual machines use a hypervisor to run networking software and processes such as routing and load balancing. NFV allows for the separation of communication services from dedicated hardware, such as routers and firewalls. This separation means network operations can provide new services dynamically and without installing new hardware. Deploying network components with network functions virtualization only takes hours compared to months like with traditional networking solutions.
[Software Defined Networking (SDN)](https://www.vmware.com/topics/glossary/content/software-defined-networking) is an approach to networking that uses software-based controllers or application programming interfaces (APIs) to communicate with underlying hardware infrastructure and direct traffic on a network. This model differs from that of traditional networks, which use dedicated hardware devices (routers and switches) to control network traffic.
[Virtualized Infrastructure Manager (VIM)](https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/net_mgmt/network_function_virtualization_Infrastructure/3_2_2/install_guide/Cisco_VIM_Install_Guide_3_2_2/Cisco_VIM_Install_Guide_3_2_2_chapter_00.html) is a service delivery and reduce costs with high performance lifecycle management Manage the full lifecycle of the software and hardware comprising your NFV infrastructure (NFVI), and maintaining a live inventory and allocation plan of both physical and virtual resources.
[Management and Orchestration(MANO)](https://www.etsi.org/technologies/open-source-mano) is an ETSI-hosted initiative to develop an Open Source NFV Management and Orchestration (MANO) software stack aligned with ETSI NFV. Two of the key components of the ETSI NFV architectural framework are the NFV Orchestrator and VNF Manager, known as NFV MANO.
[Magma](https://www.magmacore.org/) is an open source software platform that gives network operators an open, flexible and extendable mobile core network solution. Their mission is to connect the world to a faster network by enabling service providers to build cost-effective and extensible carrier-grade networks. Magma is 3GPP generation (2G, 3G, 4G or upcoming 5G networks) and access network agnostic (cellular or WiFi). It can flexibly support a radio access network with minimal development and deployment effort.
[OpenRAN](https://open-ran.org/) is an intelligent Radio Access Network(RAN) integrated on general purpose platforms with open interface between software defined functions. Open RANecosystem enables enormous flexibility and interoperability with a complete openess to multi-vendor deployments.
[Open vSwitch(OVS)](https://www.openvswitch.org/)is an open source production quality, multilayer virtual switch licensed under the open source Apache 2.0 license. It is designed to enable massive network automation through programmatic extension, while still supporting standard management interfaces and protocols (NetFlow, sFlow, IPFIX, RSPAN, CLI, LACP, 802.1ag).
[Edge](https://www.ibm.com/cloud/what-is-edge-computing) is a distributed computing framework that brings enterprise applications closer to data sources such as IoT devices or local edge servers. This proximity to data at its source can deliver strong business benefits, including faster insights, improved response times and better bandwidth availability.
[Multi-access edge computing (MEC)](https://www.etsi.org/technologies/multi-access-edge-computing) is an Industry Specification Group (ISG) within ETSI to create a standardized, open environment which will allow the efficient and seamless integration of applications from vendors, service providers, and third-parties across multi-vendor Multi-access Edge Computing platforms.
[Virtualized network functions(VNFs)](https://www.juniper.net/documentation/en_US/cso4.1/topics/concept/nsd-vnf-overview.html) is a software application used in a Network Functions Virtualization (NFV) implementation that has well defined interfaces, and provides one or more component networking functions in a defined way. For example, a security VNF provides Network Address Translation (NAT) and firewall component functions.
[Cloud-Native Network Functions(CNF)](https://www.cncf.io/announcements/2020/11/18/cloud-native-network-functions-conformance-launched-by-cncf/) is a network function designed and implemented to run inside containers. CNFs inherit all the cloud native architectural and operational principles including Kubernetes(K8s) lifecycle management, agility, resilience, and observability.
[Physical Network Function(PNF)](https://www.mpirical.com/glossary/pnf-physical-network-function) is a physical network node which has not undergone virtualization. Both PNFs and VNFs (Virtualized Network Functions) can be used to form an overall Network Service.
[Network functions virtualization infrastructure(NFVI)](https://docs.vmware.com/en/VMware-vCloud-NFV/2.0/vmware-vcloud-nfv-reference-architecture-20/GUID-FBEA6C6B-54D8-4A37-87B1-D825F9E0DBC7.html) is the foundation of the overall NFV architecture. It provides the physical compute, storage, and networking hardware that hosts the VNFs. Each NFVI block can be thought of as an NFVI node and many nodes can be deployed and controlled geographically.
# Open Source Security
[Back to the Top](https://github.com/mikeroyal/Self-Hosting-Guide#table-of-contents)
[Open Source Security Foundation (OpenSSF)](https://openssf.org/) is a cross-industry collaboration that brings together leaders to improve the security of open source software by building a broader community, targeted initiatives, and best practices. The OpenSSF brings together open source security initiatives under one foundation to accelerate work through cross-industry support. Along with the Core Infrastructure Initiative and the Open Source Security Coalition, and will include new working groups that address vulnerability disclosures, security tooling and more.
## Security Standards, Frameworks and Benchmarks
[STIGs Benchmarks - Security Technical Implementation Guides](https://public.cyber.mil/stigs/)
[CIS Benchmarks - CIS Center for Internet Security](https://www.cisecurity.org/cis-benchmarks/)
[NIST - Current FIPS](https://www.nist.gov/itl/current-fips)
[ISO Standards Catalogue](https://www.iso.org/standards.html)
[Common Criteria for Information Technology Security Evaluation (CC)](https://www.commoncriteriaportal.org/cc/) is an international standard (ISO / IEC 15408) for computer security. It allows an objective evaluation to validate that a particular product satisfies a defined set of security requirements.
[ISO 22301](https://www.iso.org/en/contents/data/standard/07/51/75106.html) is the international standard that provides a best-practice framework for implementing an optimised BCMS (business continuity management system).
[ISO27001](https://www.iso.org/isoiec-27001-information-security.html) is the international standard that describes the requirements for an ISMS (information security management system). The framework is designed to help organizations manage their security practices in one place, consistently and cost-effectively.
[ISO 27701](https://www.iso.org/en/contents/data/standard/07/16/71670.html) specifies the requirements for a PIMS (privacy information management system) based on the requirements of ISO 27001.
It is extended by a set of privacy-specific requirements, control objectives and controls. Companies that have implemented ISO 27001 will be able to use ISO 27701 to extend their security efforts to cover privacy management.
[EU GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation)](https://gdpr.eu/) is a privacy and data protection law that supersedes existing national data protection laws across the EU, bringing uniformity by introducing just one main data protection law for companies/organizations to comply with.
[CCPA (California Consumer Privacy Act)](https://www.oag.ca.gov/privacy/ccpa) is a data privacy law that took effect on January 1, 2020 in the State of California. It applies to businesses that collect California residents’ personal information, and its privacy requirements are similar to those of the EU’s GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation).
[Payment Card Industry (PCI) Data Security Standards (DSS)](https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/microsoft-365/compliance/offering-pci-dss) is a global information security standard designed to prevent fraud through increased control of credit card data.
[SOC 2](https://www.aicpa.org/interestareas/frc/assuranceadvisoryservices/aicpasoc2report.html) is an auditing procedure that ensures your service providers securely manage your data to protect the interests of your comapny/organization and the privacy of their clients.
[NIST CSF](https://www.nist.gov/national-security-standards) is a voluntary framework primarily intended for critical infrastructure organizations to manage and mitigate cybersecurity risk based on existing best practice.
## Security Tools
[SELinux](https://github.com/SELinuxProject/selinux) is a security enhancement to Linux which allows users and administrators more control over access control. Access can be constrained on such variables as which users and applications can access which resources. These resources may take the form of files. Standard Linux access controls, such as file modes (-rwxr-xr-x) are modifiable by the user and the applications which the user runs. Conversely, SELinux access controls are determined by a policy loaded on the system which may not be changed by careless users or misbehaving applications.
[AppArmor](https://www.apparmor.net/) is an effective and easy-to-use Linux application security system. AppArmor proactively protects the operating system and applications from external or internal threats, even zero-day attacks, by enforcing good behavior and preventing both known and unknown application flaws from being exploited. AppArmor supplements the traditional Unix discretionary access control (DAC) model by providing mandatory access control (MAC). It has been included in the mainline Linux kernel since version 2.6.36 and its development has been supported by Canonical since 2009.
[Control Groups(Cgroups)](https://www.redhat.com/sysadmin/cgroups-part-one) is a Linux kernel feature that allows you to allocate resources such as CPU time, system memory, network bandwidth, or any combination of these resources for user-defined groups of tasks (processes) running on a system.
[EarlyOOM](https://github.com/rfjakob/earlyoom) is a daemon for Linux that enables users to more quickly recover and regain control over their system in low-memory situations with heavy swap usage.
[Libgcrypt](https://www.gnupg.org/related_software/libgcrypt/) is a general purpose cryptographic library originally based on code from GnuPG.
[Kali Linux](https://www.kali.org/) is an open source project that is maintained and funded by Offensive Security, a provider of world-class information security training and penetration testing services.
[Pi-hole](https://pi-hole.net/) is a [DNS sinkhole](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/DNS_Sinkhole) that protects your devices from unwanted content, without installing any client-side software, intended for use on a private network. It is designed for use on embedded devices with network capability, such as the Raspberry Pi, but it can be used on other machines running Linux and cloud implementations.
[Aircrack-ng](https://www.aircrack-ng.org/) is a network software suite consisting of a detector, packet sniffer, WEP and WPA/WPA2-PSK cracker and analysis tool for 802.11 wireless LANs. It works with any wireless network interface controller whose driver supports raw monitoring mode and can sniff 802.11a, 802.11b and 802.11g traffic.
[Burp Suite](https://portswigger.net/burp) is a leading range of cybersecurity tools.
[KernelCI](https://foundation.kernelci.org/) is a community-based open source distributed test automation system focused on upstream kernel development. The primary goal of KernelCI is to use an open testing philosophy to ensure the quality, stability and long-term maintenance of the Linux kernel.
[Continuous Kernel Integration project](https://github.com/cki-project) helps find bugs in kernel patches before they are commited to an upstram kernel tree. We are team of kernel developers, kernel testers, and automation engineers.
[eBPF](https://ebpf.io) is a revolutionary technology that can run sandboxed programs in the Linux kernel without changing kernel source code or loading kernel modules. By making the Linux kernel programmable, infrastructure software can leverage existing layers, making them more intelligent and feature-rich without continuing to add additional layers of complexity to the system.
[Cilium](https://cilium.io/) uses eBPF to accelerate getting data in and out of L7 proxies such as Envoy, enabling efficient visibility into API protocols like HTTP, gRPC, and Kafka.
[Hubble](https://github.com/cilium/hubble) is a Network, Service & Security Observability for Kubernetes using eBPF.
[Istio](https://istio.io/) is an open platform to connect, manage, and secure microservices. Istio's control plane provides an abstraction layer over the underlying cluster management platform, such as Kubernetes and Mesos.
[Certgen](https://github.com/cilium/certgen) is a convenience tool to generate and store certificates for Hubble Relay mTLS.
[Scapy](https://scapy.net/) is a python-based interactive packet manipulation program & library.
[syzkaller](https://github.com/google/syzkaller) is an unsupervised, coverage-guided kernel fuzzer.
[SchedViz](https://github.com/google/schedviz) is a tool for gathering and visualizing kernel scheduling traces on Linux machines.
[oss-fuzz](https://google.github.io/oss-fuzz/) aims to make common open source software more secure and stable by combining modern fuzzing techniques with scalable, distributed execution.
[OSSEC](https://www.ossec.net/) is a free, open-source host-based intrusion detection system. It performs log analysis, integrity checking, Windows registry monitoring, rootkit detection, time-based alerting, and active response.
[Metasploit Project](https://www.metasploit.com/) is a computer security project that provides information about security vulnerabilities and aids in penetration testing and IDS signature development.
[Wfuzz](https://github.com/xmendez/wfuzz) was created to facilitate the task in web applications assessments and it is based on a simple concept: it replaces any reference to the FUZZ keyword by the value of a given payload.
[Nmap](https://nmap.org/) is a security scanner used to discover hosts and services on a computer network, thus building a "map" of the network.
[Patchwork](https://github.com/getpatchwork/patchwork) is a web-based patch tracking system designed to facilitate the contribution and management of contributions to an open-source project.
[pfSense](https://www.pfsense.org/) is a free and open source firewall and router that also features unified threat management, load balancing, multi WAN, and more.
[Snowpatch](https://github.com/ruscur/snowpatch) is a continuous integration tool for projects using a patch-based, mailing-list-centric git workflow. This workflow is used by a number of well-known open source projects such as the Linux kernel.
[Snort](https://www.snort.org/) is an open-source, free and lightweight network intrusion detection system (NIDS) software for Linux and Windows to detect emerging threats.
[Wireshark](https://www.wireshark.org/) is a free and open-source packet analyzer. It is used for network troubleshooting, analysis, software and communications protocol development, and education.
[OpenSCAP](https://www.open-scap.org/) is U.S. standard maintained by [National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST)](https://www.nist.gov/). It provides multiple tools to assist administrators and auditors with assessment, measurement, and enforcement of security baselines. OpenSCAP maintains great flexibility and interoperability by reducing the costs of performing security audits. Whether you want to evaluate DISA STIGs, NIST‘s USGCB, or Red Hat’s Security Response Team’s content, all are supported by OpenSCAP.
[Tink](https://github.com/google/tink) is a multi-language, cross-platform, open source library that provides cryptographic APIs that are secure, easy to use correctly, and harder to misuse.
[OWASP](https://www.owasp.org/index.php/Main_Page) is an online community, produces freely-available articles, methodologies, documentation, tools, and technologies in the field of web application security.
[Open Vulnerability and Assessment Language](https://oval.mitre.org/) is a community effort to standardize how to assess and report upon the machine state of computer systems. OVAL includes a language to encode system details, and community repositories of content. Tools and services that use OVAL provide enterprises with accurate, consistent, and actionable information to improve their security.
[ClamAV](https://www.clamav.net/) is an open source antivirus engine for detecting trojans, viruses, malware & other malicious threats.
## Open Source Security Learning Resources
[Microsoft Open Source Software Security](https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/securityengineering/opensource)
[Cloudflare Open Source Security](https://cloudflare.github.io)
[The Seven Properties of Highly Secure Devices](https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/research/publication/seven-properties-highly-secure-devices/)
[How Layer 7 of the Internet Works](https://www.cloudflare.com/learning/ddos/what-is-layer-7/)
[The 7 Kinds of Security](https://www.veracode.com/sites/default/files/Resources/eBooks/7-kinds-of-security.pdf)
[The Libgcrypt Reference Manual](https://www.gnupg.org/documentation/manuals/gcrypt/)
[The Open Web Application Security Project(OWASP) Foundation Top 10](https://owasp.org/www-project-top-ten/)
[Best Practices for Using Open Source Code from The Linux Foundation](https://www.linuxfoundation.org/blog/2017/11/best-practices-using-open-source-code/)
[AWS Certified Security - Specialty Certification](https://aws.amazon.com/certification/certified-security-specialty/)
[Microsoft Certified: Azure Security Engineer Associate](https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/learn/certifications/azure-security-engineer)
[Google Cloud Certified Professional Cloud Security Engineer](https://cloud.google.com/certification/cloud-security-engineer)
[Cisco Security Certifications](https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/training-events/training-certifications/certifications/security.html)
[The Red Hat Certified Specialist in Security: Linux](https://www.redhat.com/en/services/training/ex415-red-hat-certified-specialist-security-linux-exam)
[Linux Professional Institute LPIC-3 Enterprise Security Certification](https://www.lpi.org/our-certifications/lpic-3-303-overview)
[Cybersecurity Training and Courses from IBM Skills](https://www.ibm.com/skills/topics/cybersecurity/)
[Cybersecurity Courses and Certifications by Offensive Security](https://www.offensive-security.com/courses-and-certifications/)
[RSA Certification Program](https://community.rsa.com/community/training/certification)
[Check Point Certified Security Expert(CCSE) Certification](https://training-certifications.checkpoint.com/#/courses/Check%20Point%20Certified%20Expert%20(CCSE)%20R80.x)
[Check Point Certified Security Administrator(CCSA) Certification](https://training-certifications.checkpoint.com/#/courses/Check%20Point%20Certified%20Admin%20(CCSA)%20R80.x)
[Check Point Certified Security Master (CCSM) Certification](https://training-certifications.checkpoint.com/#/courses/Check%20Point%20Certified%20Master%20(CCSM)%20R80.x)
[Certified Cloud Security Professional(CCSP) Certification](https://www.isc2.org/Certifications/CCSP)
[Certified Information Systems Security Professional (CISSP) Certification](https://www.isc2.org/Certifications/CISSP)
[CCNP Routing and Switching](https://learningnetwork.cisco.com/s/ccnp-enterprise)
[Certified Information Security Manager(CISM)](https://www.isaca.org/credentialing/cism)
[Wireshark Certified Network Analyst (WCNA)](https://www.wiresharktraining.com/certification.html)
[Juniper Networks Certification Program Enterprise (JNCP)](https://www.juniper.net/us/en/training/certification/)
[Security Training Certifications and Courses from Udemy](https://www.udemy.com/courses/search/?src=ukw&q=secuirty)
[Security Training Certifications and Courses from Coursera](https://www.coursera.org/search?query=security&)
[Security Certifications Training from Pluarlsight](https://www.pluralsight.com/browse/information-cyber-security/security-certifications)
# Differential Privacy
[Back to the Top](https://github.com/mikeroyal/Self-Hosting-Guide#table-of-contents)

 ## ML frameworks & applications
[TensorFlow](https://www.tensorflow.org) is an end-to-end open source platform for machine learning. It has a comprehensive, flexible ecosystem of tools, libraries and community resources that lets researchers push the state-of-the-art in ML and developers easily build and deploy ML powered applications.
[Tensorman](https://github.com/pop-os/tensorman) is a utility for easy management of Tensorflow containers by developed by [System76]( https://system76.com).Tensorman allows Tensorflow to operate in an isolated environment that is contained from the rest of the system. This virtual environment can operate independent of the base system, allowing you to use any version of Tensorflow on any version of a Linux distribution that supports the Docker runtime.
[Keras](https://keras.io) is a high-level neural networks API, written in Python and capable of running on top of TensorFlow, CNTK, or Theano.It was developed with a focus on enabling fast experimentation. It is capable of running on top of TensorFlow, Microsoft Cognitive Toolkit, R, Theano, or PlaidML.
[PyTorch](https://pytorch.org) is a library for deep learning on irregular input data such as graphs, point clouds, and manifolds. Primarily developed by Facebook's AI Research lab.
[Amazon SageMaker](https://aws.amazon.com/sagemaker/) is a fully managed service that provides every developer and data scientist with the ability to build, train, and deploy machine learning (ML) models quickly. SageMaker removes the heavy lifting from each step of the machine learning process to make it easier to develop high quality models.
[Azure Databricks](https://azure.microsoft.com/en-us/services/databricks/) is a fast and collaborative Apache Spark-based big data analytics service designed for data science and data engineering. Azure Databricks, sets up your Apache Spark environment in minutes, autoscale, and collaborate on shared projects in an interactive workspace. Azure Databricks supports Python, Scala, R, Java, and SQL, as well as data science frameworks and libraries including TensorFlow, PyTorch, and scikit-learn.
[Microsoft Cognitive Toolkit (CNTK)](https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/cognitive-toolkit/) is an open-source toolkit for commercial-grade distributed deep learning. It describes neural networks as a series of computational steps via a directed graph. CNTK allows the user to easily realize and combine popular model types such as feed-forward DNNs, convolutional neural networks (CNNs) and recurrent neural networks (RNNs/LSTMs). CNTK implements stochastic gradient descent (SGD, error backpropagation) learning with automatic differentiation and parallelization across multiple GPUs and servers.
[Apache Airflow](https://airflow.apache.org) is an open-source workflow management platform created by the community to programmatically author, schedule and monitor workflows. Install. Principles. Scalable. Airflow has a modular architecture and uses a message queue to orchestrate an arbitrary number of workers. Airflow is ready to scale to infinity.
[Open Neural Network Exchange(ONNX)](https://github.com/onnx) is an open ecosystem that empowers AI developers to choose the right tools as their project evolves. ONNX provides an open source format for AI models, both deep learning and traditional ML. It defines an extensible computation graph model, as well as definitions of built-in operators and standard data types.
[Apache MXNet](https://mxnet.apache.org/) is a deep learning framework designed for both efficiency and flexibility. It allows you to mix symbolic and imperative programming to maximize efficiency and productivity. At its core, MXNet contains a dynamic dependency scheduler that automatically parallelizes both symbolic and imperative operations on the fly. A graph optimization layer on top of that makes symbolic execution fast and memory efficient. MXNet is portable and lightweight, scaling effectively to multiple GPUs and multiple machines. Support for Python, R, Julia, Scala, Go, Javascript and more.
[AutoGluon](https://autogluon.mxnet.io/index.html) is toolkit for Deep learning that automates machine learning tasks enabling you to easily achieve strong predictive performance in your applications. With just a few lines of code, you can train and deploy high-accuracy deep learning models on tabular, image, and text data.
[Anaconda](https://www.anaconda.com/) is a very popular Data Science platform for machine learning and deep learning that enables users to develop models, train them, and deploy them.
[PlaidML](https://github.com/plaidml/plaidml) is an advanced and portable tensor compiler for enabling deep learning on laptops, embedded devices, or other devices where the available computing hardware is not well supported or the available software stack contains unpalatable license restrictions.
[OpenCV](https://opencv.org) is a highly optimized library with focus on real-time computer vision applications. The C++, Python, and Java interfaces support Linux, MacOS, Windows, iOS, and Android.
[Scikit-Learn](https://scikit-learn.org/stable/index.html) is a Python module for machine learning built on top of SciPy, NumPy, and matplotlib, making it easier to apply robust and simple implementations of many popular machine learning algorithms.
[Weka](https://www.cs.waikato.ac.nz/ml/weka/) is an open source machine learning software that can be accessed through a graphical user interface, standard terminal applications, or a Java API. It is widely used for teaching, research, and industrial applications, contains a plethora of built-in tools for standard machine learning tasks, and additionally gives transparent access to well-known toolboxes such as scikit-learn, R, and Deeplearning4j.
[Caffe](https://github.com/BVLC/caffe) is a deep learning framework made with expression, speed, and modularity in mind. It is developed by Berkeley AI Research (BAIR)/The Berkeley Vision and Learning Center (BVLC) and community contributors.
[Theano](https://github.com/Theano/Theano) is a Python library that allows you to define, optimize, and evaluate mathematical expressions involving multi-dimensional arrays efficiently including tight integration with NumPy.
[nGraph](https://github.com/NervanaSystems/ngraph) is an open source C++ library, compiler and runtime for Deep Learning. The nGraph Compiler aims to accelerate developing AI workloads using any deep learning framework and deploying to a variety of hardware targets.It provides the freedom, performance, and ease-of-use to AI developers.
[NVIDIA cuDNN](https://developer.nvidia.com/cudnn) is a GPU-accelerated library of primitives for [deep neural networks](https://developer.nvidia.com/deep-learning). cuDNN provides highly tuned implementations for standard routines such as forward and backward convolution, pooling, normalization, and activation layers. cuDNN accelerates widely used deep learning frameworks, including [Caffe2](https://caffe2.ai/), [Chainer](https://chainer.org/), [Keras](https://keras.io/), [MATLAB](https://www.mathworks.com/solutions/deep-learning.html), [MxNet](https://mxnet.incubator.apache.org/), [PyTorch](https://pytorch.org/), and [TensorFlow](https://www.tensorflow.org/).
[Jupyter Notebook](https://jupyter.org/) is an open-source web application that allows you to create and share documents that contain live code, equations, visualizations and narrative text. Jupyter is used widely in industries that do data cleaning and transformation, numerical simulation, statistical modeling, data visualization, data science, and machine learning.
[Apache Spark](https://spark.apache.org/) is a unified analytics engine for large-scale data processing. It provides high-level APIs in Scala, Java, Python, and R, and an optimized engine that supports general computation graphs for data analysis. It also supports a rich set of higher-level tools including Spark SQL for SQL and DataFrames, MLlib for machine learning, GraphX for graph processing, and Structured Streaming for stream processing.
[Apache Spark Connector for SQL Server and Azure SQL](https://github.com/microsoft/sql-spark-connector) is a high-performance connector that enables you to use transactional data in big data analytics and persists results for ad-hoc queries or reporting. The connector allows you to use any SQL database, on-premises or in the cloud, as an input data source or output data sink for Spark jobs.
[Apache PredictionIO](https://predictionio.apache.org/) is an open source machine learning framework for developers, data scientists, and end users. It supports event collection, deployment of algorithms, evaluation, querying predictive results via REST APIs. It is based on scalable open source services like Hadoop, HBase (and other DBs), Elasticsearch, Spark and implements what is called a Lambda Architecture.
[Cluster Manager for Apache Kafka(CMAK)](https://github.com/yahoo/CMAK) is a tool for managing [Apache Kafka](https://kafka.apache.org/) clusters.
[BigDL](https://bigdl-project.github.io/) is a distributed deep learning library for Apache Spark. With BigDL, users can write their deep learning applications as standard Spark programs, which can directly run on top of existing Spark or Hadoop clusters.
[Koalas](https://pypi.org/project/koalas/) is project makes data scientists more productive when interacting with big data, by implementing the pandas DataFrame API on top of Apache Spark.
[Apache Spark™ MLflow](https://mlflow.org/) is an open source platform to manage the ML lifecycle, including experimentation, reproducibility, deployment, and a central model registry. MLflow currently offers four components:
**[MLflow Tracking](https://mlflow.org/docs/latest/tracking.html)**: Record and query experiments: code, data, config, and results.
**[MLflow Projects](https://mlflow.org/docs/latest/projects.html)**: Package data science code in a format to reproduce runs on any platform.
**[MLflow Models](https://mlflow.org/docs/latest/models.html)**: Deploy machine learning models in diverse serving environments.
**[Model Registry](https://mlflow.org/docs/latest/model-registry.html)**: Store, annotate, discover, and manage models in a central repository.
[Eclipse Deeplearning4J (DL4J)](https://deeplearning4j.konduit.ai/) is a set of projects intended to support all the needs of a JVM-based(Scala, Kotlin, Clojure, and Groovy) deep learning application. This means starting with the raw data, loading and preprocessing it from wherever and whatever format it is in to building and tuning a wide variety of simple and complex deep learning networks.
[Numba](https://github.com/numba/numba) is an open source, NumPy-aware optimizing compiler for Python sponsored by Anaconda, Inc. It uses the LLVM compiler project to generate machine code from Python syntax. Numba can compile a large subset of numerically-focused Python, including many NumPy functions. Additionally, Numba has support for automatic parallelization of loops, generation of GPU-accelerated code, and creation of ufuncs and C callbacks.
[Chainer](https://chainer.org/) is a Python-based deep learning framework aiming at flexibility. It provides automatic differentiation APIs based on the define-by-run approach (dynamic computational graphs) as well as object-oriented high-level APIs to build and train neural networks. It also supports CUDA/cuDNN using [CuPy](https://github.com/cupy/cupy) for high performance training and inference.
[cuML](https://github.com/rapidsai/cuml) is a suite of libraries that implement machine learning algorithms and mathematical primitives functions that share compatible APIs with other RAPIDS projects. cuML enables data scientists, researchers, and software engineers to run traditional tabular ML tasks on GPUs without going into the details of CUDA programming. In most cases, cuML's Python API matches the API from scikit-learn.
## Online ML Learning Resources
[Machine Learning by Stanford University from Coursera](https://www.coursera.org/learn/machine-learning)
[Machine Learning Courses Online from Coursera](https://www.coursera.org/courses?query=machine%20learning&)
[Machine Learning Courses Online from Udemy](https://www.udemy.com/topic/machine-learning/)
[Learn Machine Learning with Online Courses and Classes from edX](https://www.edx.org/learn/machine-learning)
# IoT Protocols
[Back to the Top](https://github.com/mikeroyal/Self-Hosting-Guide#table-of-contents)
[DBus](https://www.freedesktop.org/wiki/Software/dbus/) is an open source software bus developed Red Hat for inter-process communication, and remote procedure call mechanism that allows communication between multiple processes running concurrently on the same machine.
[SOAP](https://www.soapui.org) is a messaging protocol specification for exchanging structured information in the implementation of web services in computer networks. SOAP can extend HTTP for XML messaging. SOAP provides data transport for Web services. SOAP can exchange complete documents or call a remote procedure. SOAP can be used for broadcasting a message.
[gRPC](https://grpc.io) is a modern, open source remote procedure call (RPC) framework developed by Google that can run anywhere. It enables client and server applications to communicate transparently, and makes it easier to build connected systems.It uses HTTP/2 for transport, Protocol Buffers as the interface description language, and provides features such as authentication, bidirectional streaming and flow control, blocking or nonblocking bindings, and cancellation and timeouts.
[LWM2M](https://www.omaspecworks.org/what-is-oma-specworks/iot/lightweight-m2m-lwm2m/) is a protocol from the Open Mobile Alliance for M2M or IoT device management. Lightweight M2M enabler defines the application layer communication protocol between a LWM2M Server and a LWM2M Client, which is located in a LWM2M Device.
[Advanced Message Queuing Protocol (AMQP)](https://www.amqp.org) is an open standard for passing business messages between applications or organizations. It connects systems, feeds business processes with the information they need and reliably transmits onward the instructions that achieve their goals. The defining features of AMQP are message orientation, queuing, routing, reliability and security.
[Constrained Application Protocol (CoAP)](https://coap.technology) is a specialized web transfer protocol for use with constrained nodes and constrained networks in the Internet of Things. The protocol is designed for machine-to-machine (M2M) applications such as smart energy and building automation."
[Extensible Messaging and Presence Protocol (XMPP)](https://xmpp.org) is a communication protocol for message-oriented middleware based on XML (Extensible Markup Language). It enables the near real-time exchange of structured yet extensible data between any two or more network entities.
[OASIS Message Queuing Telemetry Transport (MQTT)](https://www.oasis-open.org) is an open OASIS and ISO standard (ISO/IEC 20922) lightweight, publish-subscribe network protocol that transports messages between devices. The protocol usually runs over TCP/IP; however, any network protocol that provides ordered, lossless, bi-directional connections can support MQTT.
[Very Simple Control Protocol (VSCP)](https://vscp.org) is a free automation protocol suitable for all sorts of automation task where building- or home-automation is in the main focus. Its main advantage is that each VSCP-node can work completely autonomous, being part of distributed network of other nodes.
# Operating systems
[Back to the Top](https://github.com/mikeroyal/Self-Hosting-Guide#table-of-contents)
[Raspberry Pi OS](https://www.raspberrypi.org/software/operating-systems/)
[Hass.io(Home Assistant OS)](https://www.home-assistant.io/hassio/installation/)
[Manjaro Linux ARM](https://manjaro.org/download/#ARM)
[Arch Linux ARM](https://archlinuxarm.org/platforms/armv8/broadcom/raspberry-pi-4)
[Ubuntu MATE for Raspberry Pi](https://ubuntu-mate.org/ports/raspberry-pi/)
[Ubuntu Desktop for Raspberry Pi](https://ubuntu.com/raspberry-pi)
[Ubuntu Core on a Raspberry Pi](https://ubuntu.com/download/raspberry-pi-core)
[Ubuntu Server for ARM](https://ubuntu.com/download/server/arm)
[Debian](https://wiki.debian.org)
[Fedora ARM](https://arm.fedoraproject.org)
[openSUSE](https://en.opensuse.org/openSUSE)
[SUSE](https://documentation.suse.com/)
[Kali Linux for the Raspberry Pi](https://www.kali.org/docs/arm/kali-linux-raspberry-pi/)
[RetroArch](https://www.retroarch.com/?page=platforms)
[RetroPie](https://retropie.org.uk/)
[LibreELEC](https://libreelec.tv/)
[OSMC](https://osmc.tv)
[RISC OS](https://www.riscosopen.org/content/)
[Windows 10 IoT Core](https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/iot-core/windows-iot-core)
[HeliOS](https://www.arduino.cc/reference/en/libraries/helios/) is an embedded operating system that is free for anyone to use. While called an operating system for simplicity, HeliOS is better described as a multitasking kernel for embedded systems.
[Simba](https://simba-os.readthedocs.io/en/latest/getting-started.html) is a small OS for an Embedded Programming Platform like Arduino. It aims to make embedded programming easy and portable.
[Trampoline](https://github.com/TrampolineRTOS/) is a static RTOS for small embedded systems.
[DuinOS](https://github.com/DuinOS/DuinOS) is Framework (a wrapper) for use the FreeRTOSwith Arduino.
[VxWorks](https://www.windriver.com/products/vxworks) is an industry-leading real-time operating systems (RTOS) for building embedded devices and systems for more than 30 years.
[LynxOS](https://www.lynx.com/products/lynxos-posix-real-time-operating-system-rtos) is a native POSIX, hard real-time partitioning operating system developed by Lynx Software Technologies.
[Zephyr OS](https://www.zephyrproject.org/zephyr-rtos-featured-in-risc-v-getting-started-guide/) is a popular security-oriented RTOS with a small-footprint kernel designed for use on resource-constrained and embedded systems. Zephyr has a small-foorprint Kernel focusing on embedded devices compatible with x86, ARM, RISC-V, Xtensa and [others](https://docs.zephyrproject.org/latest/boards/index.html).
[FreeRTOS](https://freertos.org/) is an open source, real-time operating system for microcontrollers that makes small, low-power edge devices easy to program, deploy, secure, connect, and manage.
[Arm Mbed TLS](https://os.mbed.com) provides a comprehensive SSL/TLS solution and makes it easy for developers to include cryptographic and SSL/TLS capabilities in their software and embedded products. As an SSL library, it provides an intuitive API, readable source code and a minimal and highly configurable code footprint.
[Contiki-os](https://github.com/contiki-os) is an operating system for networked, memory-constrained systems with a focus on low-power wireless Internet of Things devices.
# Middleware
[Back to the Top](https://github.com/mikeroyal/Self-Hosting-Guide#table-of-contents)
[IoTSyS](https://iotsyst.com) is an integration middleware for the Internet of Things. It provides a communication stack for embedded devices based on IPv6, Web services, and OBIX to establish interoperable interfaces for smart objects.
[OpenIoT](https://github.com/OpenIotOrg/openiot) is an open source middleware infrastructure will support flexible configuration and deployment of algorithms for collection, and filtering information streams stemming from the internet-connected objects, while at the same time generating and processing important business/applications events.
[OpenRemote](https://github.com/openremote/openremote) is an open source middleware project, which integrates many different protocols and solutions available for smart building, and smart city automation, and offers visualization tools.
[Kaa](https://www.kaaproject.org/platform/) is a Enterprise IoT Platform has been designed with heavy-duty, enterprise-grade IoT solutions in mind. It banishes a monolithic approach to architecture in favour of highly portable microservices, which allow for flexible rearrangement and customization even in the middle of the solution's lifecycle.
# Node flow editors
[Back to the Top](https://github.com/mikeroyal/Self-Hosting-Guide#table-of-contents)
[Node-RED](https://nodered.org) is a programming tool for wiring together hardware devices, APIs and online services in new and interesting ways. It provides a browser-based editor that makes it easy to wire together flows using the wide range of nodes in the palette that can be deployed to its runtime in a single-click.
### Toolkits
[Back to the Top](https://github.com/mikeroyal/Self-Hosting-Guide#table-of-contents)
[KinomaJS](https://github.com/Kinoma/kinomajs) is a visual code editor designed to help developers build starter projects for Kinoma Create and Kinoma Element. The project is built on Angular 2(RC7) and runs in a web browser. The live version is hosted using Google App Engine, but you can modify and build it yourself by following the instructions in this document.
[IoT Toolkit](https://www.segger.com/products/security-iot/iot-toolkit/) is a collection of libraries that enables communication with modern IoT based environments and devices. It is a high-performance collection of libraries optimized for minimum memory consumption in RAM, ROM, high speed, and versatility working on any device.
# Data Visualization
[Back to the Top](https://github.com/mikeroyal/Self-Hosting-Guide#table-of-contents)
[Freeboard](https://github.com/Freeboard/freeboard) is an open source real-time dashboard builder for IOT and other web mashups. A free open-source alternative to Geckoboard.
[ThingSpeak](https://thingspeak.com) is an IoT analytics platform service that allows you to aggregate, visualize, and analyze live data streams in the cloud. You can send data to ThingSpeak from your devices, create instant visualization of live data, and send alerts.
# Search
[Back to the Top](https://github.com/mikeroyal/Self-Hosting-Guide#table-of-contents)
[Thingful](https://www.thingful.net) is a Search Engine for the Internet of Things Find & use open IoT data from around the world.
# Hardware
[Back to the Top](https://github.com/mikeroyal/Self-Hosting-Guide#table-of-contents)
[Arduino Ethernet Shield 2](https://www.arduino.cc/en/Guide/ArduinoEthernetShield) allows an Arduino board to connect to the internet using the Ethernet library and to read and write an SD card using the SD library.This shield is fully compatible with the former version, but relies on the newer W5500 chip.
[Raspberry Pi](https://www.raspberrypi.org) is a series of small single-board computers developed in the United Kingdom by the Raspberry Pi Foundation to promote teaching of basic computer science in schools and in developing countries. Price range from $10-45 depending on model.
[BeagleBone](https://beagleboard.org/bone) is a low-power open-source single-board computer produced by Texas Instruments. It runs Android, Ubuntu and other Linux flavors.
[openPicus FlyportPro](https://www.open-electronics.org/flyport-professional-iot-modules-by-openpicus/) is a system on a module dedicated to IoT and M2M application, especially for professional use. Following some details on the solution: Why FlyportPRO SoM? A system-on-module is the best solution for those customers looking for flexibility and for development time and risk reduction.
[Pinoccio](https://www.open-electronics.org/pinoccio-wifi-mesh-networking-for-arduino-and-iot-available-now/) is a solution to add mesh networking capability and WiFi-Internet access to all yout IoT devices, and it is Arduino compatible. Each board can assume the role of Scout in a Troop and one of the Scouts is the Lead to connect internet: Field Scouts talk to each other using a mesh network (called a Troop), using an extremely low-power radio.
### In-memory data grids
[Back to the Top](https://github.com/mikeroyal/Self-Hosting-Guide#table-of-contents)
[Ehcache](https://www.ehcache.org) is an open source, standards-based cache that boosts performance, offloads your database, and simplifies scalability. It's the most widely-used Java-based cache because it's robust, proven, full-featured, and integrates with other popular libraries and frameworks.
[Hazelcast](https://hazelcast.com) is an open source in-memory data grid based on Java.
# Home automation
[Back to the Top](https://github.com/mikeroyal/Self-Hosting-Guide#table-of-contents)
[Home Assistant](https://github.com/home-assistant/core) is open source home automation that puts local control and privacy first. Powered by a worldwide community of tinkerers and DIY enthusiasts. Perfect to run on a Raspberry Pi or a local server.
[openHAB](https://github.com/openhab) is a cross-platform software with the aim to integrate all kinds of Smart Home technologies, devices, etc.
[Eclipse SmartHome](https://www.eclipse.org/smarthome/) is a framework, not a ready-to-use solution. It offers a large set of features to choose from and leaves enough possibilities to design a Smart Home solution specific to your expectations. Its modular design brings millions of combinations and proves to be easily extensible by custom parts.
[The Thing System](https://github.com/TheThingSystem) is a set of software components and network protocols that aims to fix the Internet of Things. Our steward software is written in node.js making it both portable and easily extensible. It can run on your laptop, or fit onto a small single board computer like the Raspberry Pi.
# Robotics
[Back to the Top](https://github.com/mikeroyal/Self-Hosting-Guide#table-of-contents)
## ML frameworks & applications
[TensorFlow](https://www.tensorflow.org) is an end-to-end open source platform for machine learning. It has a comprehensive, flexible ecosystem of tools, libraries and community resources that lets researchers push the state-of-the-art in ML and developers easily build and deploy ML powered applications.
[Tensorman](https://github.com/pop-os/tensorman) is a utility for easy management of Tensorflow containers by developed by [System76]( https://system76.com).Tensorman allows Tensorflow to operate in an isolated environment that is contained from the rest of the system. This virtual environment can operate independent of the base system, allowing you to use any version of Tensorflow on any version of a Linux distribution that supports the Docker runtime.
[Keras](https://keras.io) is a high-level neural networks API, written in Python and capable of running on top of TensorFlow, CNTK, or Theano.It was developed with a focus on enabling fast experimentation. It is capable of running on top of TensorFlow, Microsoft Cognitive Toolkit, R, Theano, or PlaidML.
[PyTorch](https://pytorch.org) is a library for deep learning on irregular input data such as graphs, point clouds, and manifolds. Primarily developed by Facebook's AI Research lab.
[Amazon SageMaker](https://aws.amazon.com/sagemaker/) is a fully managed service that provides every developer and data scientist with the ability to build, train, and deploy machine learning (ML) models quickly. SageMaker removes the heavy lifting from each step of the machine learning process to make it easier to develop high quality models.
[Azure Databricks](https://azure.microsoft.com/en-us/services/databricks/) is a fast and collaborative Apache Spark-based big data analytics service designed for data science and data engineering. Azure Databricks, sets up your Apache Spark environment in minutes, autoscale, and collaborate on shared projects in an interactive workspace. Azure Databricks supports Python, Scala, R, Java, and SQL, as well as data science frameworks and libraries including TensorFlow, PyTorch, and scikit-learn.
[Microsoft Cognitive Toolkit (CNTK)](https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/cognitive-toolkit/) is an open-source toolkit for commercial-grade distributed deep learning. It describes neural networks as a series of computational steps via a directed graph. CNTK allows the user to easily realize and combine popular model types such as feed-forward DNNs, convolutional neural networks (CNNs) and recurrent neural networks (RNNs/LSTMs). CNTK implements stochastic gradient descent (SGD, error backpropagation) learning with automatic differentiation and parallelization across multiple GPUs and servers.
[Apache Airflow](https://airflow.apache.org) is an open-source workflow management platform created by the community to programmatically author, schedule and monitor workflows. Install. Principles. Scalable. Airflow has a modular architecture and uses a message queue to orchestrate an arbitrary number of workers. Airflow is ready to scale to infinity.
[Open Neural Network Exchange(ONNX)](https://github.com/onnx) is an open ecosystem that empowers AI developers to choose the right tools as their project evolves. ONNX provides an open source format for AI models, both deep learning and traditional ML. It defines an extensible computation graph model, as well as definitions of built-in operators and standard data types.
[Apache MXNet](https://mxnet.apache.org/) is a deep learning framework designed for both efficiency and flexibility. It allows you to mix symbolic and imperative programming to maximize efficiency and productivity. At its core, MXNet contains a dynamic dependency scheduler that automatically parallelizes both symbolic and imperative operations on the fly. A graph optimization layer on top of that makes symbolic execution fast and memory efficient. MXNet is portable and lightweight, scaling effectively to multiple GPUs and multiple machines. Support for Python, R, Julia, Scala, Go, Javascript and more.
[AutoGluon](https://autogluon.mxnet.io/index.html) is toolkit for Deep learning that automates machine learning tasks enabling you to easily achieve strong predictive performance in your applications. With just a few lines of code, you can train and deploy high-accuracy deep learning models on tabular, image, and text data.
[Anaconda](https://www.anaconda.com/) is a very popular Data Science platform for machine learning and deep learning that enables users to develop models, train them, and deploy them.
[PlaidML](https://github.com/plaidml/plaidml) is an advanced and portable tensor compiler for enabling deep learning on laptops, embedded devices, or other devices where the available computing hardware is not well supported or the available software stack contains unpalatable license restrictions.
[OpenCV](https://opencv.org) is a highly optimized library with focus on real-time computer vision applications. The C++, Python, and Java interfaces support Linux, MacOS, Windows, iOS, and Android.
[Scikit-Learn](https://scikit-learn.org/stable/index.html) is a Python module for machine learning built on top of SciPy, NumPy, and matplotlib, making it easier to apply robust and simple implementations of many popular machine learning algorithms.
[Weka](https://www.cs.waikato.ac.nz/ml/weka/) is an open source machine learning software that can be accessed through a graphical user interface, standard terminal applications, or a Java API. It is widely used for teaching, research, and industrial applications, contains a plethora of built-in tools for standard machine learning tasks, and additionally gives transparent access to well-known toolboxes such as scikit-learn, R, and Deeplearning4j.
[Caffe](https://github.com/BVLC/caffe) is a deep learning framework made with expression, speed, and modularity in mind. It is developed by Berkeley AI Research (BAIR)/The Berkeley Vision and Learning Center (BVLC) and community contributors.
[Theano](https://github.com/Theano/Theano) is a Python library that allows you to define, optimize, and evaluate mathematical expressions involving multi-dimensional arrays efficiently including tight integration with NumPy.
[nGraph](https://github.com/NervanaSystems/ngraph) is an open source C++ library, compiler and runtime for Deep Learning. The nGraph Compiler aims to accelerate developing AI workloads using any deep learning framework and deploying to a variety of hardware targets.It provides the freedom, performance, and ease-of-use to AI developers.
[NVIDIA cuDNN](https://developer.nvidia.com/cudnn) is a GPU-accelerated library of primitives for [deep neural networks](https://developer.nvidia.com/deep-learning). cuDNN provides highly tuned implementations for standard routines such as forward and backward convolution, pooling, normalization, and activation layers. cuDNN accelerates widely used deep learning frameworks, including [Caffe2](https://caffe2.ai/), [Chainer](https://chainer.org/), [Keras](https://keras.io/), [MATLAB](https://www.mathworks.com/solutions/deep-learning.html), [MxNet](https://mxnet.incubator.apache.org/), [PyTorch](https://pytorch.org/), and [TensorFlow](https://www.tensorflow.org/).
[Jupyter Notebook](https://jupyter.org/) is an open-source web application that allows you to create and share documents that contain live code, equations, visualizations and narrative text. Jupyter is used widely in industries that do data cleaning and transformation, numerical simulation, statistical modeling, data visualization, data science, and machine learning.
[Apache Spark](https://spark.apache.org/) is a unified analytics engine for large-scale data processing. It provides high-level APIs in Scala, Java, Python, and R, and an optimized engine that supports general computation graphs for data analysis. It also supports a rich set of higher-level tools including Spark SQL for SQL and DataFrames, MLlib for machine learning, GraphX for graph processing, and Structured Streaming for stream processing.
[Apache Spark Connector for SQL Server and Azure SQL](https://github.com/microsoft/sql-spark-connector) is a high-performance connector that enables you to use transactional data in big data analytics and persists results for ad-hoc queries or reporting. The connector allows you to use any SQL database, on-premises or in the cloud, as an input data source or output data sink for Spark jobs.
[Apache PredictionIO](https://predictionio.apache.org/) is an open source machine learning framework for developers, data scientists, and end users. It supports event collection, deployment of algorithms, evaluation, querying predictive results via REST APIs. It is based on scalable open source services like Hadoop, HBase (and other DBs), Elasticsearch, Spark and implements what is called a Lambda Architecture.
[Cluster Manager for Apache Kafka(CMAK)](https://github.com/yahoo/CMAK) is a tool for managing [Apache Kafka](https://kafka.apache.org/) clusters.
[BigDL](https://bigdl-project.github.io/) is a distributed deep learning library for Apache Spark. With BigDL, users can write their deep learning applications as standard Spark programs, which can directly run on top of existing Spark or Hadoop clusters.
[Koalas](https://pypi.org/project/koalas/) is project makes data scientists more productive when interacting with big data, by implementing the pandas DataFrame API on top of Apache Spark.
[Apache Spark™ MLflow](https://mlflow.org/) is an open source platform to manage the ML lifecycle, including experimentation, reproducibility, deployment, and a central model registry. MLflow currently offers four components:
**[MLflow Tracking](https://mlflow.org/docs/latest/tracking.html)**: Record and query experiments: code, data, config, and results.
**[MLflow Projects](https://mlflow.org/docs/latest/projects.html)**: Package data science code in a format to reproduce runs on any platform.
**[MLflow Models](https://mlflow.org/docs/latest/models.html)**: Deploy machine learning models in diverse serving environments.
**[Model Registry](https://mlflow.org/docs/latest/model-registry.html)**: Store, annotate, discover, and manage models in a central repository.
[Eclipse Deeplearning4J (DL4J)](https://deeplearning4j.konduit.ai/) is a set of projects intended to support all the needs of a JVM-based(Scala, Kotlin, Clojure, and Groovy) deep learning application. This means starting with the raw data, loading and preprocessing it from wherever and whatever format it is in to building and tuning a wide variety of simple and complex deep learning networks.
[Numba](https://github.com/numba/numba) is an open source, NumPy-aware optimizing compiler for Python sponsored by Anaconda, Inc. It uses the LLVM compiler project to generate machine code from Python syntax. Numba can compile a large subset of numerically-focused Python, including many NumPy functions. Additionally, Numba has support for automatic parallelization of loops, generation of GPU-accelerated code, and creation of ufuncs and C callbacks.
[Chainer](https://chainer.org/) is a Python-based deep learning framework aiming at flexibility. It provides automatic differentiation APIs based on the define-by-run approach (dynamic computational graphs) as well as object-oriented high-level APIs to build and train neural networks. It also supports CUDA/cuDNN using [CuPy](https://github.com/cupy/cupy) for high performance training and inference.
[cuML](https://github.com/rapidsai/cuml) is a suite of libraries that implement machine learning algorithms and mathematical primitives functions that share compatible APIs with other RAPIDS projects. cuML enables data scientists, researchers, and software engineers to run traditional tabular ML tasks on GPUs without going into the details of CUDA programming. In most cases, cuML's Python API matches the API from scikit-learn.
## Online ML Learning Resources
[Machine Learning by Stanford University from Coursera](https://www.coursera.org/learn/machine-learning)
[Machine Learning Courses Online from Coursera](https://www.coursera.org/courses?query=machine%20learning&)
[Machine Learning Courses Online from Udemy](https://www.udemy.com/topic/machine-learning/)
[Learn Machine Learning with Online Courses and Classes from edX](https://www.edx.org/learn/machine-learning)
# IoT Protocols
[Back to the Top](https://github.com/mikeroyal/Self-Hosting-Guide#table-of-contents)
[DBus](https://www.freedesktop.org/wiki/Software/dbus/) is an open source software bus developed Red Hat for inter-process communication, and remote procedure call mechanism that allows communication between multiple processes running concurrently on the same machine.
[SOAP](https://www.soapui.org) is a messaging protocol specification for exchanging structured information in the implementation of web services in computer networks. SOAP can extend HTTP for XML messaging. SOAP provides data transport for Web services. SOAP can exchange complete documents or call a remote procedure. SOAP can be used for broadcasting a message.
[gRPC](https://grpc.io) is a modern, open source remote procedure call (RPC) framework developed by Google that can run anywhere. It enables client and server applications to communicate transparently, and makes it easier to build connected systems.It uses HTTP/2 for transport, Protocol Buffers as the interface description language, and provides features such as authentication, bidirectional streaming and flow control, blocking or nonblocking bindings, and cancellation and timeouts.
[LWM2M](https://www.omaspecworks.org/what-is-oma-specworks/iot/lightweight-m2m-lwm2m/) is a protocol from the Open Mobile Alliance for M2M or IoT device management. Lightweight M2M enabler defines the application layer communication protocol between a LWM2M Server and a LWM2M Client, which is located in a LWM2M Device.
[Advanced Message Queuing Protocol (AMQP)](https://www.amqp.org) is an open standard for passing business messages between applications or organizations. It connects systems, feeds business processes with the information they need and reliably transmits onward the instructions that achieve their goals. The defining features of AMQP are message orientation, queuing, routing, reliability and security.
[Constrained Application Protocol (CoAP)](https://coap.technology) is a specialized web transfer protocol for use with constrained nodes and constrained networks in the Internet of Things. The protocol is designed for machine-to-machine (M2M) applications such as smart energy and building automation."
[Extensible Messaging and Presence Protocol (XMPP)](https://xmpp.org) is a communication protocol for message-oriented middleware based on XML (Extensible Markup Language). It enables the near real-time exchange of structured yet extensible data between any two or more network entities.
[OASIS Message Queuing Telemetry Transport (MQTT)](https://www.oasis-open.org) is an open OASIS and ISO standard (ISO/IEC 20922) lightweight, publish-subscribe network protocol that transports messages between devices. The protocol usually runs over TCP/IP; however, any network protocol that provides ordered, lossless, bi-directional connections can support MQTT.
[Very Simple Control Protocol (VSCP)](https://vscp.org) is a free automation protocol suitable for all sorts of automation task where building- or home-automation is in the main focus. Its main advantage is that each VSCP-node can work completely autonomous, being part of distributed network of other nodes.
# Operating systems
[Back to the Top](https://github.com/mikeroyal/Self-Hosting-Guide#table-of-contents)
[Raspberry Pi OS](https://www.raspberrypi.org/software/operating-systems/)
[Hass.io(Home Assistant OS)](https://www.home-assistant.io/hassio/installation/)
[Manjaro Linux ARM](https://manjaro.org/download/#ARM)
[Arch Linux ARM](https://archlinuxarm.org/platforms/armv8/broadcom/raspberry-pi-4)
[Ubuntu MATE for Raspberry Pi](https://ubuntu-mate.org/ports/raspberry-pi/)
[Ubuntu Desktop for Raspberry Pi](https://ubuntu.com/raspberry-pi)
[Ubuntu Core on a Raspberry Pi](https://ubuntu.com/download/raspberry-pi-core)
[Ubuntu Server for ARM](https://ubuntu.com/download/server/arm)
[Debian](https://wiki.debian.org)
[Fedora ARM](https://arm.fedoraproject.org)
[openSUSE](https://en.opensuse.org/openSUSE)
[SUSE](https://documentation.suse.com/)
[Kali Linux for the Raspberry Pi](https://www.kali.org/docs/arm/kali-linux-raspberry-pi/)
[RetroArch](https://www.retroarch.com/?page=platforms)
[RetroPie](https://retropie.org.uk/)
[LibreELEC](https://libreelec.tv/)
[OSMC](https://osmc.tv)
[RISC OS](https://www.riscosopen.org/content/)
[Windows 10 IoT Core](https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/iot-core/windows-iot-core)
[HeliOS](https://www.arduino.cc/reference/en/libraries/helios/) is an embedded operating system that is free for anyone to use. While called an operating system for simplicity, HeliOS is better described as a multitasking kernel for embedded systems.
[Simba](https://simba-os.readthedocs.io/en/latest/getting-started.html) is a small OS for an Embedded Programming Platform like Arduino. It aims to make embedded programming easy and portable.
[Trampoline](https://github.com/TrampolineRTOS/) is a static RTOS for small embedded systems.
[DuinOS](https://github.com/DuinOS/DuinOS) is Framework (a wrapper) for use the FreeRTOSwith Arduino.
[VxWorks](https://www.windriver.com/products/vxworks) is an industry-leading real-time operating systems (RTOS) for building embedded devices and systems for more than 30 years.
[LynxOS](https://www.lynx.com/products/lynxos-posix-real-time-operating-system-rtos) is a native POSIX, hard real-time partitioning operating system developed by Lynx Software Technologies.
[Zephyr OS](https://www.zephyrproject.org/zephyr-rtos-featured-in-risc-v-getting-started-guide/) is a popular security-oriented RTOS with a small-footprint kernel designed for use on resource-constrained and embedded systems. Zephyr has a small-foorprint Kernel focusing on embedded devices compatible with x86, ARM, RISC-V, Xtensa and [others](https://docs.zephyrproject.org/latest/boards/index.html).
[FreeRTOS](https://freertos.org/) is an open source, real-time operating system for microcontrollers that makes small, low-power edge devices easy to program, deploy, secure, connect, and manage.
[Arm Mbed TLS](https://os.mbed.com) provides a comprehensive SSL/TLS solution and makes it easy for developers to include cryptographic and SSL/TLS capabilities in their software and embedded products. As an SSL library, it provides an intuitive API, readable source code and a minimal and highly configurable code footprint.
[Contiki-os](https://github.com/contiki-os) is an operating system for networked, memory-constrained systems with a focus on low-power wireless Internet of Things devices.
# Middleware
[Back to the Top](https://github.com/mikeroyal/Self-Hosting-Guide#table-of-contents)
[IoTSyS](https://iotsyst.com) is an integration middleware for the Internet of Things. It provides a communication stack for embedded devices based on IPv6, Web services, and OBIX to establish interoperable interfaces for smart objects.
[OpenIoT](https://github.com/OpenIotOrg/openiot) is an open source middleware infrastructure will support flexible configuration and deployment of algorithms for collection, and filtering information streams stemming from the internet-connected objects, while at the same time generating and processing important business/applications events.
[OpenRemote](https://github.com/openremote/openremote) is an open source middleware project, which integrates many different protocols and solutions available for smart building, and smart city automation, and offers visualization tools.
[Kaa](https://www.kaaproject.org/platform/) is a Enterprise IoT Platform has been designed with heavy-duty, enterprise-grade IoT solutions in mind. It banishes a monolithic approach to architecture in favour of highly portable microservices, which allow for flexible rearrangement and customization even in the middle of the solution's lifecycle.
# Node flow editors
[Back to the Top](https://github.com/mikeroyal/Self-Hosting-Guide#table-of-contents)
[Node-RED](https://nodered.org) is a programming tool for wiring together hardware devices, APIs and online services in new and interesting ways. It provides a browser-based editor that makes it easy to wire together flows using the wide range of nodes in the palette that can be deployed to its runtime in a single-click.
### Toolkits
[Back to the Top](https://github.com/mikeroyal/Self-Hosting-Guide#table-of-contents)
[KinomaJS](https://github.com/Kinoma/kinomajs) is a visual code editor designed to help developers build starter projects for Kinoma Create and Kinoma Element. The project is built on Angular 2(RC7) and runs in a web browser. The live version is hosted using Google App Engine, but you can modify and build it yourself by following the instructions in this document.
[IoT Toolkit](https://www.segger.com/products/security-iot/iot-toolkit/) is a collection of libraries that enables communication with modern IoT based environments and devices. It is a high-performance collection of libraries optimized for minimum memory consumption in RAM, ROM, high speed, and versatility working on any device.
# Data Visualization
[Back to the Top](https://github.com/mikeroyal/Self-Hosting-Guide#table-of-contents)
[Freeboard](https://github.com/Freeboard/freeboard) is an open source real-time dashboard builder for IOT and other web mashups. A free open-source alternative to Geckoboard.
[ThingSpeak](https://thingspeak.com) is an IoT analytics platform service that allows you to aggregate, visualize, and analyze live data streams in the cloud. You can send data to ThingSpeak from your devices, create instant visualization of live data, and send alerts.
# Search
[Back to the Top](https://github.com/mikeroyal/Self-Hosting-Guide#table-of-contents)
[Thingful](https://www.thingful.net) is a Search Engine for the Internet of Things Find & use open IoT data from around the world.
# Hardware
[Back to the Top](https://github.com/mikeroyal/Self-Hosting-Guide#table-of-contents)
[Arduino Ethernet Shield 2](https://www.arduino.cc/en/Guide/ArduinoEthernetShield) allows an Arduino board to connect to the internet using the Ethernet library and to read and write an SD card using the SD library.This shield is fully compatible with the former version, but relies on the newer W5500 chip.
[Raspberry Pi](https://www.raspberrypi.org) is a series of small single-board computers developed in the United Kingdom by the Raspberry Pi Foundation to promote teaching of basic computer science in schools and in developing countries. Price range from $10-45 depending on model.
[BeagleBone](https://beagleboard.org/bone) is a low-power open-source single-board computer produced by Texas Instruments. It runs Android, Ubuntu and other Linux flavors.
[openPicus FlyportPro](https://www.open-electronics.org/flyport-professional-iot-modules-by-openpicus/) is a system on a module dedicated to IoT and M2M application, especially for professional use. Following some details on the solution: Why FlyportPRO SoM? A system-on-module is the best solution for those customers looking for flexibility and for development time and risk reduction.
[Pinoccio](https://www.open-electronics.org/pinoccio-wifi-mesh-networking-for-arduino-and-iot-available-now/) is a solution to add mesh networking capability and WiFi-Internet access to all yout IoT devices, and it is Arduino compatible. Each board can assume the role of Scout in a Troop and one of the Scouts is the Lead to connect internet: Field Scouts talk to each other using a mesh network (called a Troop), using an extremely low-power radio.
### In-memory data grids
[Back to the Top](https://github.com/mikeroyal/Self-Hosting-Guide#table-of-contents)
[Ehcache](https://www.ehcache.org) is an open source, standards-based cache that boosts performance, offloads your database, and simplifies scalability. It's the most widely-used Java-based cache because it's robust, proven, full-featured, and integrates with other popular libraries and frameworks.
[Hazelcast](https://hazelcast.com) is an open source in-memory data grid based on Java.
# Home automation
[Back to the Top](https://github.com/mikeroyal/Self-Hosting-Guide#table-of-contents)
[Home Assistant](https://github.com/home-assistant/core) is open source home automation that puts local control and privacy first. Powered by a worldwide community of tinkerers and DIY enthusiasts. Perfect to run on a Raspberry Pi or a local server.
[openHAB](https://github.com/openhab) is a cross-platform software with the aim to integrate all kinds of Smart Home technologies, devices, etc.
[Eclipse SmartHome](https://www.eclipse.org/smarthome/) is a framework, not a ready-to-use solution. It offers a large set of features to choose from and leaves enough possibilities to design a Smart Home solution specific to your expectations. Its modular design brings millions of combinations and proves to be easily extensible by custom parts.
[The Thing System](https://github.com/TheThingSystem) is a set of software components and network protocols that aims to fix the Internet of Things. Our steward software is written in node.js making it both portable and easily extensible. It can run on your laptop, or fit onto a small single board computer like the Raspberry Pi.
# Robotics
[Back to the Top](https://github.com/mikeroyal/Self-Hosting-Guide#table-of-contents)









